This
post was originally published on
this siteStarting today, you can use your own AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) keys to encrypt identity data, such as user and group attributes, stored in AWS IAM Identity Center organization instances.
Many organizations operating in regulated industries need complete control over encryption key management. While Identity Center already encrypts data at rest using AWS-owned keys, some customers require the ability to manage their own encryption keys for audit and compliance purposes.
With this launch, you can now use customer-managed KMS keys (CMKs) to encrypt Identity Center identity data at rest. CMKs provide you with full control over the key lifecycle, including creation, rotation, and deletion. You can configure granular access controls to keys with AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) key policies and IAM policies, helping to ensure that only authorized principals can access your encrypted data. At launch time, the CMK must reside in the same AWS account and Region as your IAM Identity Center instance. The integration between Identity Center and KMS provides detailed AWS CloudTrail logs for auditing key usage and helps meet regulatory compliance requirements.
Identity Center supports both single-Region and multi-Region keys to match your deployment needs. While Identity Center instances can currently only be deployed in a single Region, we recommend using multi-Region AWS KMS keys unless your company policies restrict you to single-Region keys. Multi-Region keys provide consistent key material across Regions while maintaining independent key infrastructure in each Region. This gives you more flexibility in your encryption strategy and helps future-proof your deployment.
Let’s get started
Let’s imagine I want to use a CMK to encrypt the identity data of my Identity Center organization instance. My organization uses Identity Center to give employees access to AWS managed applications, such as Amazon Q Business or Amazon Athena.
As of today, some AWS managed applications cannot be used with Identity Center configured with a customer managed KMS key. See AWS managed applications that you can use with Identity Center to keep you updated with the ever evolving list of compatible applications.
The high-level process requires first to create a symmetric customer managed key (CMK) in AWS KMS. The key must be configured for encrypt and decrypt operations. Next, I configure the key policies to grant access to Identity Center, AWS managed applications, administrators, and other principals who need access the Identity Center and IAM Identity Center service APIs. Depending on your usage of Identity Center, you’ll have to define different policies for the key and IAM policies for IAM principals. The service documentation has more details to help you cover the most common use cases.
This demo is in three parts. I first create a customer managed key in AWS KMS and configure it with permissions that will authorize Identity Center and AWS managed applications to use it. Second, I update the IAM policies for the principals that will use the key from another AWS account, such as AWS applications administrators. Finally, I configure Identity Center to use the key.
Part 1: Create the key and define permissions
First, let’s create a new CMK in AWS KMS.

The key must be in the same AWS Region and AWS account as the Identity Center instance. You must create the Identity Center instance and the key in the management account of your organization within AWS Organization.
I navigate to the AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) console in the same Region as my Identity Center instance, then I choose Create a key. This launches me into the key creation wizard.
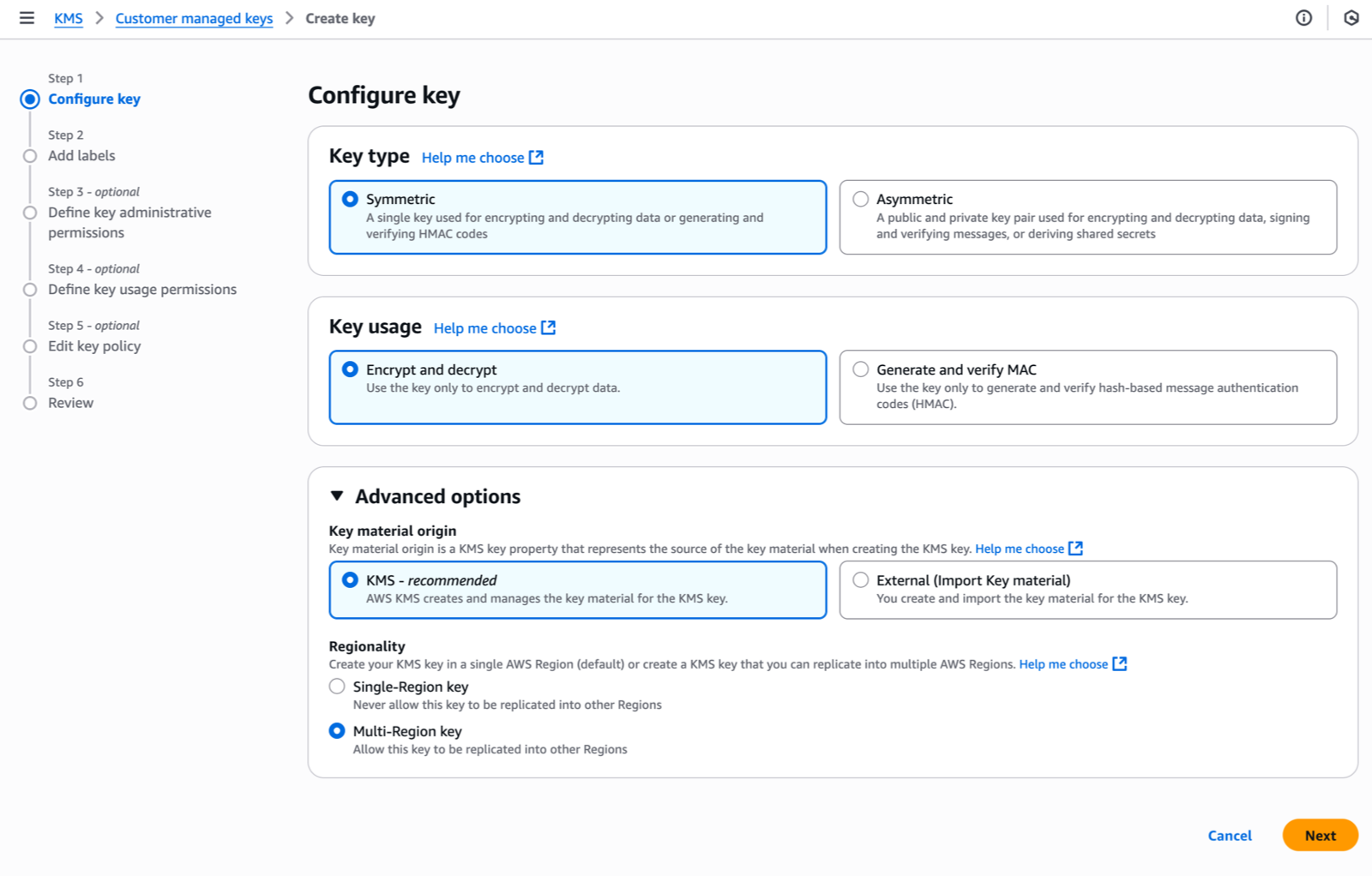
Under Step 1–Configure key, I select the key type–either Symmetric (a single key used for both encryption and decryption) or Asymmetric (a public-private key pair for encryption/decryption and signing/verification). Identity Center requires symmetric keys for encryption at rest. I select Symmetric.
For key usage, I select Encrypt and decrypt which allows the key to be used only for encrypting and decrypting data.
Under Advanced options, I select KMS – recommended for Key material origin, so AWS KMS creates and manages the key material.
For Regionality, I choose between Single-Region or Multi-Region key. I select Multi-Region key to allow key administrators to replicate the key to other Regions. As explained already, Identity Center doesn’t require this today but it helps to future-proof your configuration. Remember that you can not transform a single-Region key to a multi-Region one after its creation (but you can change the key used by Identity Center).
Then, I choose Next to proceed with additional configuration steps, such as adding labels, defining administrative permissions, setting usage permissions, and reviewing the final configuration before creating the key.
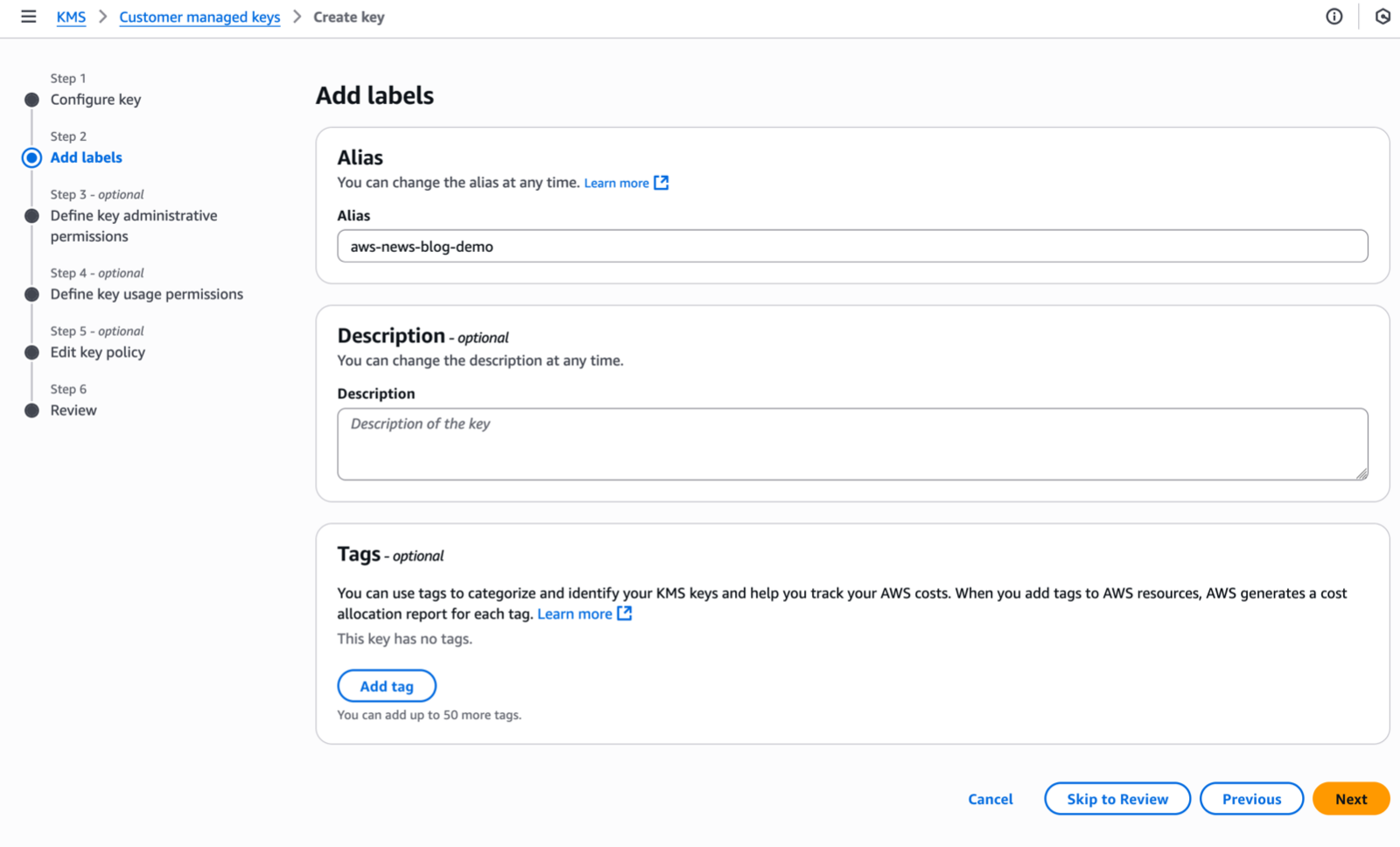
Under Step 2–Add Labels, I enter an Alias name for my key and select Next.
In this demo, I am editing the key policy by adding policy statements using templates provided in the documentation. I skip Step 3 and Step 4 and navigate to Step 5–Edit key policy.
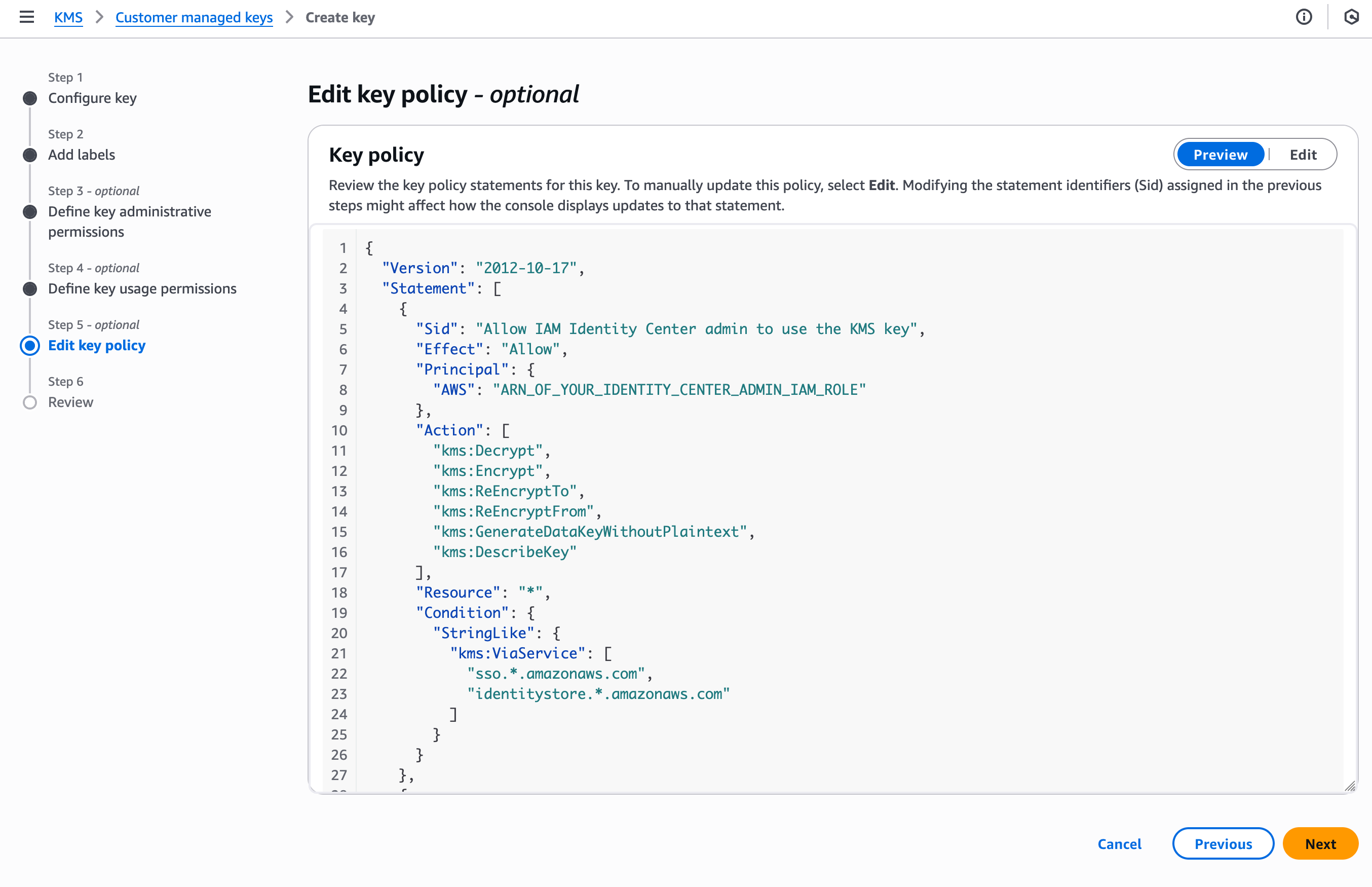
Identity Center requires, at the minimum, permissions allowing Identity Center and its administrators to use the key. Therefore, I add three policy statements, the first and second authorize the administrators of the service, the third one to authorize the Identity Center service itself.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Id": "key-consolepolicy-3",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "Allow_IAMIdentityCenter_Admin_to_use_the_KMS_key_via_IdentityCenter_and_IdentityStore",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "ARN_OF_YOUR_IDENTITY_CENTER_ADMIN_IAM_ROLE"
},
"Action": [
"kms:Decrypt",
"kms:Encrypt",
"kms:GenerateDataKeyWithoutPlaintext"
],
"Resource": "*",
"Condition": {
"StringLike": {
"kms:ViaService": [
"sso.*.amazonaws.com",
"identitystore.*.amazonaws.com"
]
}
}
},
{
"Sid": "Allow_IdentityCenter_admin_to_describe_the_KMS_key",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "ARN_OF_YOUR_IDENTITY_CENTER_ADMIN_IAM_ROLE"
},
"Action": "kms:DescribeKey",
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Sid": "Allow_IdentityCenter_and_IdentityStore_to_use_the_KMS_key",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": [
"sso.amazonaws.com",
"identitystore.amazonaws.com"
]
},
"Action": [
"kms:Decrypt",
"kms:ReEncryptTo",
"kms:ReEncryptFrom",
"kms:GenerateDataKeyWithoutPlaintext"
],
"Resource": "*",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"aws:SourceAccount": "<Identity Center Account ID>"
}
}
},
{
"Sid": "Allow_IdentityCenter_and_IdentityStore_to_describe_the_KMS_key",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": [
"sso.amazonaws.com",
"identitystore.amazonaws.com"
]
},
"Action": [
"kms:DescribeKey"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
I also have to add additional policy statements to allow my use case: the use of AWS managed applications. I add these two policy statements to authorize AWS managed applications and their administrators to use the KMS key. The document lists additional use cases and their respective policies.
{
"Sid": "Allow_AWS_app_admins_in_the_same_AWS_organization_to_use_the_KMS_key",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": "*",
"Action": [
"kms:Decrypt"
],
"Resource": "*",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals" : {
"aws:PrincipalOrgID": "MY_ORG_ID (format: o-xxxxxxxx)"
},
"StringLike": {
"kms:ViaService": [
"sso.*.amazonaws.com", "identitystore.*.amazonaws.com"
]
}
}
},
{
"Sid": "Allow_managed_apps_to_use_the_KMS_Key",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": "*",
"Action": [
"kms:Decrypt"
],
"Resource": "*",
"Condition": {
"Bool": { "aws:PrincipalIsAWSService": "true" },
"StringLike": {
"kms:ViaService": [
"sso.*.amazonaws.com", "identitystore.*.amazonaws.com"
]
},
"StringEquals": { "aws:SourceOrgID": "MY_ORG_ID (format: o-xxxxxxxx)" }
}
}
You can further restrict the key usage to a specific Identity Center instance, specific application instances, or specific application administrators. The documentation contains examples of advanced key policies for your use cases.
To help protect against IAM role name changes when permission sets are recreated, use the approach described in the Custom trust policy example.
Part 2: Update IAM policies to allow use of the KMS key from another AWS account
Any IAM principal that uses the Identity Center service APIs from another AWS account, such as Identity Center delegated administrators and AWS application administrators, need an IAM policy statement that allows use of the KMS key via these APIs.
I grant permissions to access the key by creating a new policy and attaching the policy to the IAM role relevant for my use case. You can also add these statements to the existing identity-based policies of the IAM role.
To do so, after the key is created, I locate its ARN and replace the key_ARNin the template below. Then, I attach the policy to the managed application administrator IAM principal. The documentation also covers IAM policies that grants Identity Center delegated administrators permissions to access the key.
Here is an example for managed application administrators:
{
"Sid": "Allow_app_admins_to_use_the_KMS_key_via_IdentityCenter_and_IdentityStore",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action":
"kms:Decrypt",
"Resource": "<key_ARN>",
"Condition": {
"StringLike": {
"kms:ViaService": [
"sso.*.amazonaws.com",
"identitystore.*.amazonaws.com"
]
}
}
}
The documentation shares IAM policies template for the most common use cases.
Part 3: Configure IAM Identity Center to use the key
I can configure a CMK either during the enablement of an Identity Center organization instance or on an existing instance, and I can change the encryption configuration at any time by switching between CMKs or reverting to AWS-owned keys.
Please note that an incorrect configuration of KMS key permissions can disrupt Identity Center operations and access to AWS managed applications and accounts through Identity Center. Proceed carefully to this final step and ensure you have read and understood the documentation.
After I have created and configured my CMK, I can select it under Advanced configuration when enabling Identity Center.
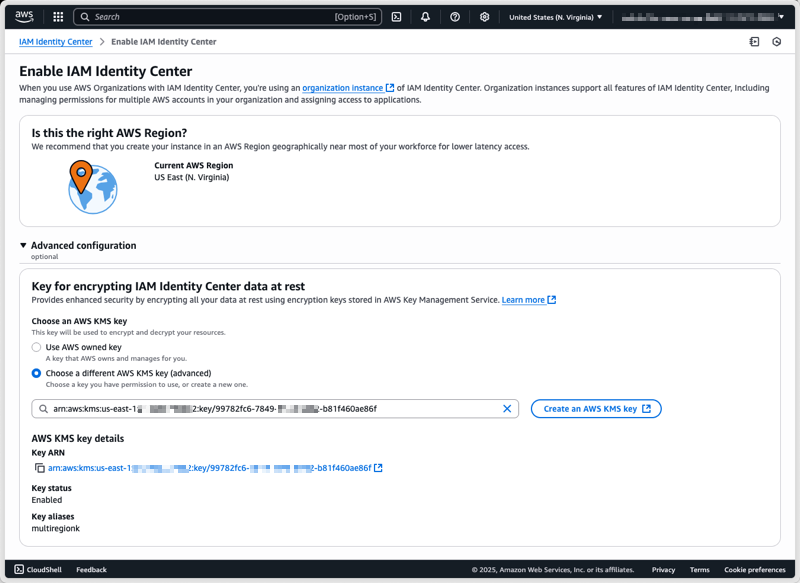
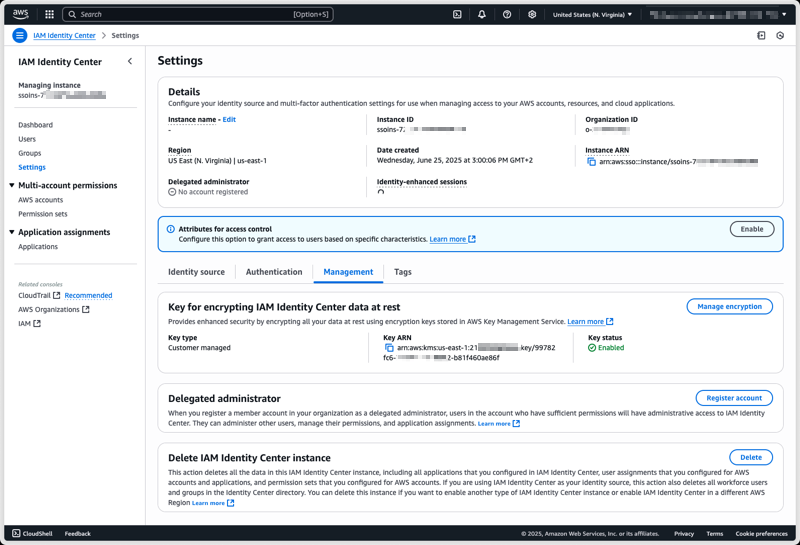
To configure a CMK on an existing Identity Center instance using the AWS Management Console, I start by navigating to the Identity Center section of the AWS Management Console. From there, I select Settings from the navigation pane, then I select the Management tab, and select Manage encryption in the Key for encrypting IAM Identity Center data at rest section.
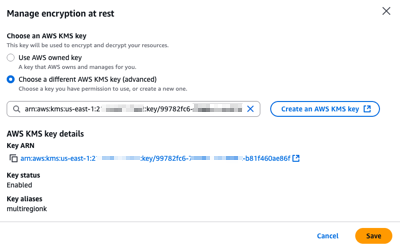
At any time, I can select another CMK from the same AWS Account, or switch back to an AWS-managed key.
After choosing Save, the key change process takes a few seconds to complete. All service functionalities continue uninterrupted during the transition. If, for whatever reasons, Identity Center can not access the new key, an error message will be returned and Identity Center will continue to use the current key, keeping your identity data encrypted with the mechanism it is already encrypted with.
Things to keep in mind
The encryption key you create becomes a crucial component of your Identity Center. When you choose to use your own managed key to encrypt identity attributes at rest, you have to verify the following points.
- Have you configured the necessary permissions to use the KMS key? Without proper permissions, enabling the CMK may fail or disrupt IAM Identity Center administration and AWS managed applications.
- Have you verified that your AWS managed applications are compatible with CMK keys? For a list of compatible applications, see AWS managed applications that you can use with IAM Identity Center. Enabling CMK for Identity Center that is used by AWS managed applications incompatible with CMK will result in operational disruption for those applications. If you have incompatible applications, do not proceed.
- Is your organization using AWS managed applications that require additional IAM role configuration to use the Identity Center and Identity Store APIs? For each such AWS managed application that’s already deployed, check the managed application’s User Guide for updated KMS key permissions for IAM Identity Centre usage and update them as instructed to prevent application disruption.
- For brevity, the KMS key policy statements in this post omit the encryption context, which allows you to restrict the use of the KMS key to Identity Center including a specific instance. For your production scenarios, you can add a condition like this for Identity Center:
"Condition": {
"StringLike": {
"kms:EncryptionContext:aws:sso:instance-arn": "${identity_center_arn}",
"kms:ViaService": "sso.*.amazonaws.com"
}
}
or this for Identity Store:
"Condition": {
"StringLike": {
"kms:EncryptionContext:aws:identitystore:identitystore-arn": "${identity_store_arn}",
"kms:ViaService": "identitystore.*.amazonaws.com"
}
}
Pricing and availability
Standard AWS KMS charges apply for key storage and API usage. Identity Center remains available at no additional cost.
This capability is now available in all AWS commercial Regions, AWS GovCloud (US), and AWS China Regions. To learn more, visit the IAM Identity Center User Guide.
We look forward to learning how you use this new capability to meet your security and compliance requirements.
— seb














 This announcement builds upon two significant storage integration milestones we achieved in the past year. In December 2024, we introduced
This announcement builds upon two significant storage integration milestones we achieved in the past year. In December 2024, we introduced