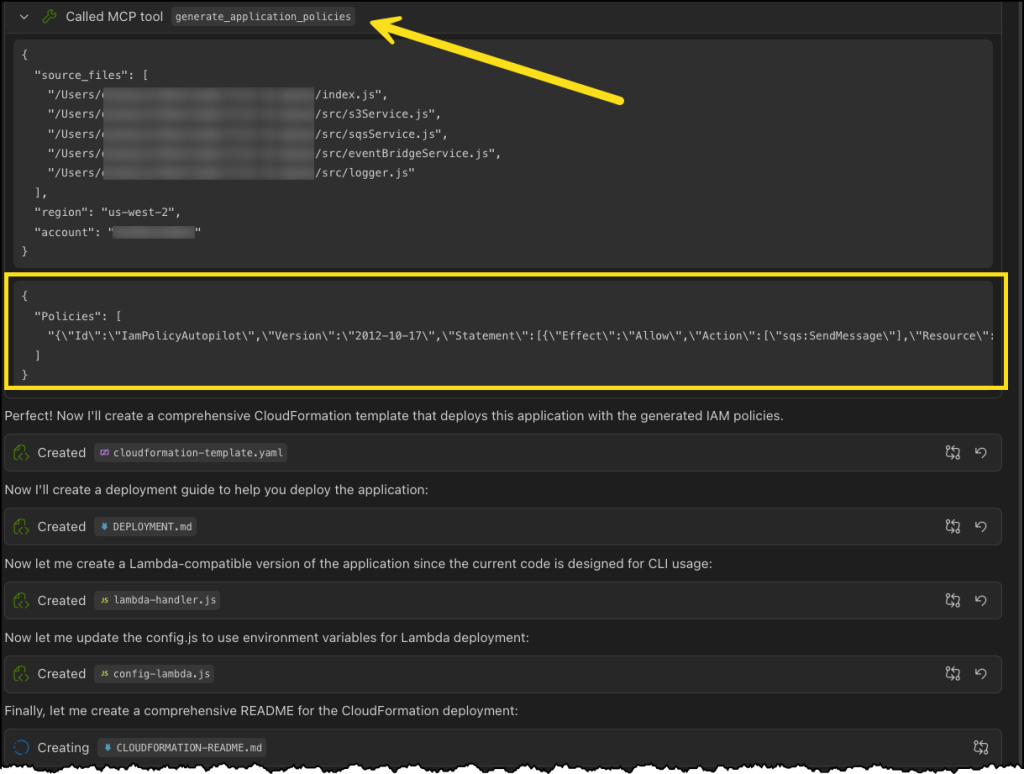
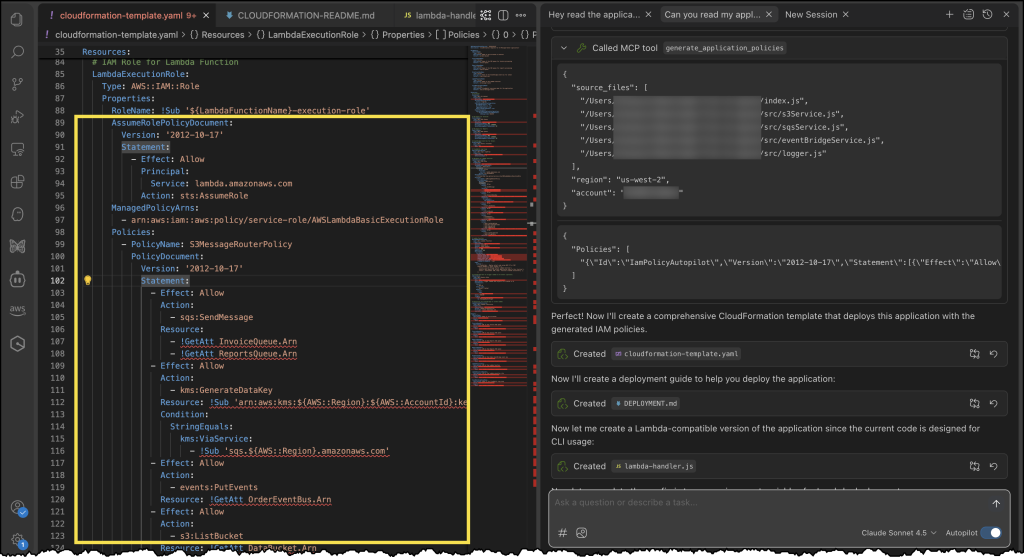
Earlier this year in May, we announced the general availability of AWS Transform for .NET, the first agentic AI service for modernizing .NET applications at scale. During the early adoption period of the service, we received valuable feedback indicating that, in addition to .NET application modernization, you would like to modernize SQL Server and legacy UI frameworks. Your applications typically follow a three-tier architecture—presentation tier, application tier, and database tier—and you need a comprehensive solution that can transform all of these tiers in a coordinated way.
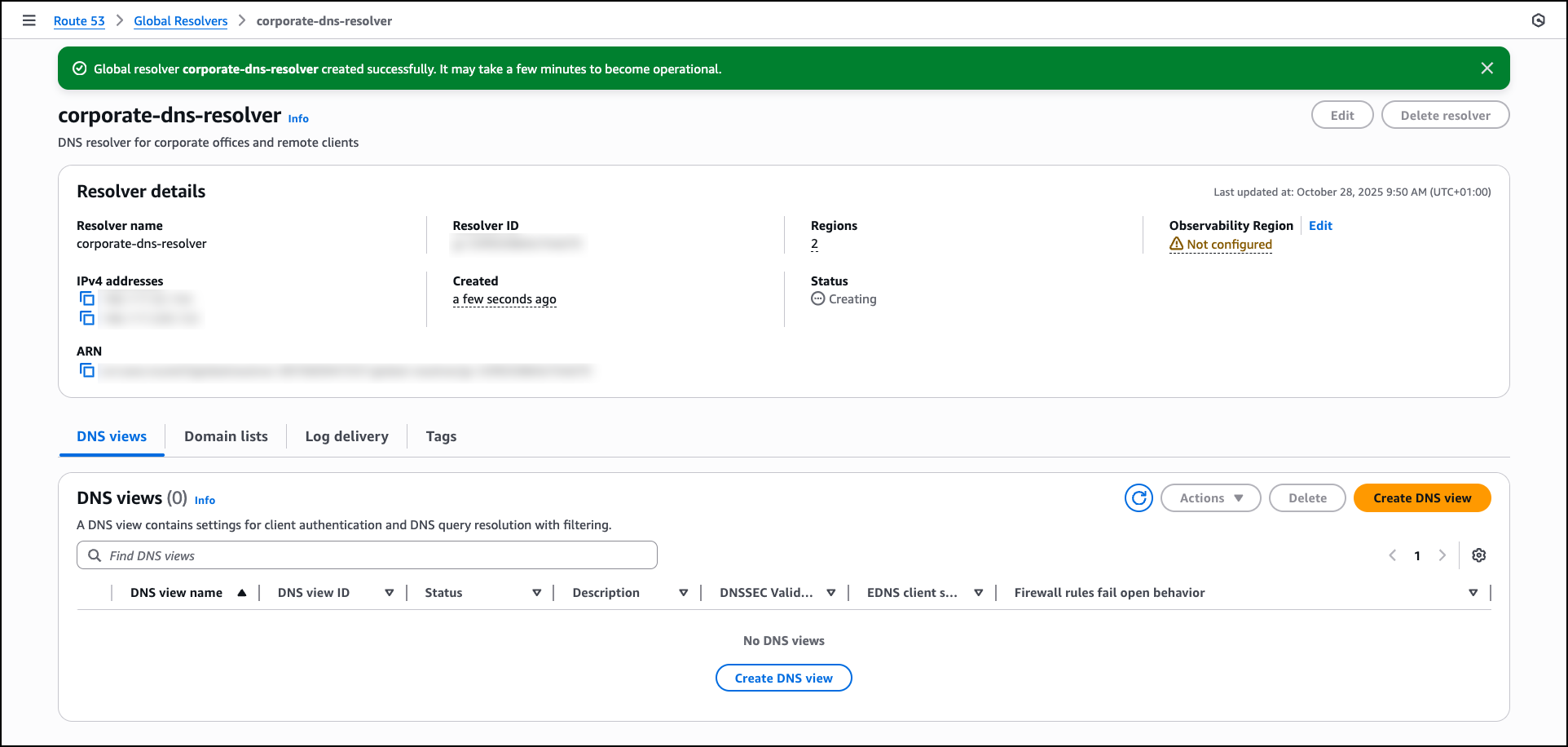
Today, based on your feedback, we’re excited to announce AWS Transform for full-stack Windows modernization, to offload complex, tedious modernization work across the Windows application stack. You can now identify application and database dependencies and modernize them in an orchestrated way through a centralized experience.
AWS Transform accelerates full-stack Windows modernization by up to five times across application, UI, database, and deployment layers. Along with porting .NET Framework applications to cross-platform .NET, it migrates SQL Server databases to Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible Edition with intelligent stored procedure conversion and dependent application code refactoring. For validation and testing, AWS Transform deploys applications to Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) Linux or Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS), and provides customizable AWS CloudFormation templates and deployment configurations for production use. AWS Transform has also added capabilities to modernize ASP.NET Web Forms UI to Blazor.
There is much to explore, so in this post I’ll provide the first look at AWS Transform for full-stack Windows modernization capabilities across all layers.
Create a full-stack Windows modernization transformation job
AWS Transform connects to your source code repositories and database servers, analyzes application and database dependencies, creates modernization waves, and orchestrates full-stack transformations for each wave.
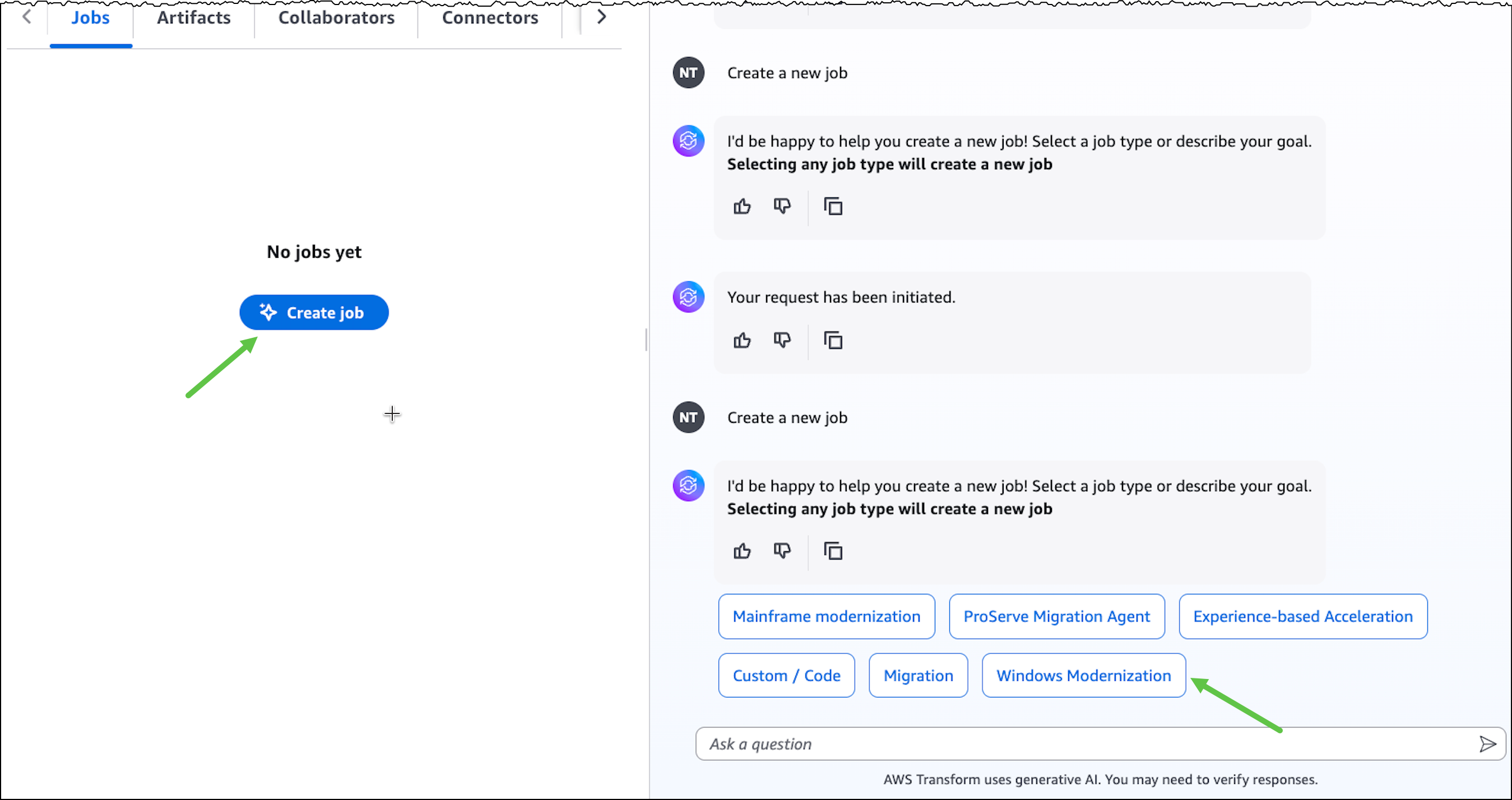
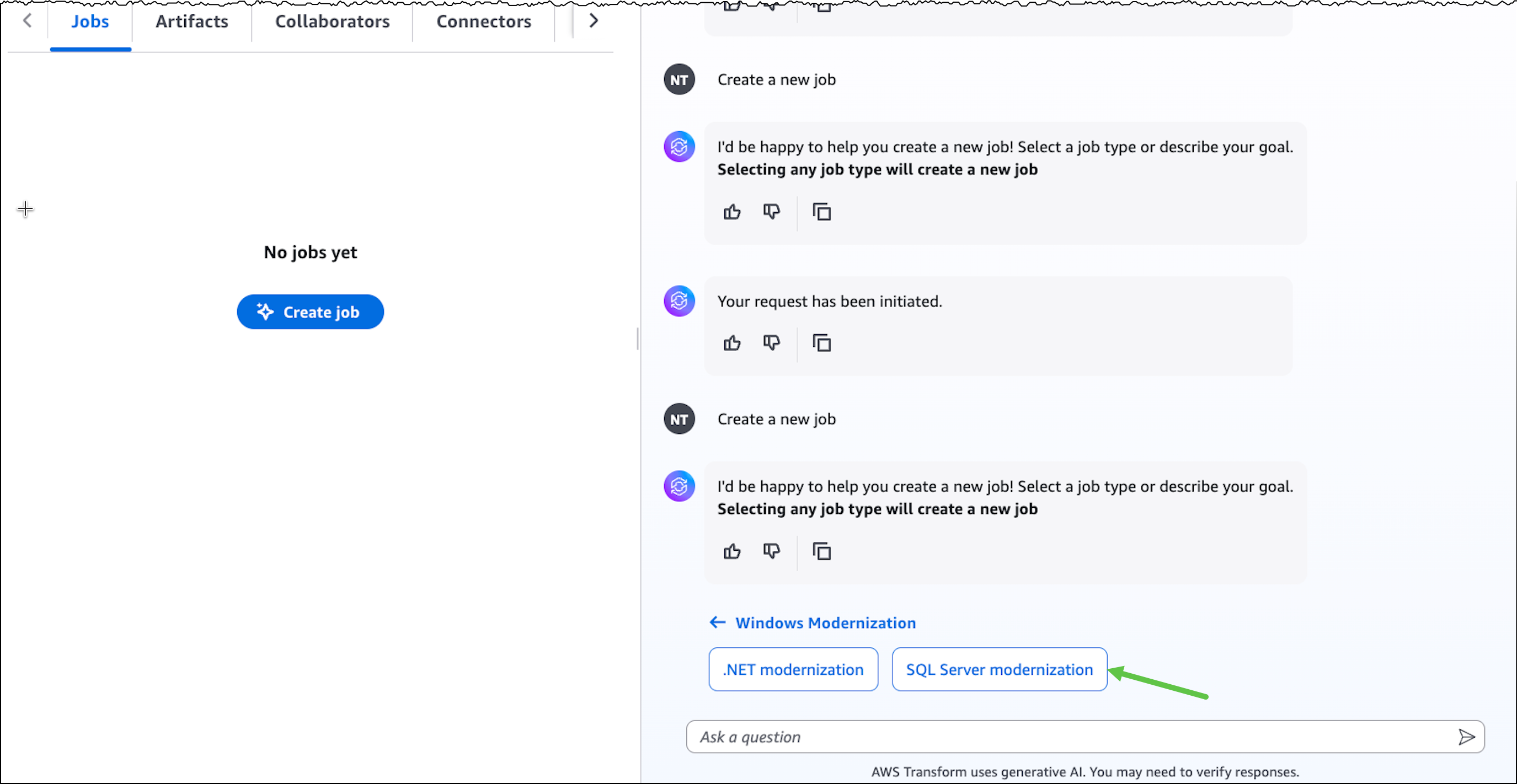
To get started with AWS Transform, I first complete the onboarding steps outlined in the getting started with AWS Transform user guide. After onboarding, I sign in to the AWS Transform console using my credentials and create a job for full-stack Windows modernization.
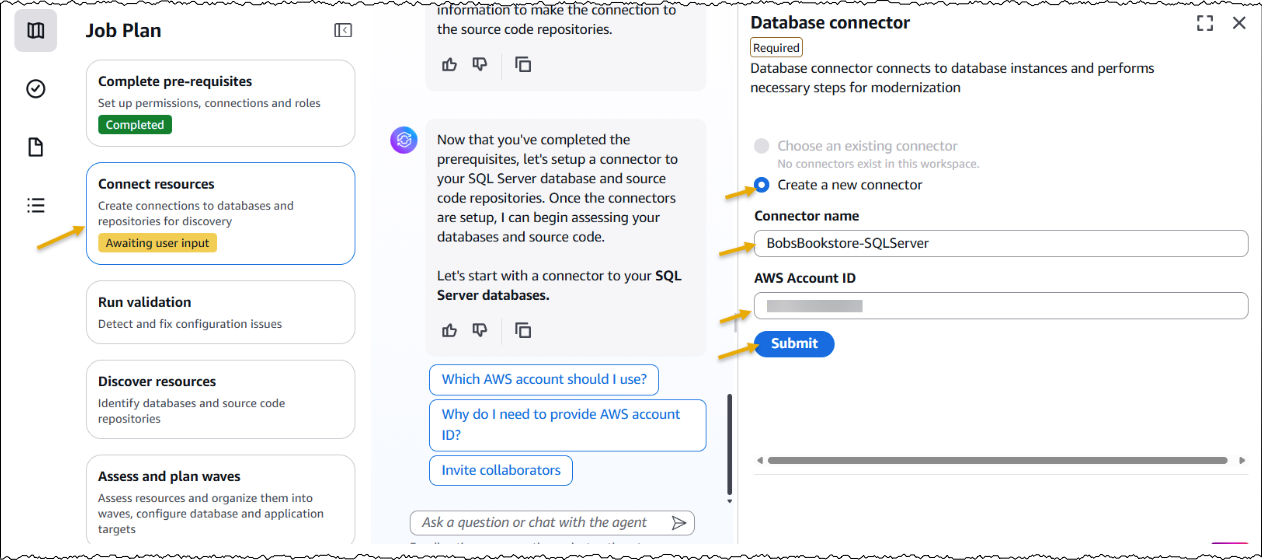
After creating the job, I complete the prerequisites. Then, I configure the database connector for AWS Transform to securely access SQL Server databases running on Amazon EC2 and Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS). The connector can connect to multiple databases within the same SQL Server instance.
Next, I set up a connector to connect to my source code repositories.
Furthermore, I have the option to choose if I would like AWS Transform to deploy the transformed applications. I choose Yes and provide the target AWS account ID and AWS Region for deploying the applications. The deployment option can be configured later as well.
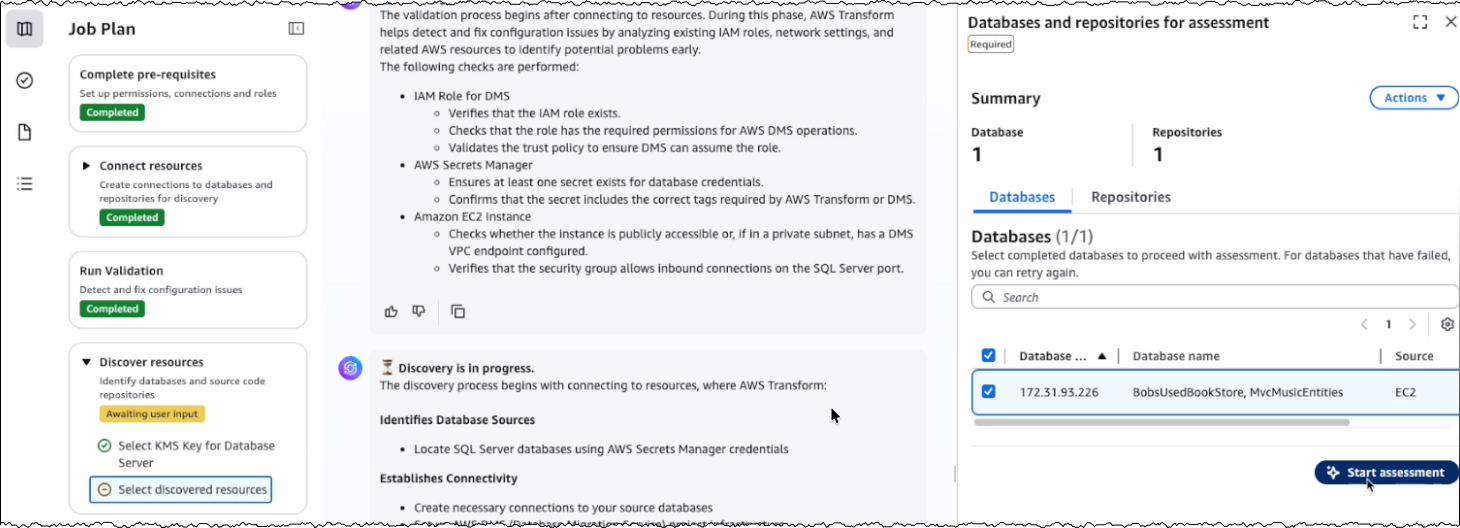
After the connectors are set up, AWS Transform connects to the resources and runs the validation to verify IAM roles, network settings, and related AWS resources.
After the successful validation, AWS Transform discovers databases and their associated source code repositories. It identifies dependencies between databases and applications to create waves for transforming related components together. Based on this analysis, AWS Transform creates a wave-based transformation plan.
Assessing database and dependent applications
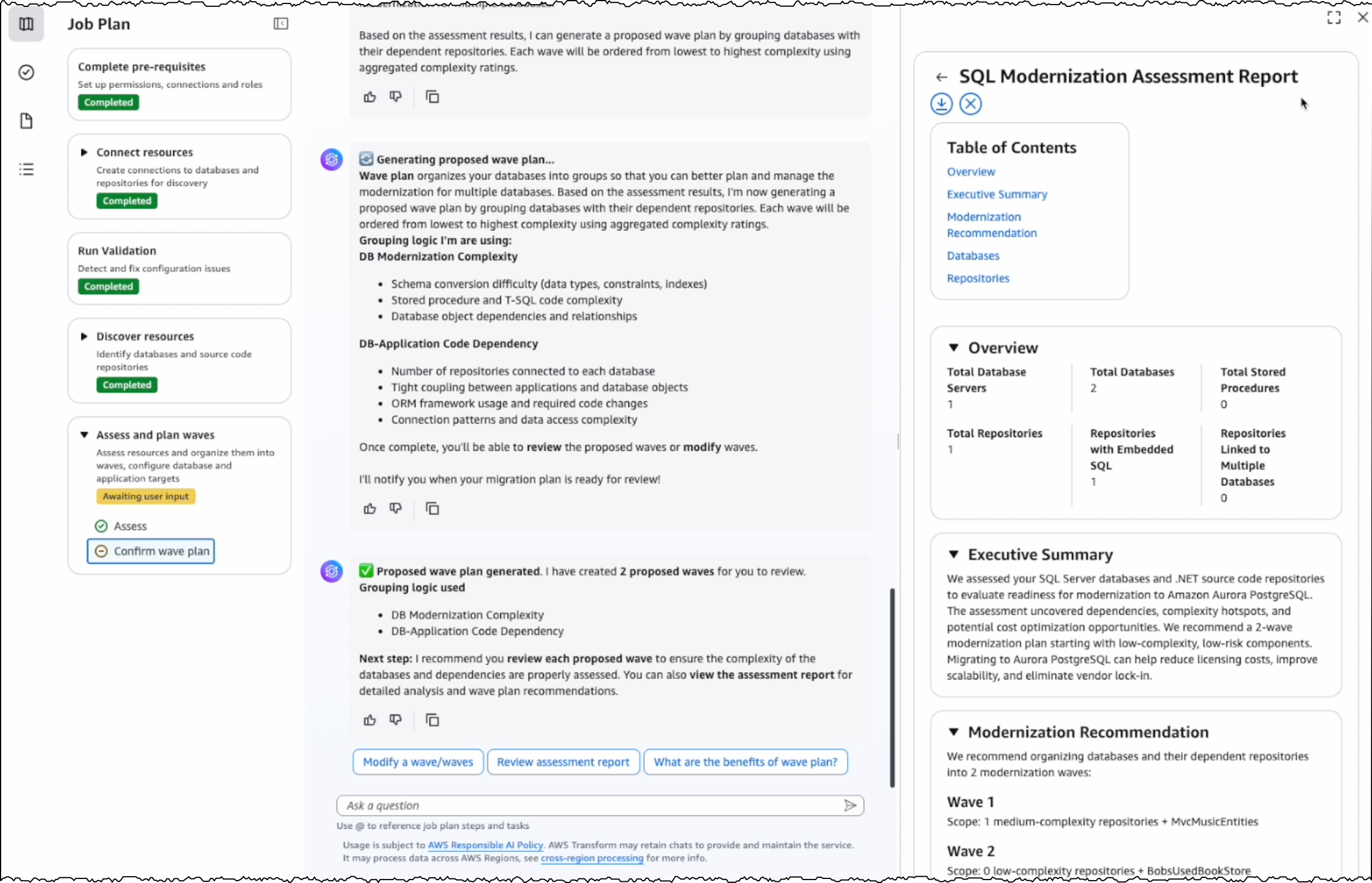
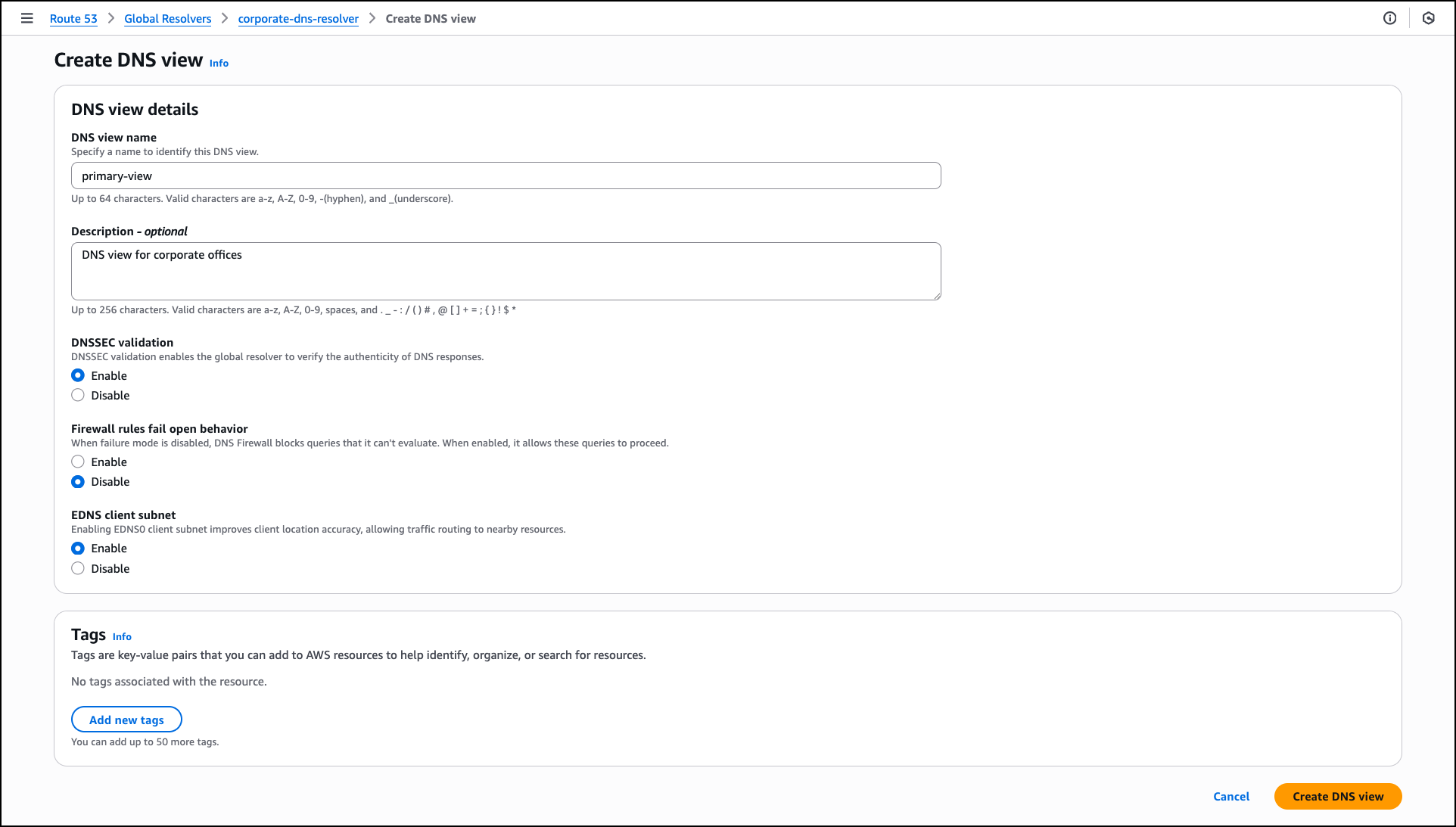
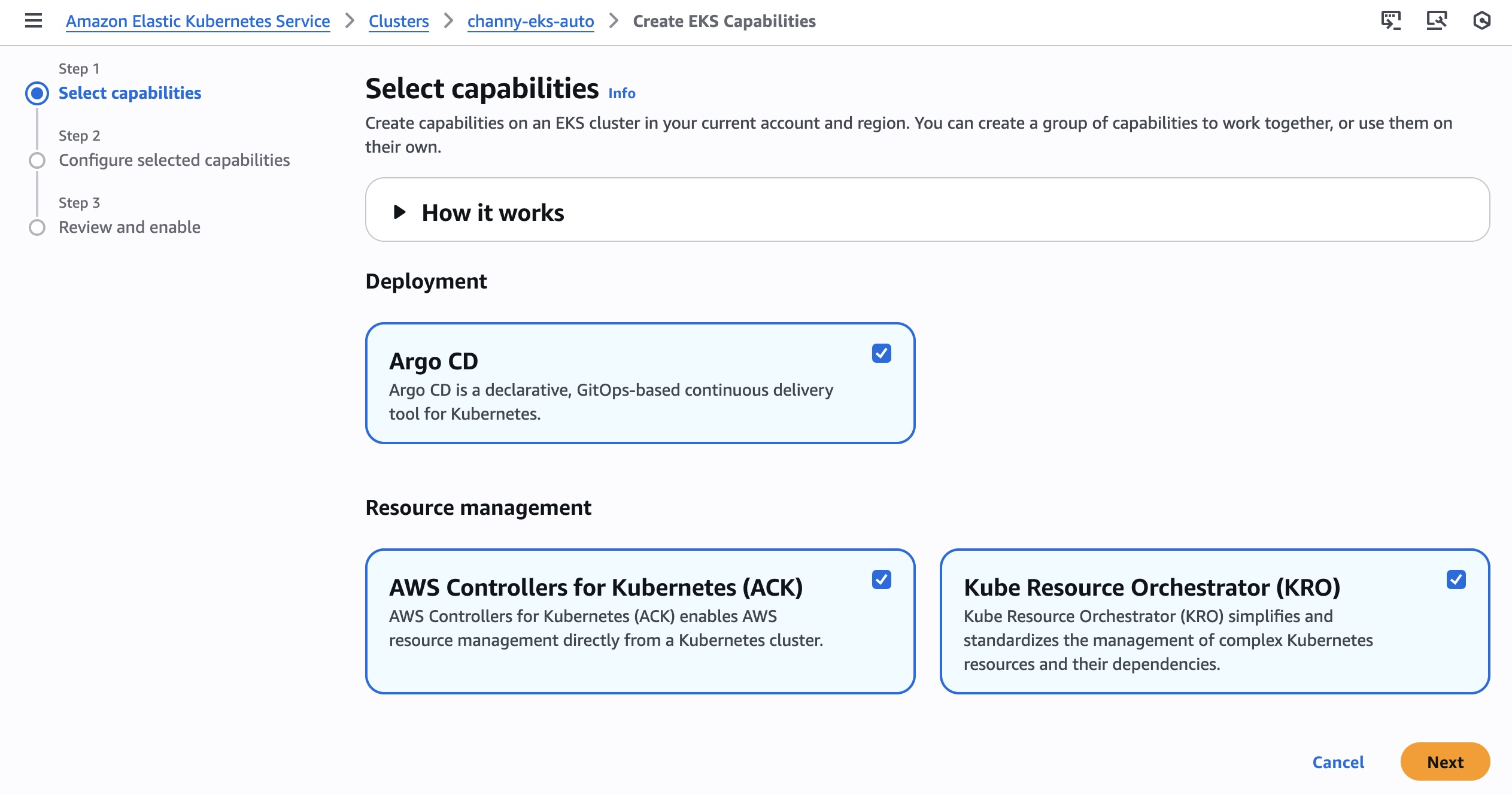
For the assessment, I review the databases and source code repositories discovered by AWS Transform and choose the appropriate branches for code repositories. AWS Transform scans these databases and source code repositories, then presents a list of databases along with their dependent .NET applications and transformation complexity.
I choose the target databases and repositories for modernization. AWS Transform analyzes these selections and generates a comprehensive SQL Modernization Assessment Report with a detailed wave plan. I download the report to review the proposed modernization plan. The report includes an executive summary, wave plan, dependencies between databases and code repositories, and complexity analysis.
Wave transformation at scale
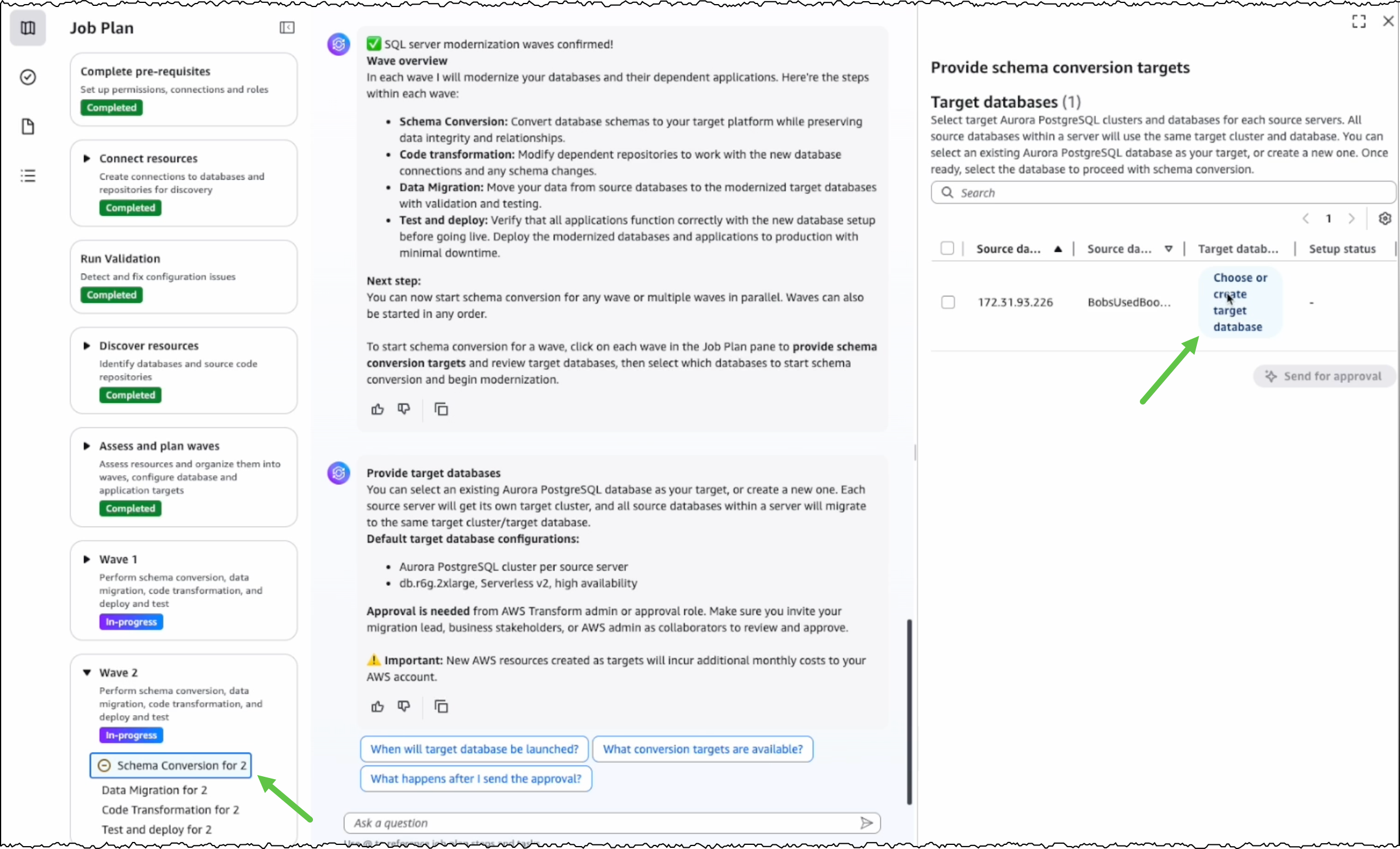
The wave plan generated by AWS Transform consists of four steps for each wave. First, it converts the SQL Server schema to PostgreSQL. Second, it migrates the data. Third, it transforms the dependent .NET application code to make it PostgreSQL compatible. Finally, it deploys the application for testing.
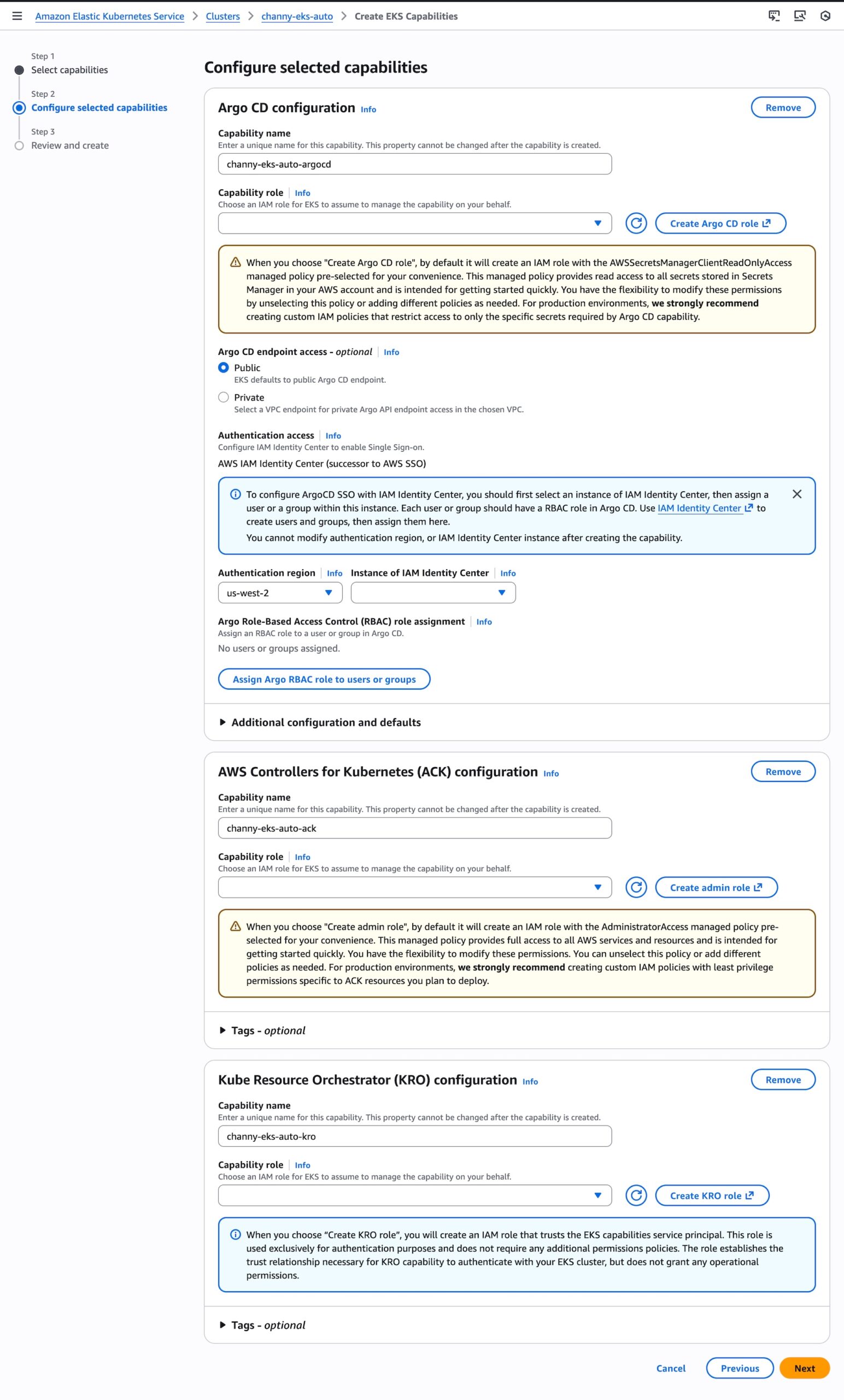
Before converting the SQL Server schema, I can either create a new PostgreSQL database or choose an existing one as the target database.
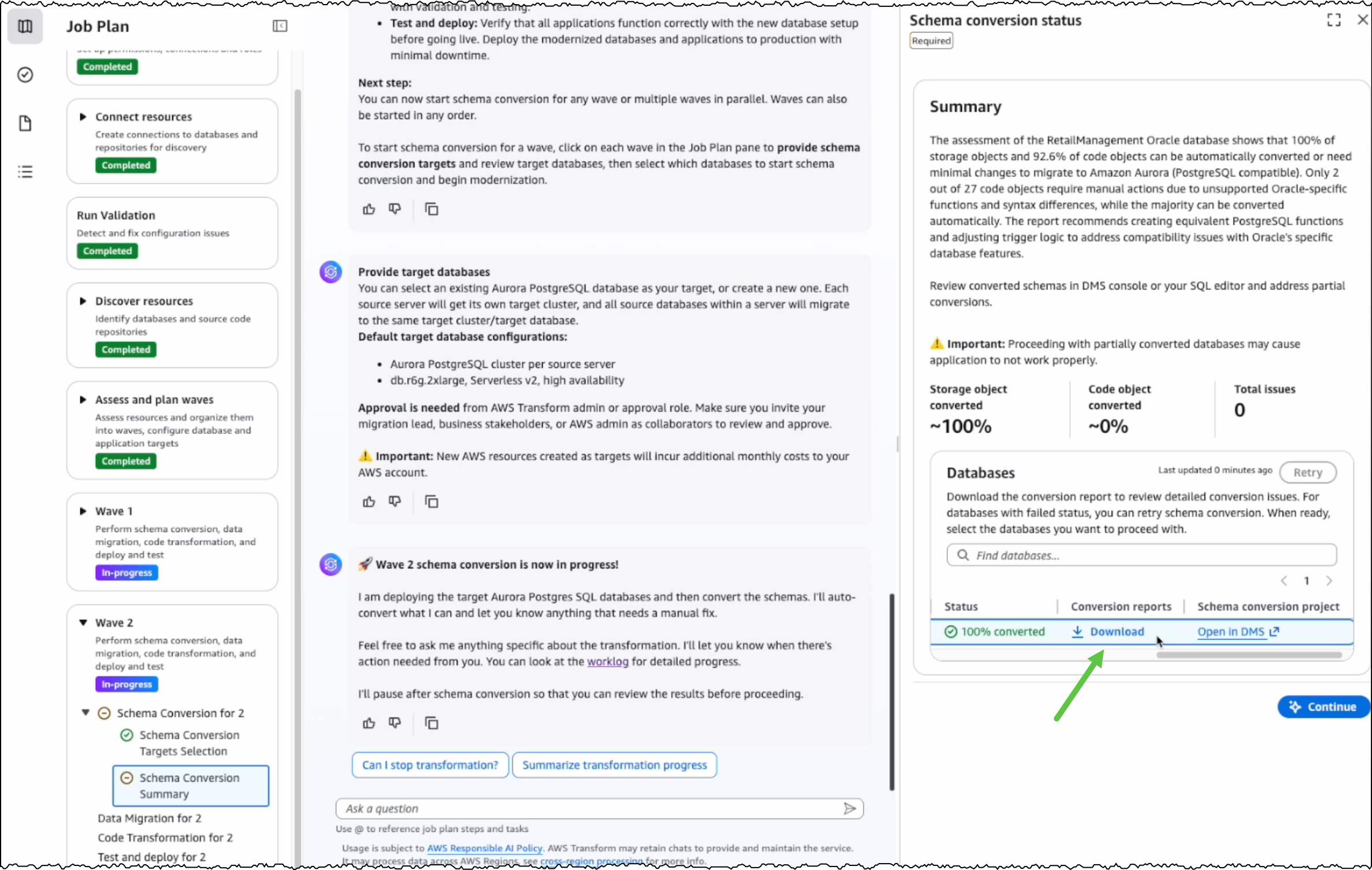
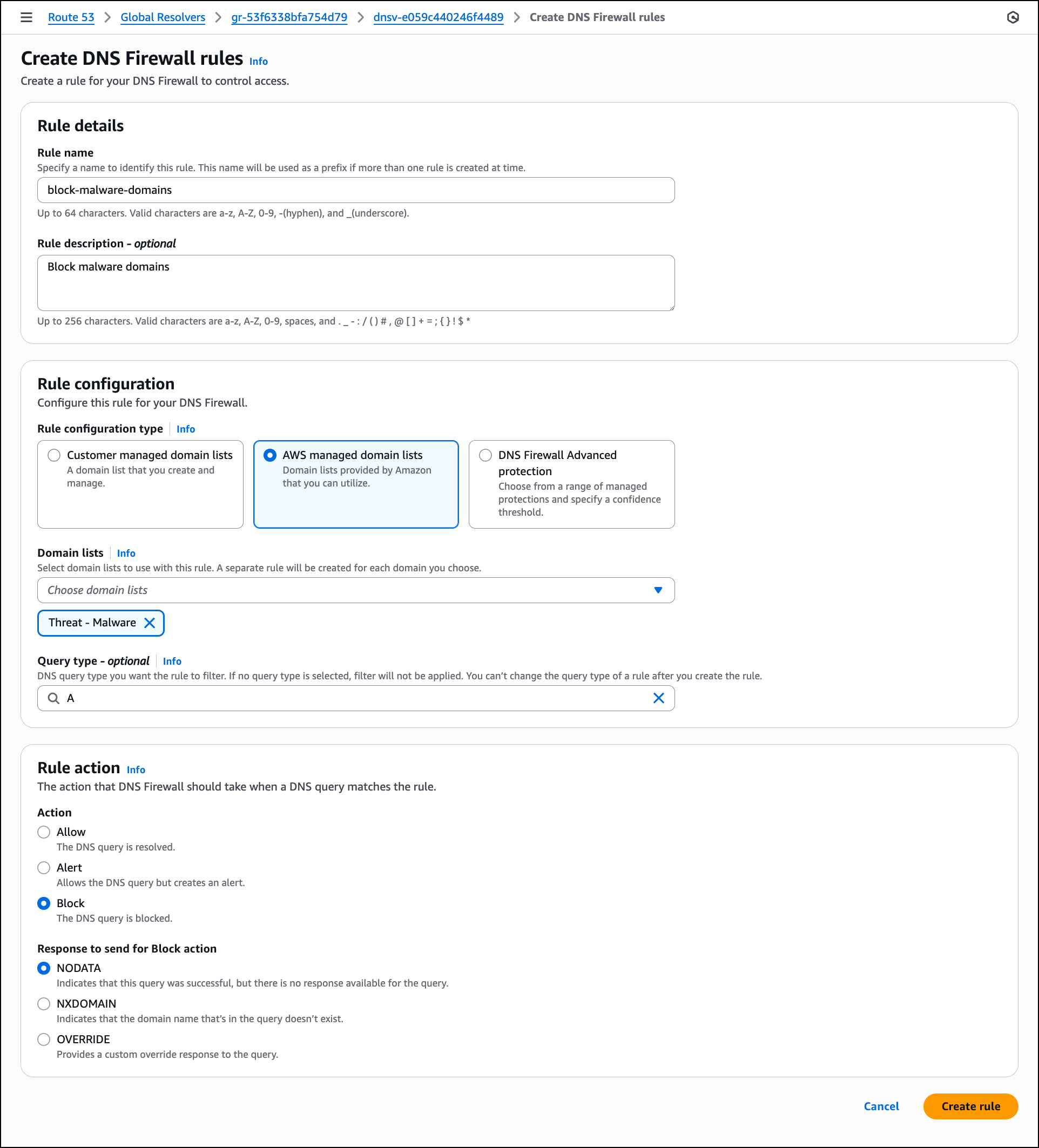
After I choose the source and target databases, AWS Transform generates conversion reports for my review. AWS Transform converts the SQL Server schema to PostgreSQL-compatible structures, including tables, indexes, constraints, and stored procedures.
For any schema that AWS Transform can’t automatically convert, I can manually address them in the AWS Database Migration Service (AWS DMS) console. Alternatively, I can fix them in my preferred SQL editor and update the target database instance.
After completing schema conversion, I have the option to proceed with data migration, which is an optional step. AWS Transform uses AWS DMS to migrate data from my SQL Server instance to the PostgreSQL database instance. I can choose to perform data migration later, after completing all transformations, or work with test data by loading it into my target database.
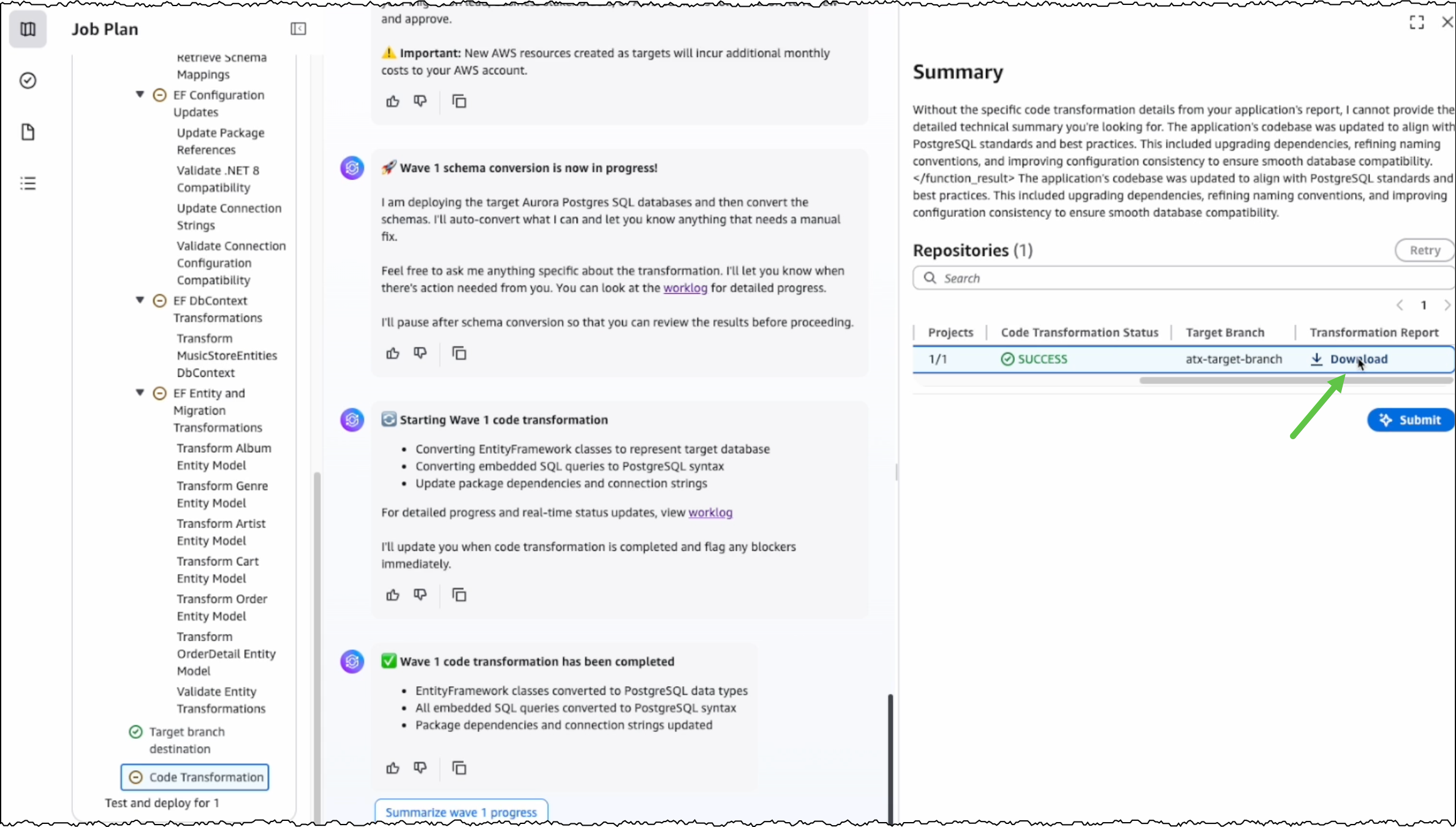
The next step is code transformation. I specify a target branch for AWS Transform to upload the transformed code artifacts. AWS Transform updates the codebase to make the application compatible with the converted PostgreSQL database.
With this release, AWS Transform for full-stack Windows modernization supports only codebases in .NET 6 or later. For codebases in .NET Framework 3.1+, I first use AWS Transform for .NET to port them to cross-platform .NET. I’ll expand on this in a following section.
After the conversion is completed, I can view the source and target branches along with their code transformation status. I can also download and review the transformation report.
Modernizing .NET Framework applications with UI layer
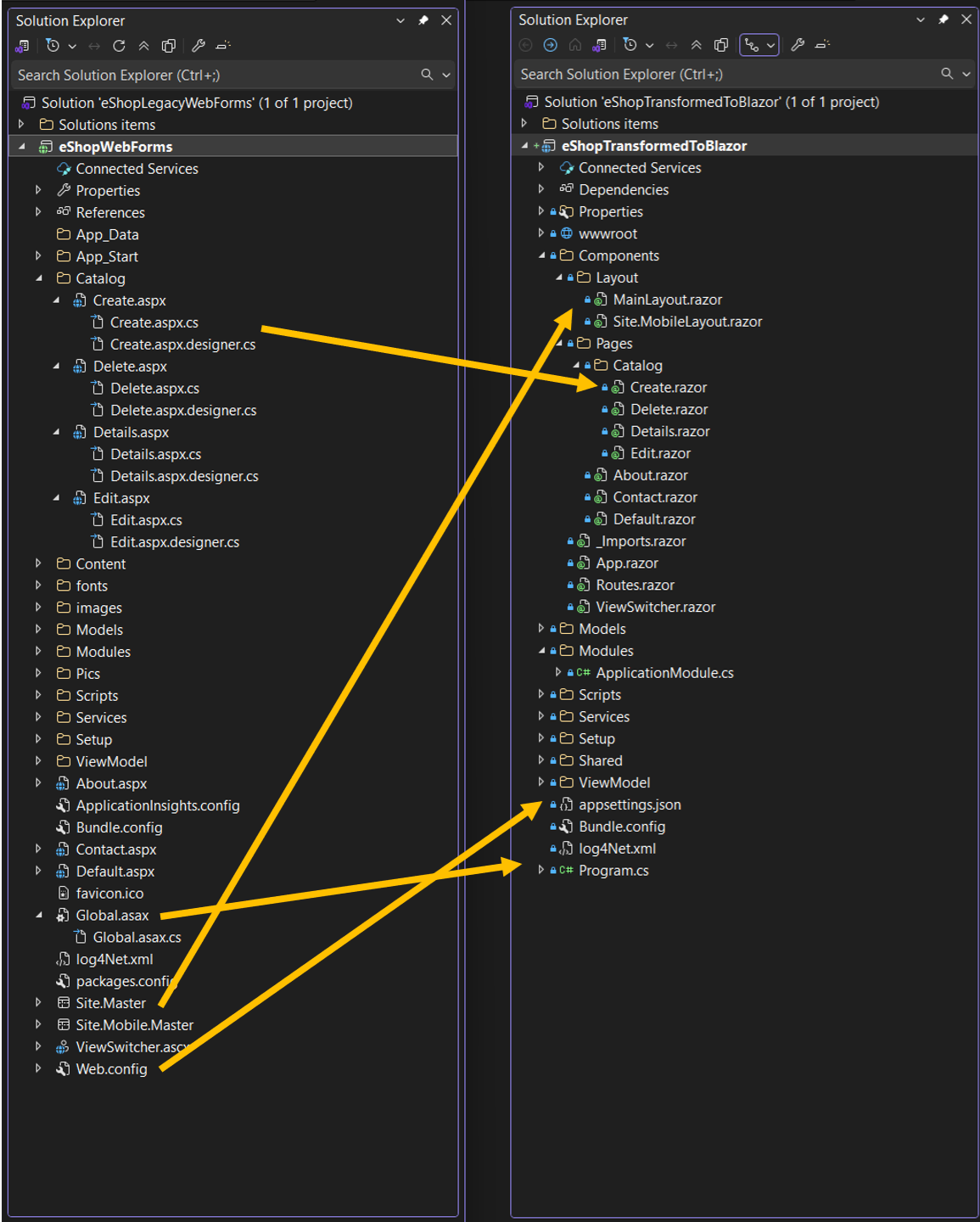
One major feature we’re releasing today is the modernization of UI frameworks from ASP.NET Web Forms to Blazor. This is added to existing support for modernizing model-view-controller (MVC) Razor views to ASP.NET Core Razor views.
As mentioned previously, if I have a .NET application in legacy .NET Framework, then I continue using AWS Transform for .NET to port it to cross-platform .NET. For legacy applications with UIs built on ASP.NET Web Forms, AWS Transform now modernizes the UI layer to Blazor along with porting the backend code.
AWS Transform for .NET converts ASP.NET Web Forms projects to Blazor on ASP.NET Core, facilitating the migration of ASP.NET websites to Linux. The UI modernization feature is enabled by default in AWS Transform for .NET on both the AWS Transform web console and Visual Studio extension.
During the modernization process, AWS Transform handles the conversion of ASPX pages, ASCX custom controls, and code-behind files, implementing them as server-side Blazor components rather than web assembly. The following project and file changes are made during the transformation:
| From | To | Description |
| *.aspx, *.ascx | *.razor | .aspx pages and .ascx custom controls become .razor files |
| Web.config | appsettings.json | Web.config settings become appsettings.json settings |
| Global.asax | Program.cs | Global .asax code becomes Program.cs code |
| *.master | *layout.razor | Master files become layout.razor files |
Other new features in AWS Transform for .NET
Along with UI porting, AWS Transform for .NET has added support for more transformation capabilities and enhanced developer experience. These new features include the following:
- Port to .NET 10 and .NET Standard – AWS Transform now supports porting to .NET 10, the latest Long-Term Support (LTS) release, which was released on November 11, 2025. It also supports porting class libraries to .NET Standard, a formal specification for a set of APIs that are common across all .NET implementations. Furthermore, AWS Transform is now available with AWS Toolkit for Visual Studio 2026.
- Editable transformation report – After the assessment is complete, you can now view and customize the transformation plan based on your specific requirements and preferences. For example, you can update package replacement details.
- Real-time transformation updates with estimated remaining time – Depending on the size and complexity of the codebase, AWS Transform can take some time to complete the porting. You can now track transformation updates in real-time along with the estimated remaining time.
- Next steps markdown – After the transformation is complete, AWS Transform now generates a next steps markdown file with the remaining tasks to complete the porting. You can use this as a revised plan to repeat the transformation with AWS Transform or use AI code-companions to complete the porting.
Things to know
Some more things to know are:
- AWS Regions – AWS Transform for full-stack Windows modernization is generally available today in the US East (N. Virginia) Region. For Regional availability and future roadmap, visit the AWS Capabilities by Region.
- Pricing – Currently, there is no added charge for Windows modernization features of AWS Transform. Any resources you create or continue to use in your AWS account using the output of AWS Transform are billed according to their standard pricing. For limits and quotas, refer to the AWS Transform User Guide.
- SQL Server versions supported – AWS Transform supports the transformation of SQL Server versions from 2008 R2 through 2022, including all editions (Express, Standard, and Enterprise). SQL Server must be hosted on Amazon RDS or Amazon EC2 in the same Region as AWS Transform.
- Entity Framework versions supported – AWS Transform supports the modernization of Entity Framework versions 6.3 through 6.5 and Entity Framework Core 1.0 through 8.0.
- Getting started – To get started, visit AWS Transform for full-stack Windows modernization User Guide.
– Prasad