This
post was originally published on
this siteToday, we are announcing that your MySQL 5.7 and PostgreSQL 11 database instances running on Amazon Aurora and Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) will be automatically enrolled into Amazon RDS Extended Support starting on February 29, 2024.
This will help avoid unplanned downtime and compatibility issues that can arise with automatically upgrading to a new major version. This provides you with more control over when you want to upgrade the major version of your database.
This automatic enrollment may mean that you will experience higher charges when RDS Extended Support begins. You can avoid these charges by upgrading your database to a newer DB version before the start of RDS Extended Support.
What is Amazon RDS Extended Support?
In September 2023, we announced Amazon RDS Extended Support, which allows you to continue running your database on a major engine version past its RDS end of standard support date on Amazon Aurora or Amazon RDS at an additional cost.
Until community end of life (EoL), the MySQL and PostgreSQL open source communities manage common vulnerabilities and exposures (CVE) identification, patch generation, and bug fixes for the respective engines. The communities release a new minor version every quarter containing these security patches and bug fixes until the database major version reaches community end of life. After the community end of life date, CVE patches or bug fixes are no longer available and the community considers those engines unsupported. For example, MySQL 5.7 and PostgreSQL 11 are no longer supported by the communities as of October and November 2023 respectively. We are grateful to the communities for their continued support of these major versions and a transparent process and timeline for transitioning to the newest major version.
With RDS Extended Support, Amazon Aurora and RDS takes on engineering the critical CVE patches and bug fixes for up to three years beyond a major version’s community EoL. For those 3 years, Amazon Aurora and RDS will work to identify CVEs and bugs in the engine, generate patches and release them to you as quickly as possible. Under RDS Extended Support, we will continue to offer support, such that the open source community’s end of support for an engine’s major version does not leave your applications exposed to critical security vulnerabilities or unresolved bugs.
You might wonder why we are charging for RDS Extended Support rather than providing it as part of the RDS service. It’s because the engineering work for maintaining security and functionality of community EoL engines requires AWS to invest developer resources for critical CVE patches and bug fixes. This is why RDS Extended Support is only charging customers who need the additional flexibility to stay on a version past community EoL.
RDS Extended Support may be useful to help you meet your business requirements for your applications if you have particular dependencies on a specific MySQL or PostgreSQL major version, such as compatibility with certain plugins or custom features. If you are currently running on-premises database servers or self-managed Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances, you can migrate to Amazon Aurora MySQL-Compatible Edition, Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible Edition, Amazon RDS for MySQL, Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL beyond the community EoL date, and continue to use these versions these versions with RDS Extended Support while benefiting from a managed service. If you need to migrate many databases, you can also utilize RDS Extended Support to split your migration into phases, ensuring a smooth transition without overwhelming IT resources.
In 2024, RDS Extended Support will be available for RDS for MySQL major versions 5.7 and higher, RDS for PostgreSQL major versions 11 and higher, Aurora MySQL-compatible version 2 and higher, and Aurora PostgreSQL-compatible version 11 and higher. For a list of all future supported versions, see Supported MySQL major versions on Amazon RDS and Amazon Aurora major versions in the AWS documentation.
| Community major version |
RDS/Aurora version |
Community end of life date |
End of RDS standard support date |
Start of RDS Extended Support pricing |
End of RDS Extended Support |
| MySQL 5.7 |
RDS for MySQL 5.7 |
October 2023 |
February 29, 2024 |
March 1, 2024 |
February 28, 2027 |
| Aurora MySQL 2 |
October 31, 2024 |
December 1, 2024 |
| PostgreSQL 11 |
RDS for PostgreSQL 11 |
November 2023 |
March 31, 2024 |
April 1, 2024 |
March 31, 2027 |
| Aurora PostgreSQL 11 |
February 29, 2024 |
RDS Extended Support is priced per vCPU per hour. Learn more about pricing details and timelines for RDS Extended Support at Amazon Aurora pricing, RDS for MySQL pricing, and RDS for PostgreSQL pricing. For more information, see the blog posts about Amazon RDS Extended Support for MySQL and PostgreSQL databases in the AWS Database Blog.
Why are we automatically enrolling all databases to Amazon RDS Extended Support?
We had originally informed you that RDS Extended Support would provide the opt-in APIs and console features in December 2023. In that announcement, we said that if you decided not to opt your database in to RDS Extended Support, it would automatically upgrade to a newer engine version starting on March 1, 2024. For example, you would be upgraded from Aurora MySQL 2 or RDS for MySQL 5.7 to Aurora MySQL 3 or RDS for MySQL 8.0 and from Aurora PostgreSQL 11 or RDS for PostgreSQL 11 to Aurora PostgreSQL 15 and RDS for PostgreSQL 15, respectively.
However, we heard lots of feedback from customers that these automatic upgrades may cause their applications to experience breaking changes and other unpredictable behavior between major versions of community DB engines. For example, an unplanned major version upgrade could introduce compatibility issues or downtime if applications are not ready for MySQL 8.0 or PostgreSQL 15.
Automatic enrollment in RDS Extended Support gives you additional time and more control to organize, plan, and test your database upgrades on your own timeline, providing you flexibility on when to transition to new major versions while continuing to receive critical security and bug fixes from AWS.
If you’re worried about increased costs due to automatic enrollment in RDS Extended Support, you can avoid RDS Extended Support and associated charges by upgrading before the end of RDS standard support.
How to upgrade your database to avoid RDS Extended Support charges
Although RDS Extended Support helps you schedule your upgrade on your own timeline, sticking with older versions indefinitely means missing out on the best price-performance for your database workload and incurring additional costs from RDS Extended Support.
MySQL 8.0 on Aurora MySQL, also known as Aurora MySQL 3, unlocks support for popular Aurora features, such as Global Database, Amazon RDS Proxy, Performance Insights, Parallel Query, and Serverless v2 deployments. Upgrading to RDS for MySQL 8.0 provides features including up to three times higher performance versus MySQL 5.7, such as Multi-AZ cluster deployments, Optimized Reads, Optimized Writes, and support for AWS Graviton2 and Graviton3-based instances.
PostgreSQL 15 on Aurora PostgreSQL supports the Aurora I/O Optimized configuration, Aurora Serverless v2, Babelfish for Aurora PostgreSQL, pgvector extension, Trusted Language Extensions for PostgreSQL (TLE), and AWS Graviton3-based instances as well as community enhancements. Upgrading to RDS for PostgreSQL 15 provides features such as Multi-AZ DB cluster deployments, RDS Optimized Reads, HypoPG extension, pgvector extension, TLEs for PostgreSQL, and AWS Graviton3-based instances.
Major version upgrades may make database changes that are not backward-compatible with existing applications. You should manually modify your database instance to upgrade to the major version. It is strongly recommended that you thoroughly test any major version upgrade on non-production instances before applying it to production to ensure compatibility with your applications. For more information about an in-place upgrade from MySQL 5.7 to 8.0, see the incompatibilities between the two versions, Aurora MySQL in-place major version upgrade, and RDS for MySQL upgrades in the AWS documentation. For the in-place upgrade from PostgreSQL 11 to 15, you can use the pg_upgrade method.
To minimize downtime during upgrades, we recommend using Fully Managed Blue/Green Deployments in Amazon Aurora and Amazon RDS. With just a few steps, you can use Amazon RDS Blue/Green Deployments to create a separate, synchronized, fully managed staging environment that mirrors the production environment. This involves launching a parallel green environment with upper version replicas of your production databases lower version. After validating the green environment, you can shift traffic over to it. Then, the blue environment can be decommissioned. To learn more, see Blue/Green Deployments for Aurora MySQL and Aurora PostgreSQL or Blue/Green Deployments for RDS for MySQL and RDS for PostgreSQL in the AWS documentation. In most cases, Blue/Green Deployments are the best option to reduce downtime, except for limited cases in Amazon Aurora or Amazon RDS.
For more information on performing a major version upgrade in each DB engine, see the following guides in the AWS documentation.
Now available
Amazon RDS Extended Support is now available for all customers running Amazon Aurora and Amazon RDS instances using MySQL 5.7, PostgreSQL 11, and higher major versions in AWS Regions, including the AWS GovCloud (US) Regions beyond the end of the standard support date in 2024. You don’t need to opt in to RDS Extended Support, and you get the flexibility to upgrade your databases and continued support for up to 3 years.
Learn more about RDS Extended Support in the Amazon Aurora User Guide and the Amazon RDS User Guide. For pricing details and timelines for RDS Extended Support, see Amazon Aurora pricing, RDS for MySQL pricing, and RDS for PostgreSQL pricing.
Please send feedback to AWS re:Post for Amazon RDS and Amazon Aurora or through your usual AWS Support contacts.
— Channy

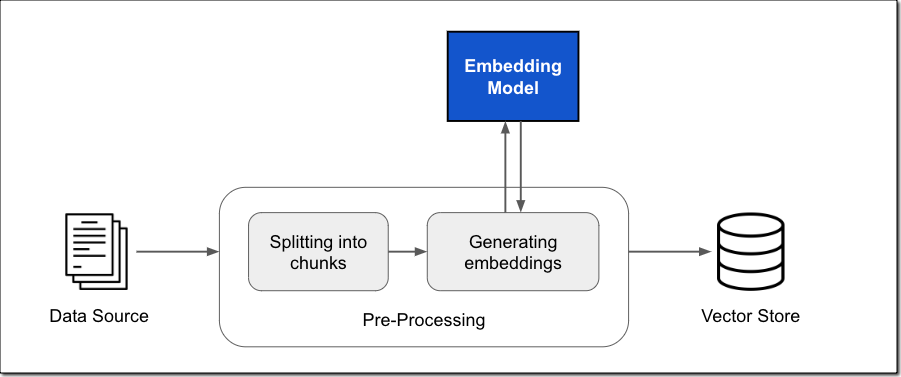
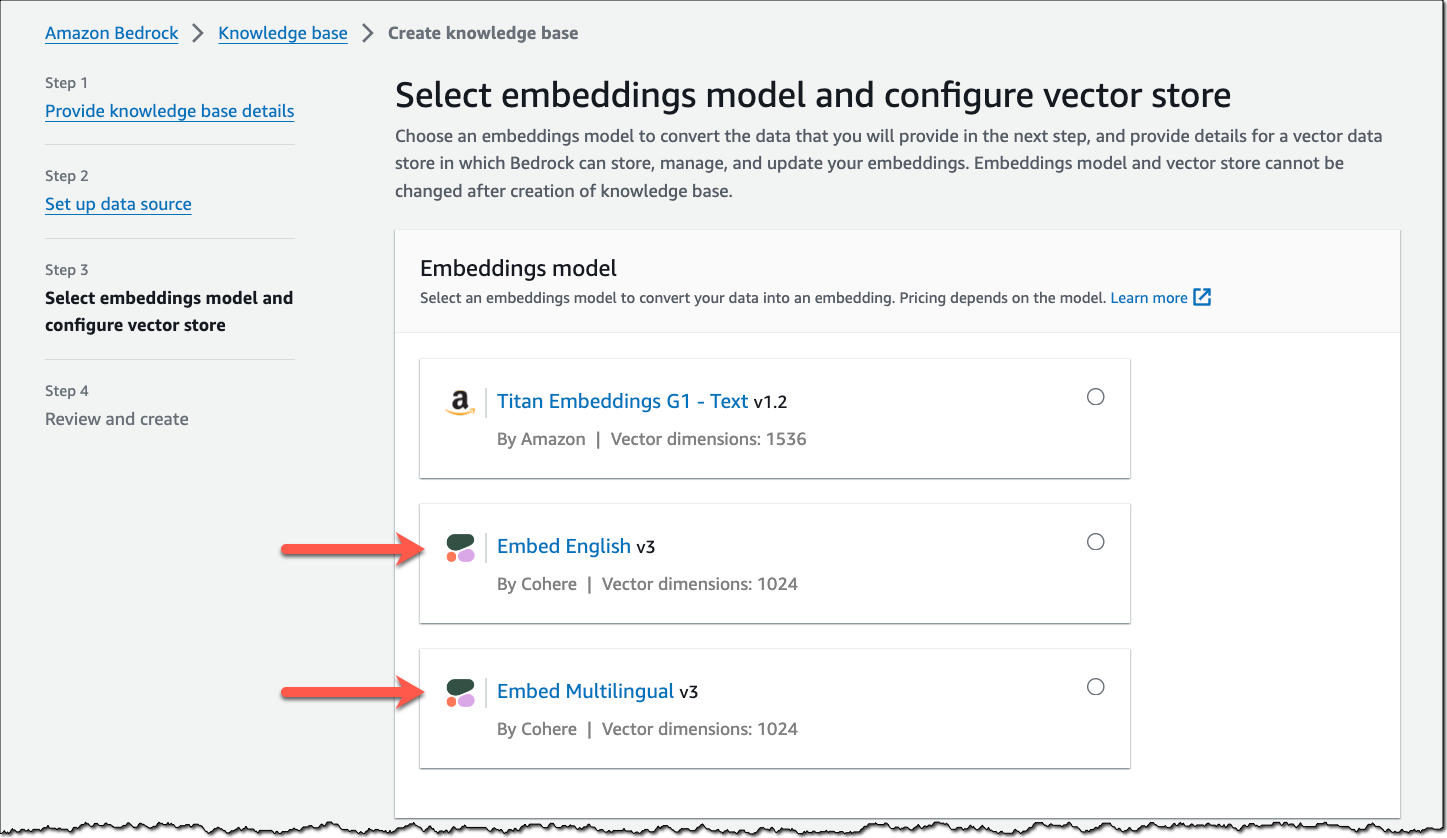
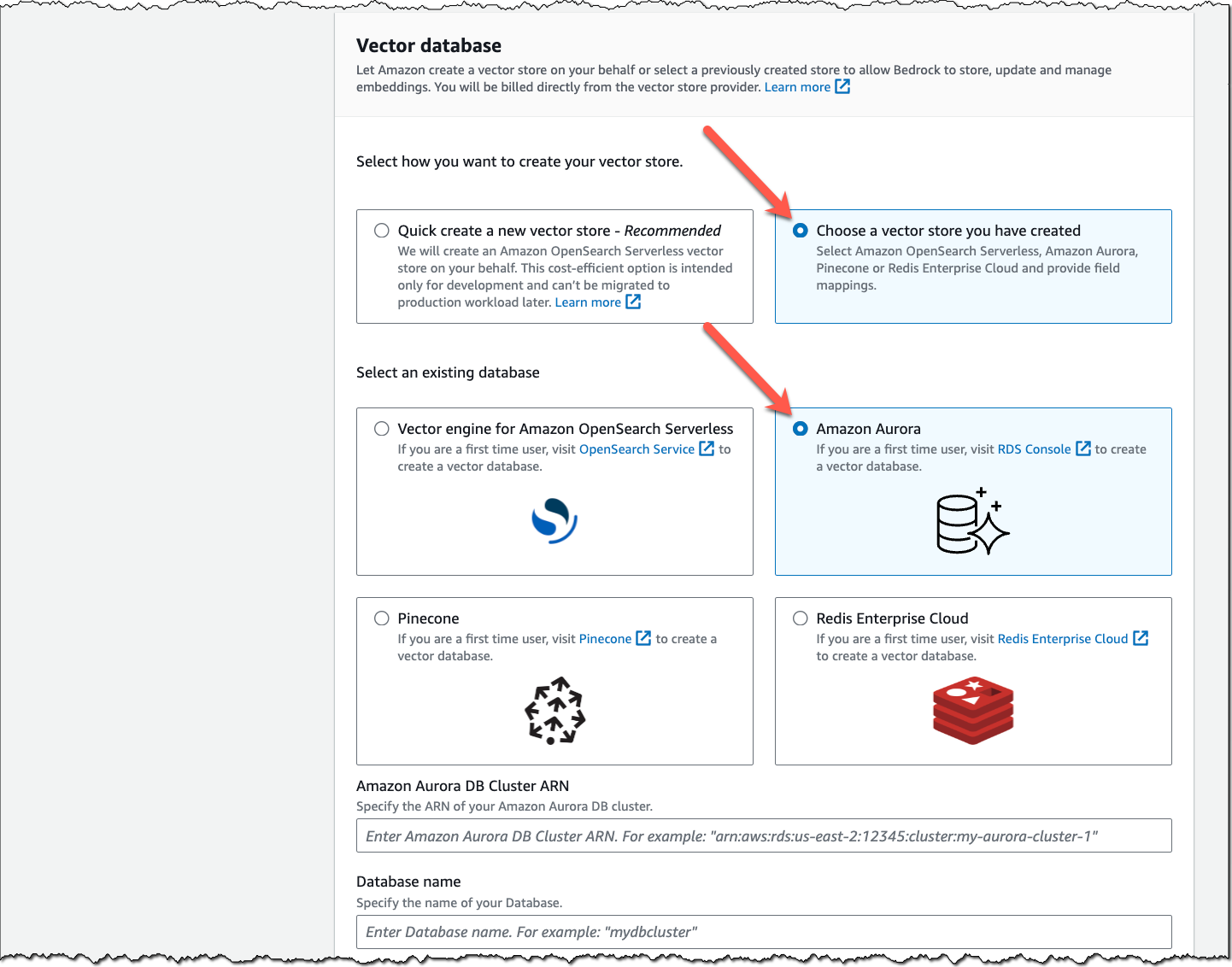
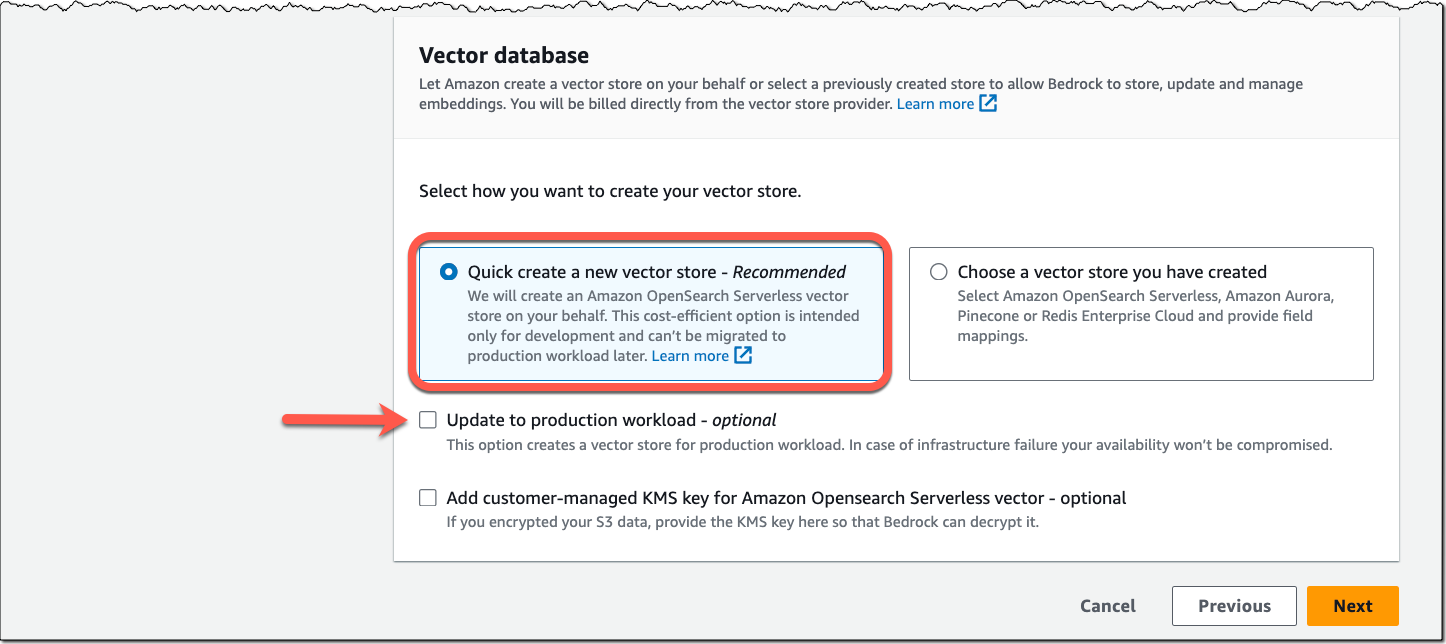
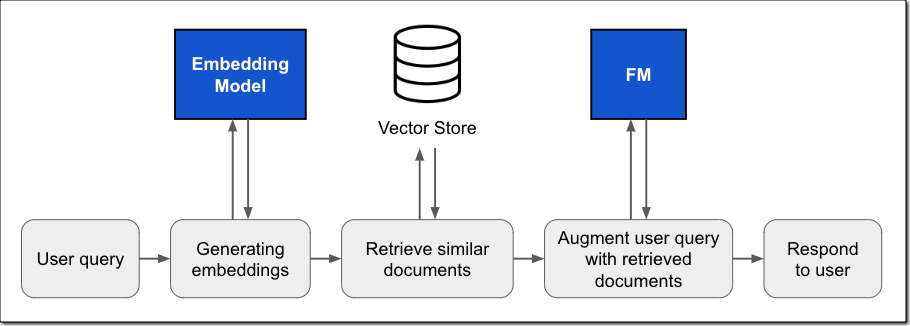
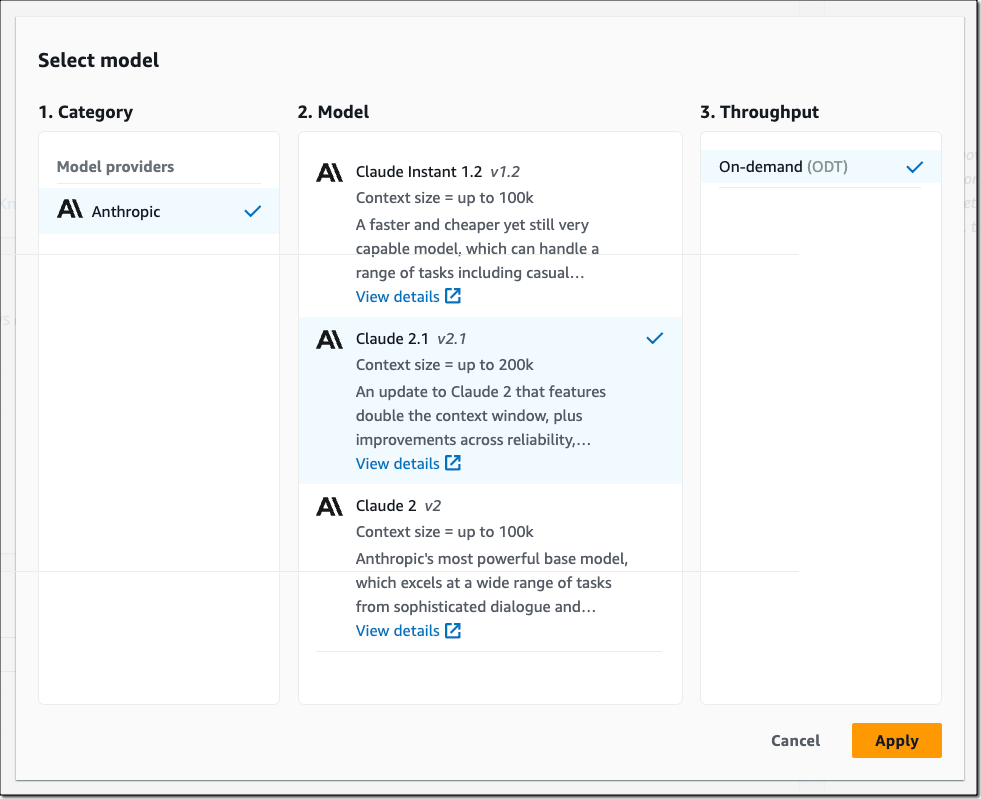







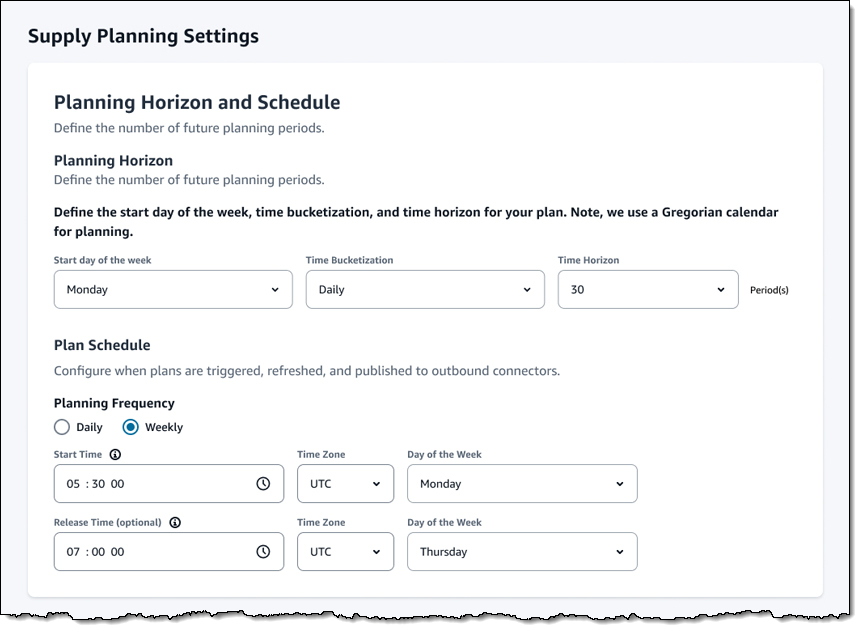
 We are launching three new modules for
We are launching three new modules for 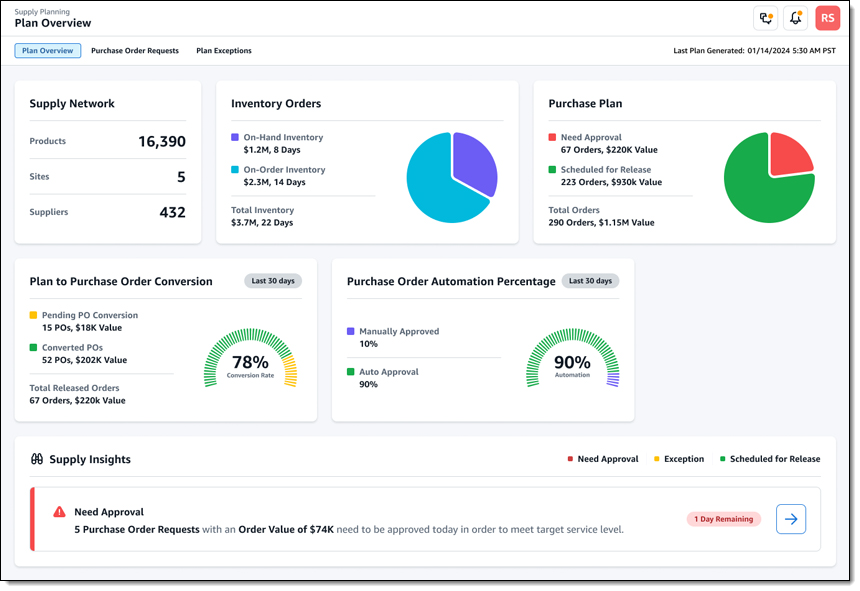

 Happy New Year! Cloud technologies, machine learning, and generative AI have become more accessible, impacting nearly every aspect of our lives. Amazon CTO Dr. Werner Vogels offers four tech predictions for 2024 and beyond:
Happy New Year! Cloud technologies, machine learning, and generative AI have become more accessible, impacting nearly every aspect of our lives. Amazon CTO Dr. Werner Vogels offers four tech predictions for 2024 and beyond: