This month's Microsoft patch update addresses a total of 111 vulnerabilities, with 17 classified as critical. Among these, one vulnerability was disclosed prior to the patch release, marking it as a zero-day. While none of the vulnerabilities have been exploited in the wild, the critical ones pose significant risks, including remote code execution and elevation of privilege. Users are strongly advised to apply the updates promptly to safeguard their systems against potential threats.
Monthly Archives: August 2025
Google Paid Ads for Fake Tesla Websites, (Sun, Aug 10th)
In recent media events, Tesla has demoed progressively more sophisticated versions of its Optimus robots. The sales pitch is pretty simple: "Current AI" is fun, but what we really need is not something to create more funny kitten pictures. We need AI to load and empty dishwashers, fold laundry, and mow lawns. But the robot has not been for sale yet, and there is no firm release date.
Do sextortion scams still work in 2025?, (Wed, Aug 6th)
Sextortion e-mails have been with us for quite a while, and these days, most security professionals tend to think of them more in terms of an “e-mail background noise” rather than as if they posed any serious threat. Given that their existence is reasonably well-known even among general public, this viewpoint would seem to be justified… But are sextortion messages really irrelevant as a threat at this point, and can we therefore safely omit this topic during security awareness trainings?
Introducing MCP Support in AI Shell Preview 6
AI Shell Preview 6 is here!
We are super excited to announce the latest preview release of AI Shell. This release focuses on
enhancing the user experience with new features, improved error handling, and better integration
with Model Context Protocol (MCP) tools.
What’s new at a glance
- MCP client integration
- Built-in tools
Resolve-Errorcommand improvements- Aliases and flows for staying in your terminal
MCP Integration
AI Shell now acts as an MCP client, which allows you to add any MCP server to your AI Shell
experience. Connecting to an MCP server massively improves the capability of your AI Shell giving
you the tools that provide more relevant data or carry out actions!
Adding MCP Servers
To add an MCP server, create an mcp.json file in $HOME.aish folder. The following example
shows two MCP servers: everything and filesystem. You can add any MCP servers you want.
{
"servers": {
"everything":{
"type":"stdio",
"command":"npx",
"args":["-y", "@modelcontextprotocol/server-everything"]
},
"filesystem": {
"type": "stdio",
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"-y",
"@modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem",
"C:/Users/username/"
]
}
}
}If it’s a remote MCP server, change the type to https. You know that you have successfully added
an MCP server when you see it in the AI Shell UI. You can confirm that it’s running by checking the
status of the server through the /mcp command. Using /mcp also lists each MCP Server and the
tools available.
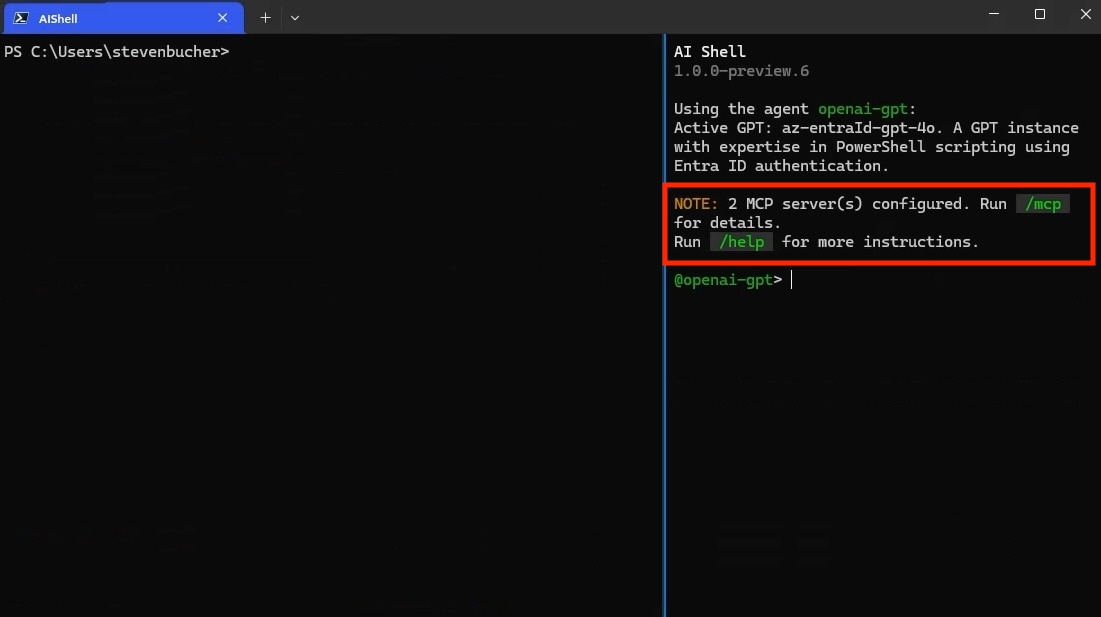
NOTE
You must have Node.js or uv installed to use MCP servers that
use those command lines tools.
Standalone experience with AI Shell and MCP Servers
MCP servers enhance your standalone experience with AI Shell, allowing your command line to use MCP
servers and AI to perform tasks. For example, @simonb97/server-win-cli is an MCP server that
allows you to run commands on your Windows machine, whether it be PowerShell, CMD, Git Bash, or any
configured shell you use! It also provides configuration settings to define which commands and
operations are allowed to run.
CAUTION
Please note this is a community MCP server and not an
official Microsoft MCP Server. We encourage you to do your own research and testing before using
it.
Additional MCP servers:
Built-in Tools for AI Shell
This release introduces built-in tools that are now accessible to agents within AI Shell. These
commands are similar to MCP Server tools, but are exclusive to the AI Shell experience. These tools
are designed to enhance the AI Shell experience by providing context-aware capabilities and
automation features. They can be used in conjunction with the MCP servers to create a powerful
AI-driven shell environment.
| Tool Name | Description |
|---|---|
get_working_directory |
Get the current working directory of the connected PowerShell session, including the provider name (e.g., FileSystem, Certificate) and the path (e.g., C:\, cert:\). |
get_command_history |
Get up to 5 of the most recent commands executed in the connected PowerShell session. |
get_terminal_content |
Get all output currently displayed in the terminal window of the connected PowerShell session. |
get_environment_variables |
Get environment variables and their values from the connected PowerShell session. Values of potentially sensitive variables are redacted. |
copy_text_to_clipboard |
Copy the provided text or code to the system clipboard, making it available for pasting elsewhere. |
post_code_to_terminal |
Insert code into the prompt of the connected PowerShell session without executing it. The user can review and choose to run it manually by pressing Enter. |
run_command_in_terminal |
This tool allows you to execute shell commands in a persistent PowerShell session, preserving environment variables, working directory, and other context across multiple commands. |
get_command_output |
Get the output of a command previously started with run_command_in_terminal. |
Note
The built-in tools rely on the side-car experience with a
connected PowerShell session and provide enhanced context awareness and automation capabilities.
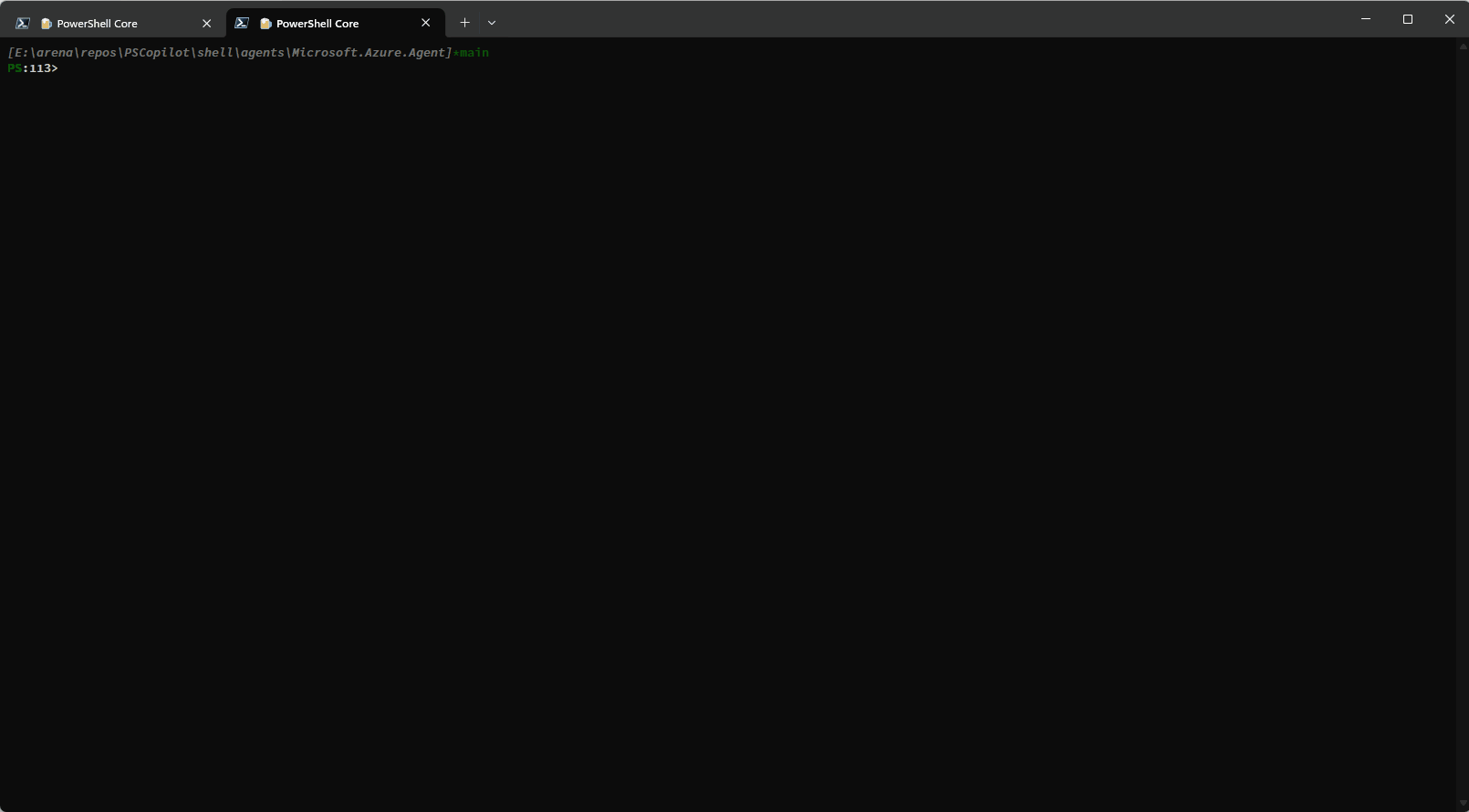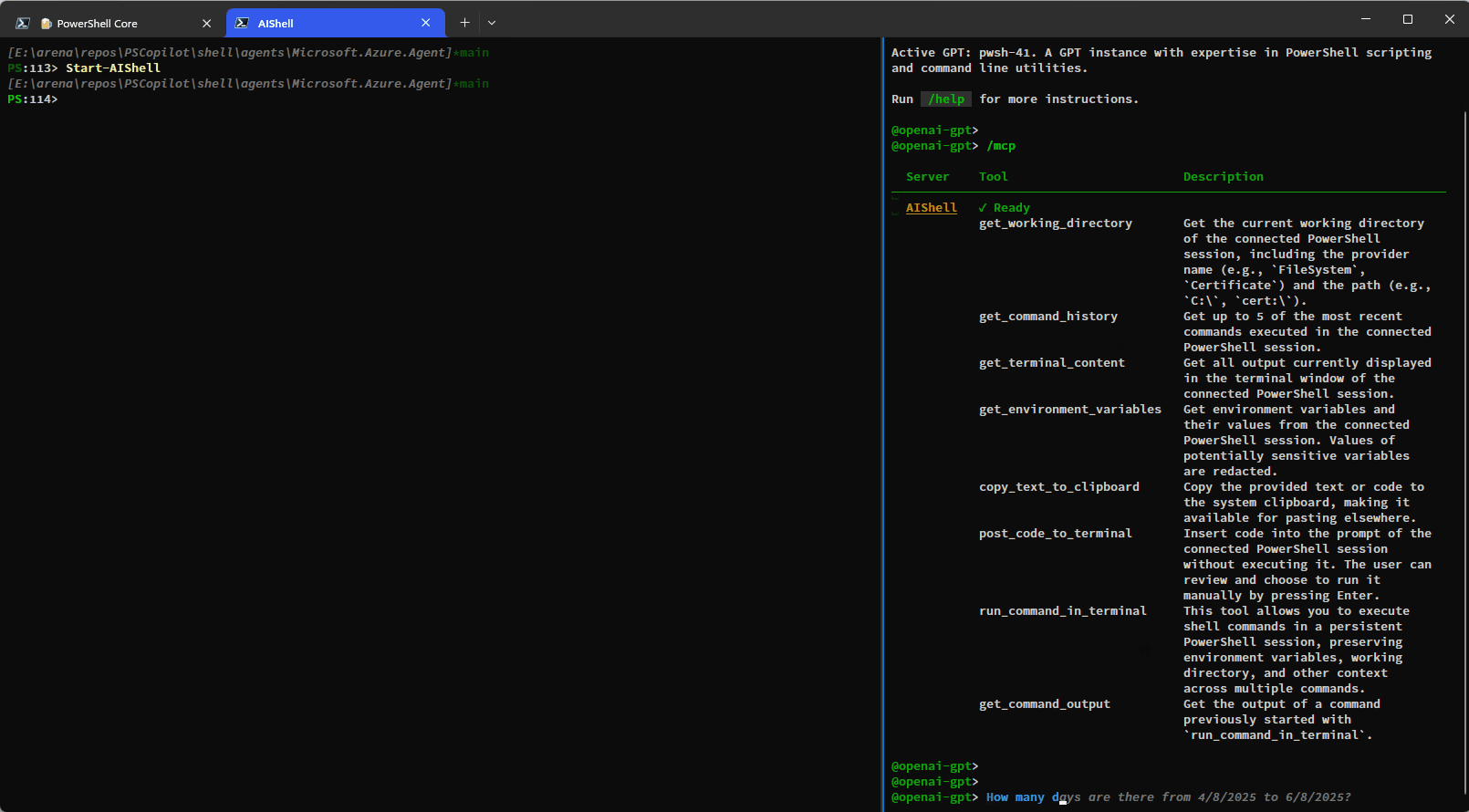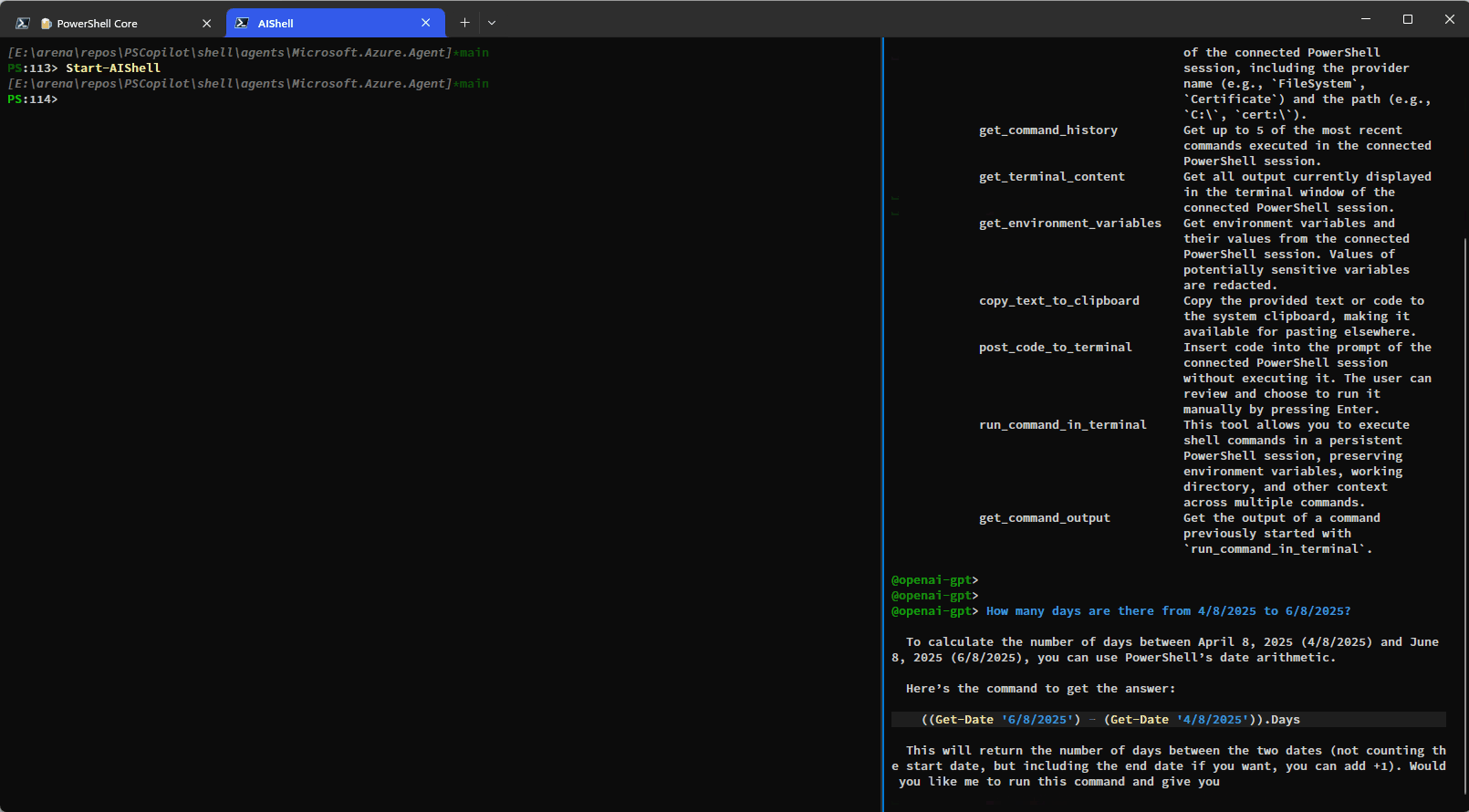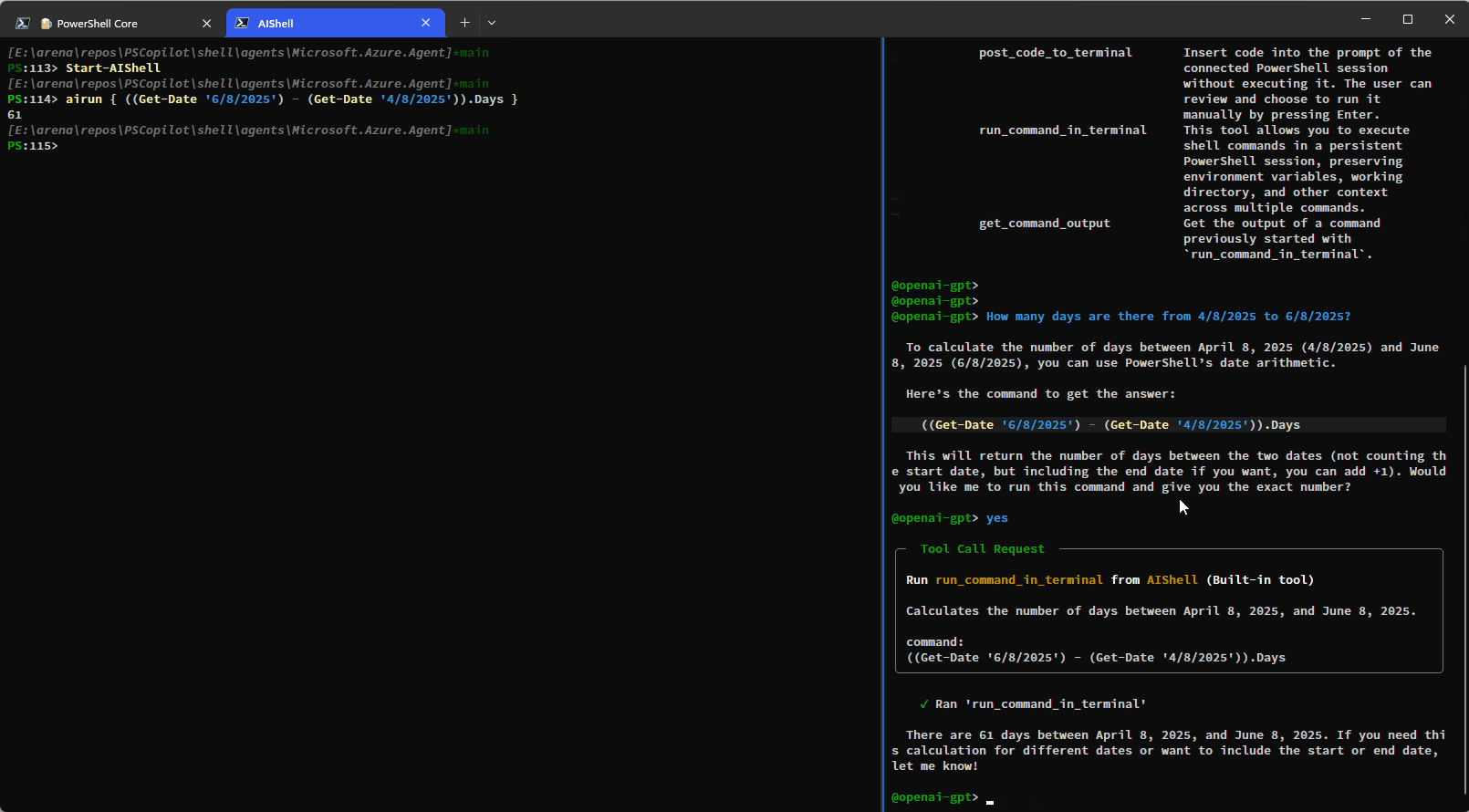
Here is a simple demo showing how you can have AI Shell run commands on your behalf using the
run_command_in_terminal tool:
This example shows how additional context is provided to AI Shell to improve results:
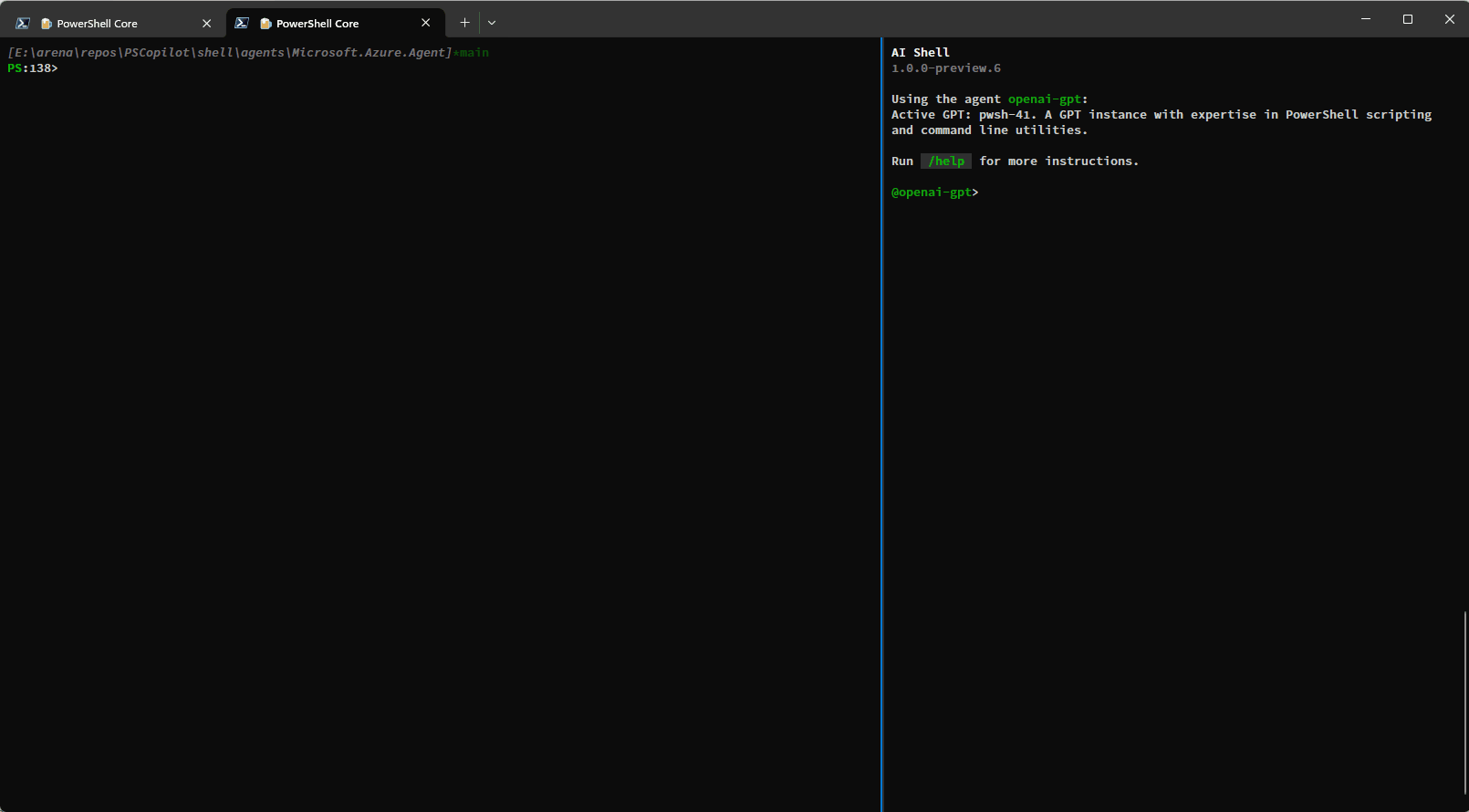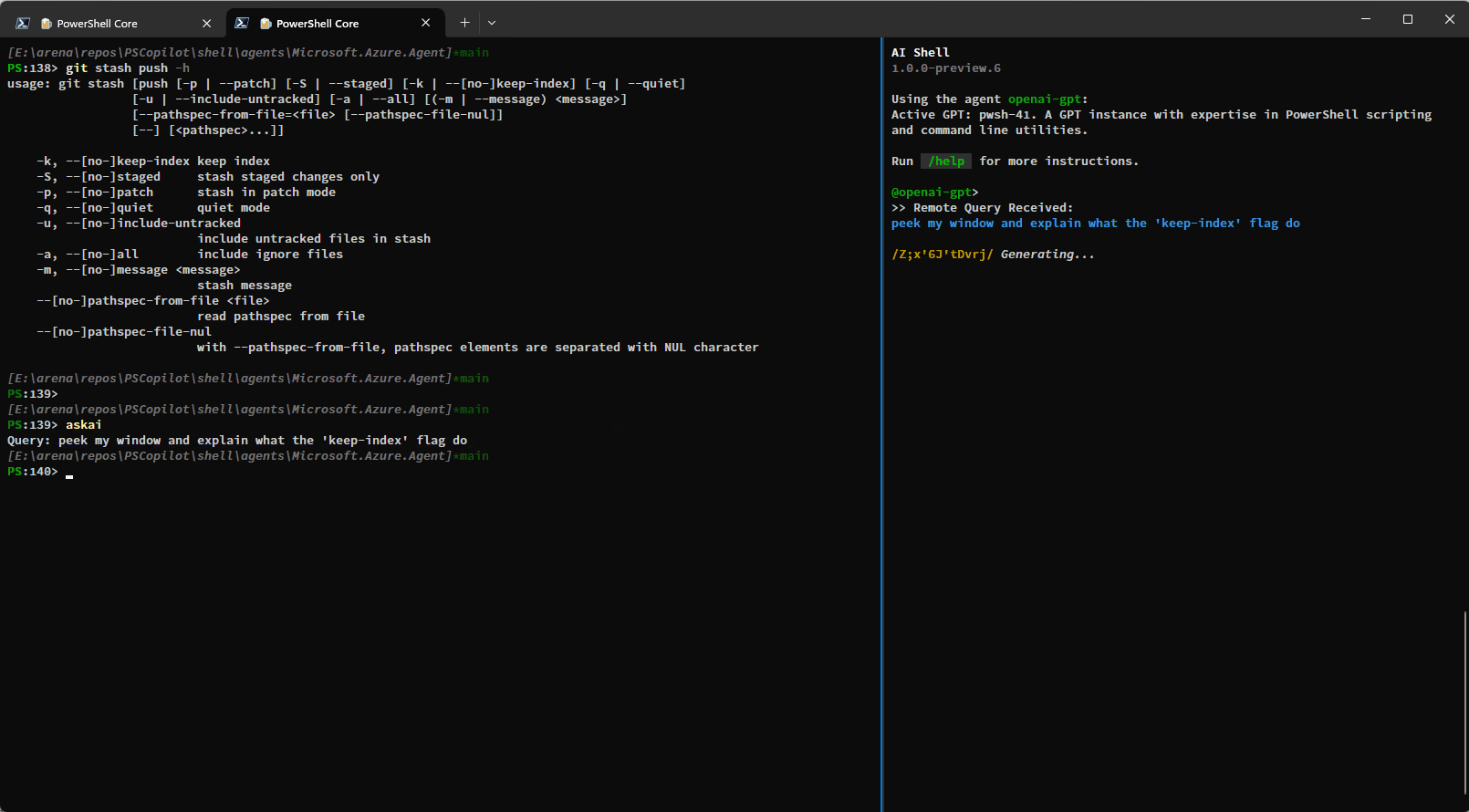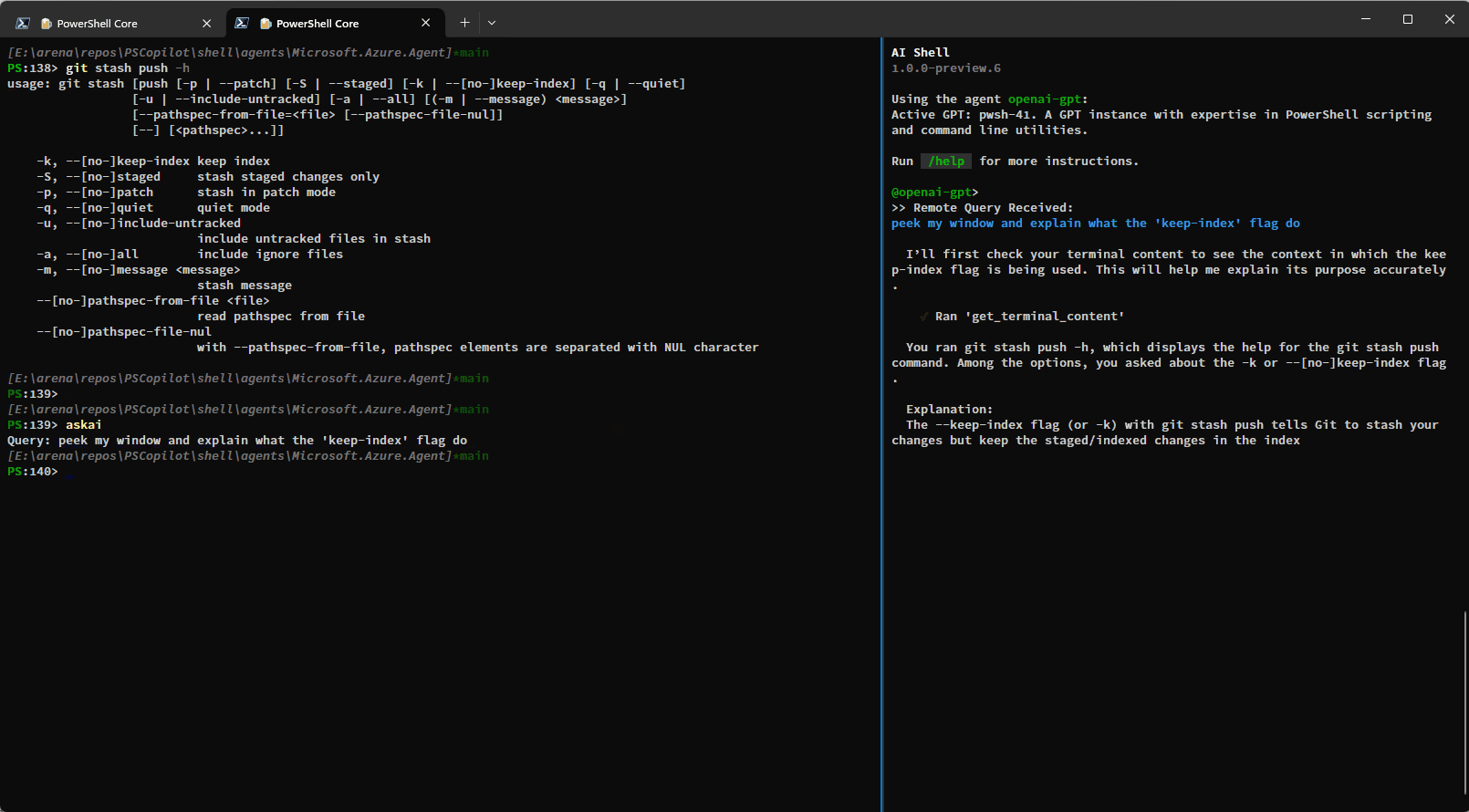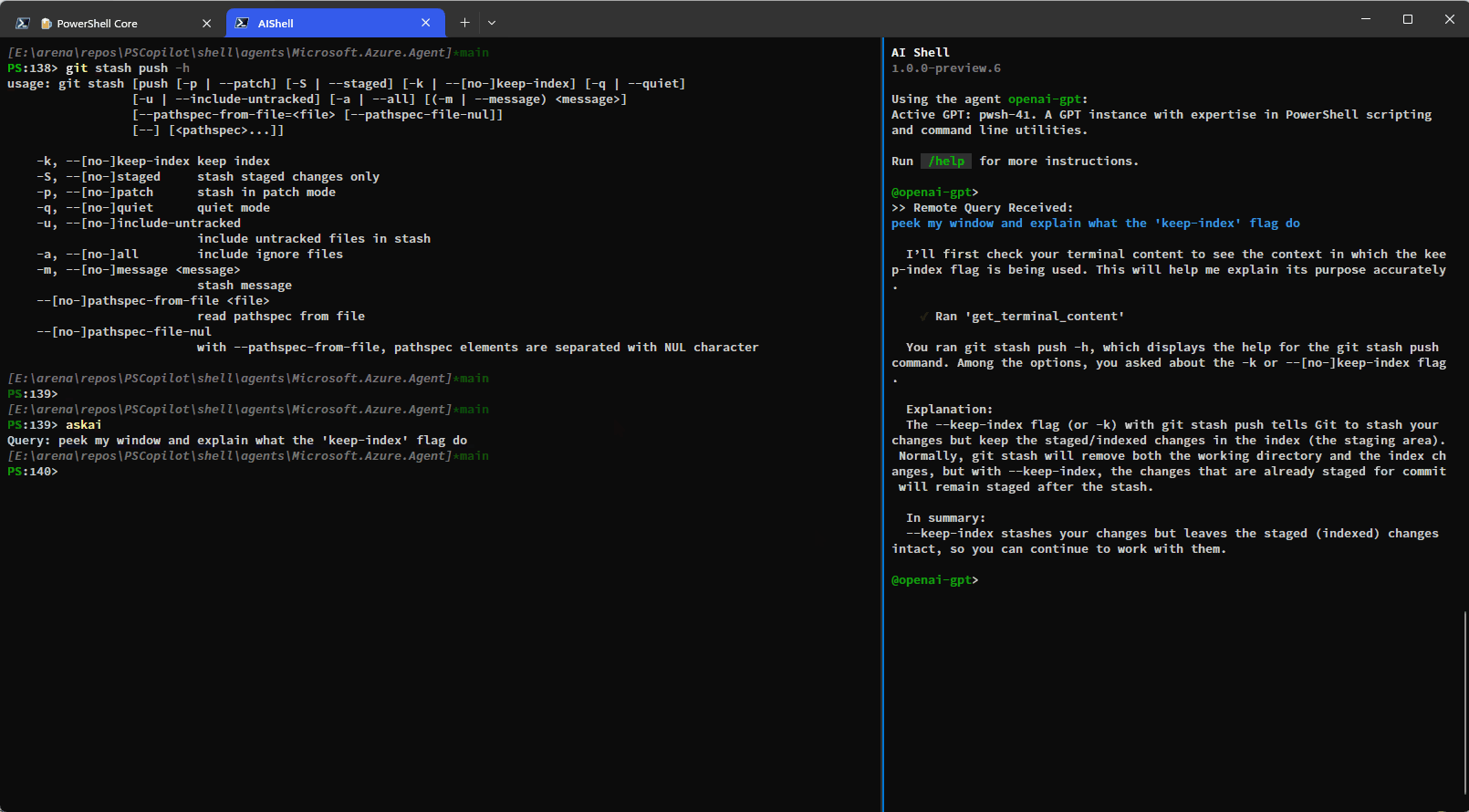
You can also use the get_terminal_content tool to get the content from the connected terminal and
provide it to AI Shell to help it understand what you are trying to do:
Resolve-Error Command Improvements
Previously the Resolve-Error command was only able to run after an error occurred in the previous
command. Now, Resolve-Error identifies which command the user wants to troubleshoot:
- If the last error’s command matches the most recent command in history, it’s assumed to be the one
the user is interested in. - If the last error’s command isn’t the most recent and
$LastErrorCodeis null or zero, the error
likely comes from an earlier command, not the very last one. - If
$LastErrorCodeis non-zero and$?is false, the last command was a failing native command. - If
$LastErrorCodeis non-zero but$?is true, it’s unclear which command or failure the user
is focused on, so the agent analyzes the terminal content to determine the relevant context.
This logic allows AI Shell to better understand what the error the user is trying to resolve is
rather than requiring you to ask for AI’s help immediately after an error occurs.
Staying in your shell
The Invoke-AIShell and Resolve-Error commands allow you to stay in your working terminal to
interact with the AI Shell agent. To learn more about the parameters added, see the
previous blog post that details these features. For your convenience, these commands have
aliases that make them quicker to use.
| Command Name | Alias |
|---|---|
Invoke-AIShell |
askai |
Resolve-Error |
fixit |
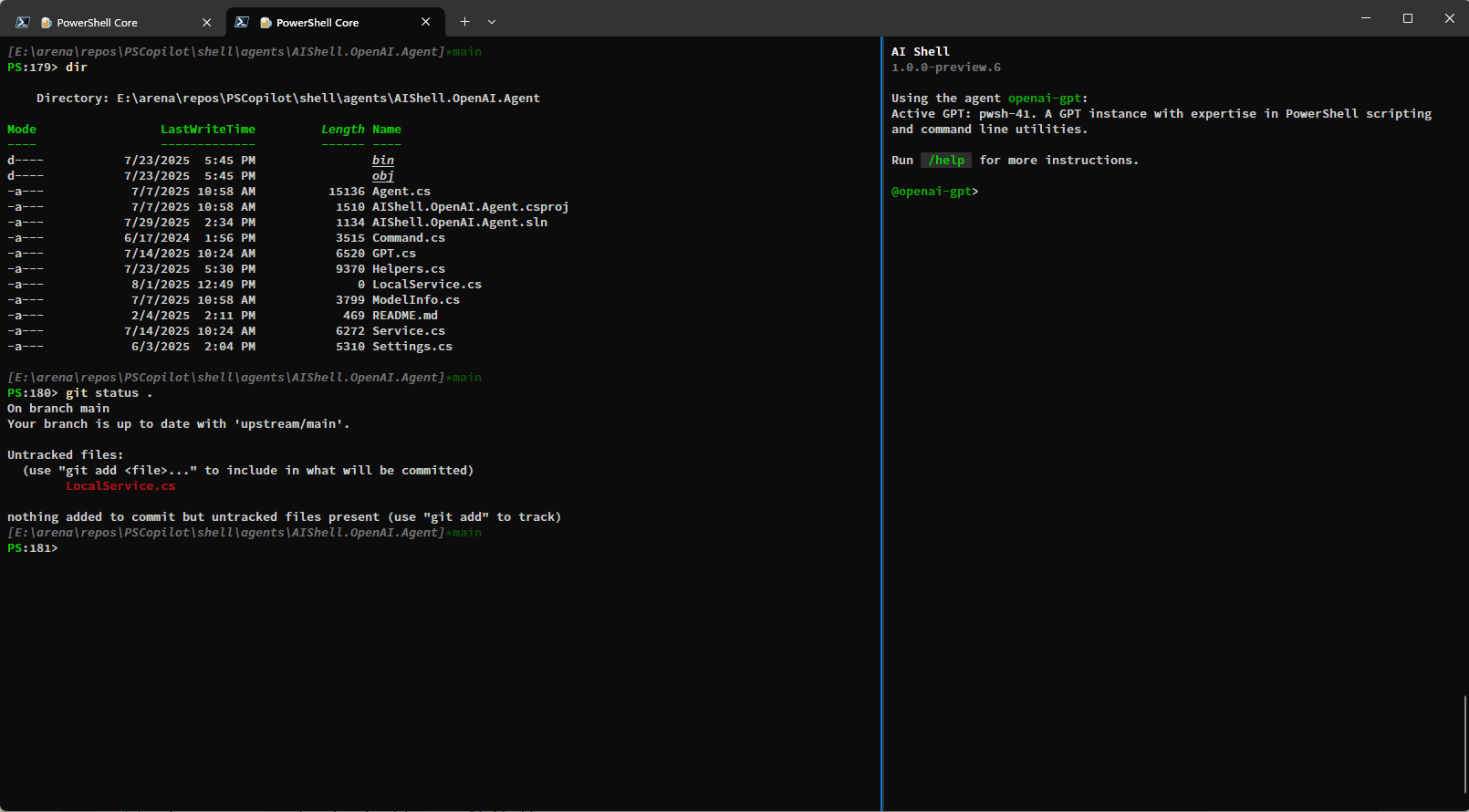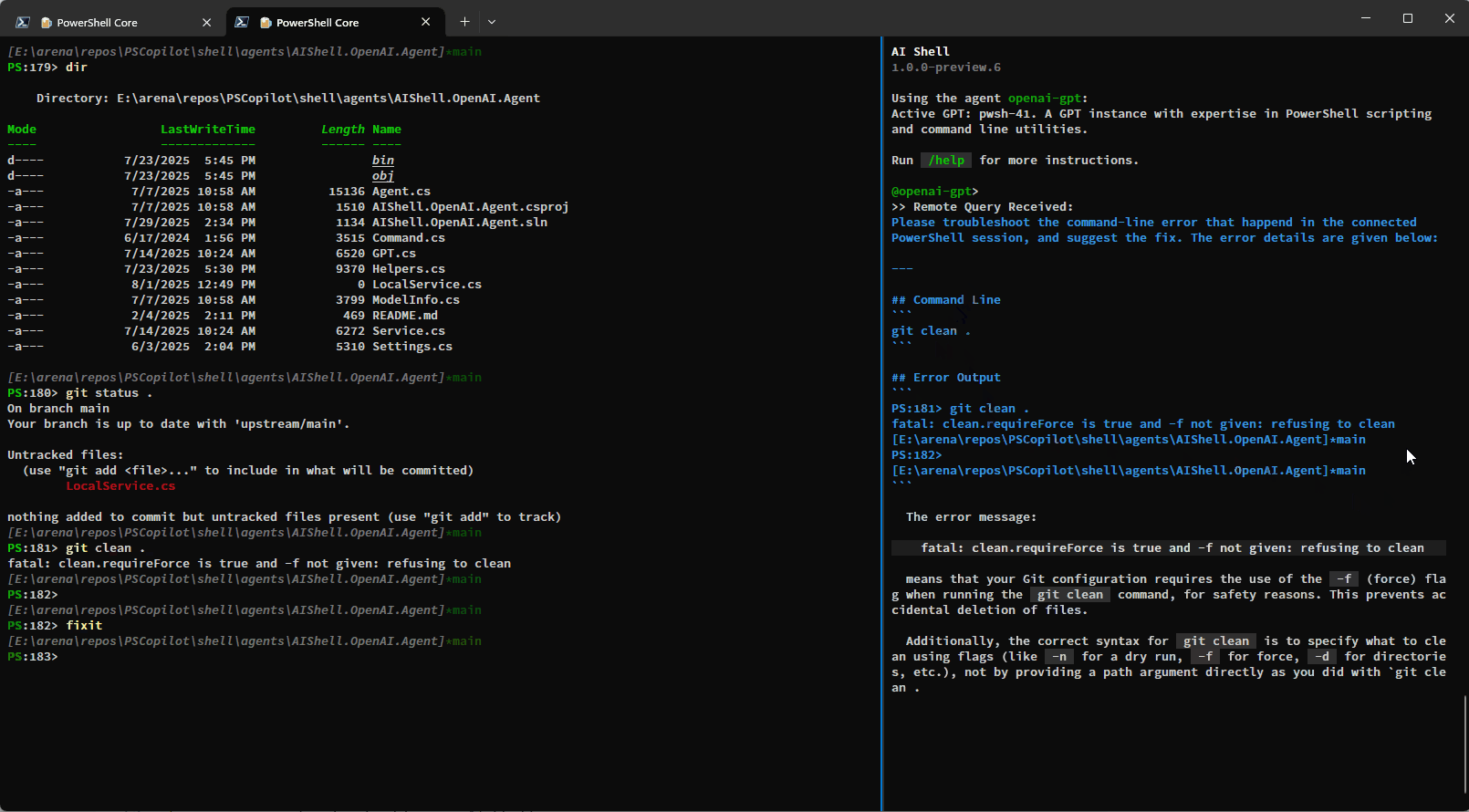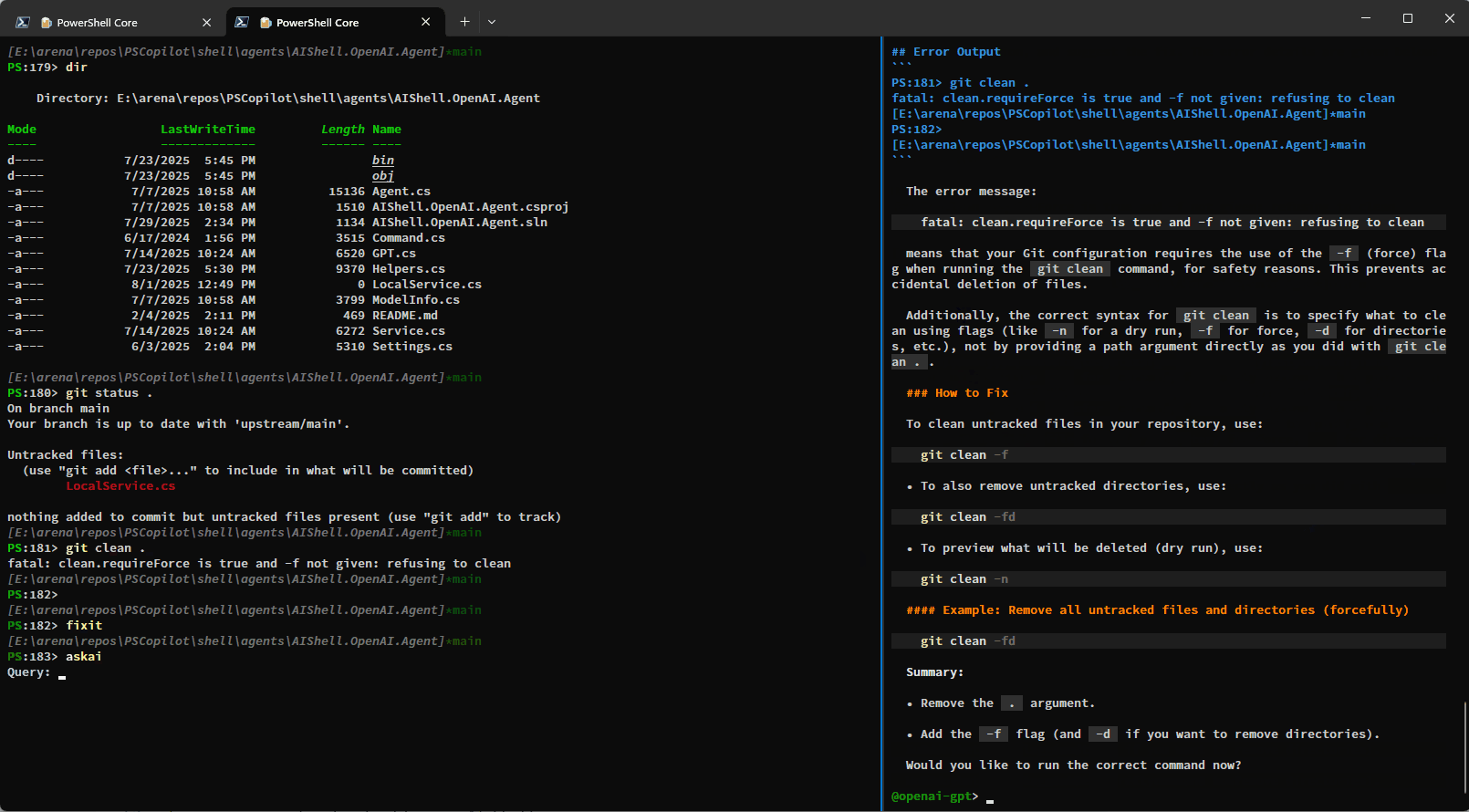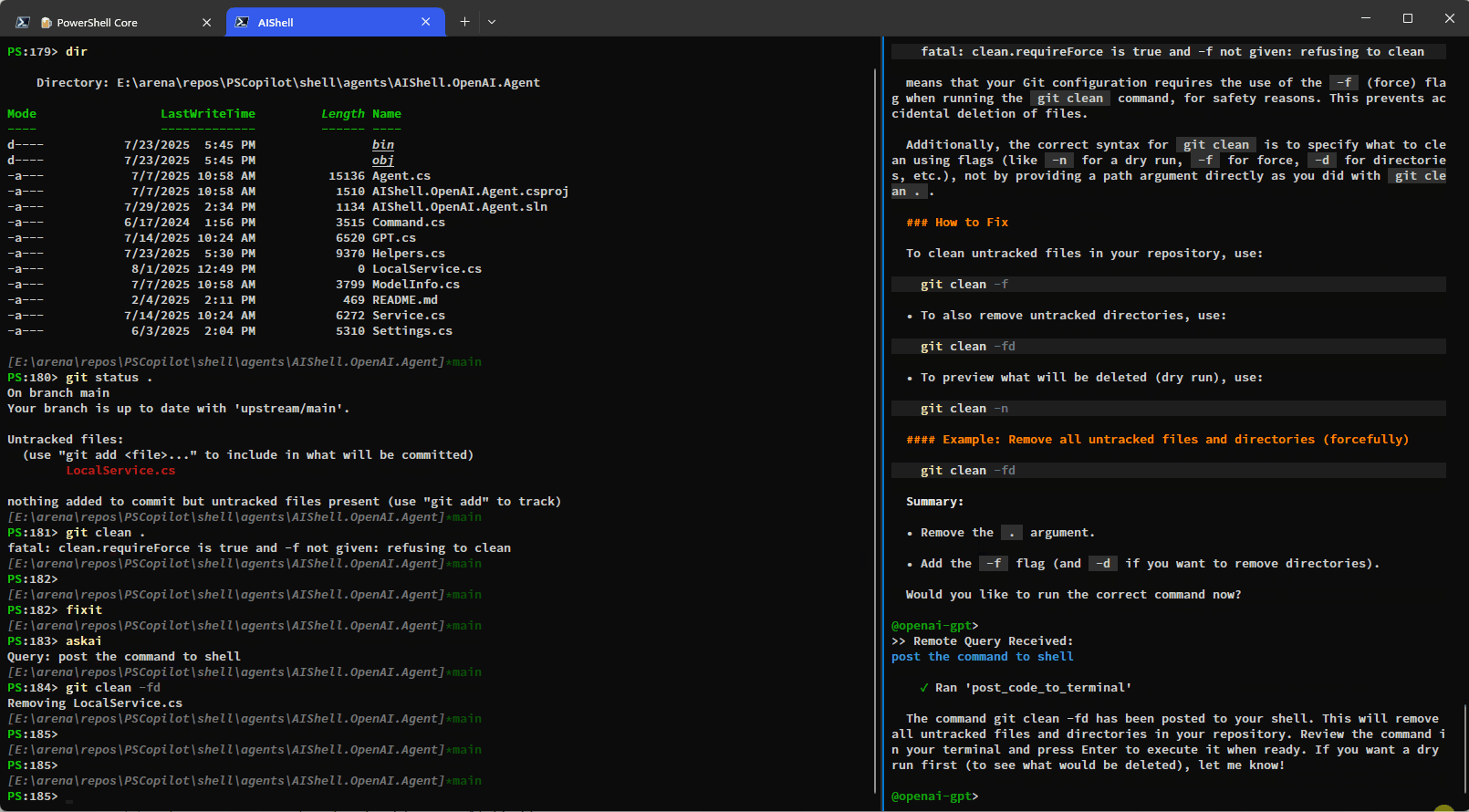
Conclusion
We hope that these enhancements make your experience with AI Shell more powerful! We are always
looking for feedback and suggestions, so please submit issues or feature requests in our
GitHub repository.
Thank you so much!
AI Shell Team
Steven Bucher & Dongbo Wang
The post Introducing MCP Support in AI Shell Preview 6 appeared first on PowerShell Team.
Introducing Amazon Elastic VMware Service for running VMware Cloud Foundation on AWS
Today, we’re announcing the general availability of Amazon Elastic VMware Service (Amazon EVS), a new AWS service that lets you run VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) environments directly within your Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC). With Amazon EVS, you can deploy fully functional VCF environments in just hours using a guided workflow, while running your VMware workloads on qualified Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) bare metal instances and seamlessly integrating with AWS services such as Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP.
Many organizations running VMware workloads on premises want to move to the cloud to benefit from improved scalability, reliability, and access to cloud services, but migrating these workloads often requires substantial changes to applications and infrastructure configurations. Amazon EVS lets customers continue using their existing VMware expertise and tools without having to re-architect applications or change established practices, thereby simplifying the migration process while providing access to AWS’s scale, reliability, and broad set of services.
With Amazon EVS, you can run VMware workloads directly in your Amazon VPC. This gives you full control over your environments while being on AWS infrastructure. You can extend your on-premises networks and migrate workloads without changing IP addresses or operational runbooks, reducing complexity and risk.
Key capabilities and features
Amazon EVS delivers a comprehensive set of capabilities designed to streamline your VMware workload migration and management experience. The service enables seamless workload migration without the need for replatforming or changing hypervisors, which means you can maintain your existing infrastructure investments while moving to AWS. Through an intuitive, guided workflow on the AWS Management Console, you can efficiently provision and configure your EVS environments, significantly reducing the complexity to migrate your workloads to AWS.
With Amazon EVS, you can deploy a fully functional VCF environment running on AWS in a few hours. This process eliminates many of the manual steps and potential configuration errors that often occur during traditional deployments. Furthermore, with Amazon EVS you can optimize your virtualization stack on AWS. Given the VCF environment runs inside your VPC, you have full full administrative access to the environment and the associated management appliances. You also have the ability to integrate third-party solutions, from external storage such as Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP or Pure Cloud Block Store or backup solutions such as Veeam Backup and Replication.
The service also gives you the ability to self-manage or work with AWS Partners to build, manage, and operate your environments. This provides you with flexibility to match your approach with your overall goals.
Setting up a new VCF environment
Organizations can streamline their setup process by ensuring they have all the necessary pre-requisites in place ahead of creating a new VCF environment. These prerequisites include having an active AWS account, configuring the appropriate AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) permissions, and setting up a Amazon VPC with sufficient CIDR space and two Route Server endpoints, with each endpoint having its own peer. Additionally, customers will need to have their VMware Cloud Foundation license keys ready, secure Amazon EC2 capacity reservations specifically for i4i.metal instances, and prepare their VLAN subnet information planning.
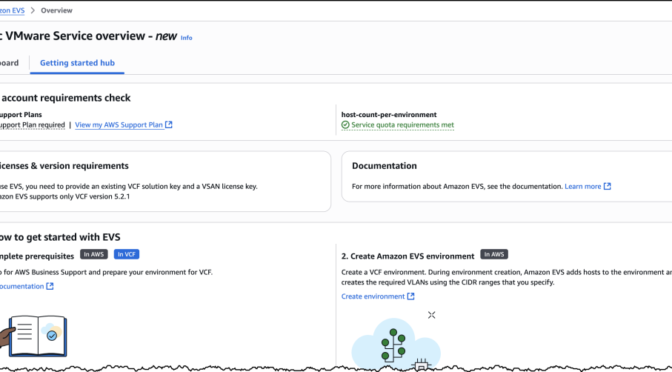
To help ensure a smooth deployment process, we’ve provided a Getting started hub, which you can access from the EVS homepage as well as a comprehensive guide in our documentation. By following these preparation steps, you can avoid potential setup delays and ensure a successful environment creation.
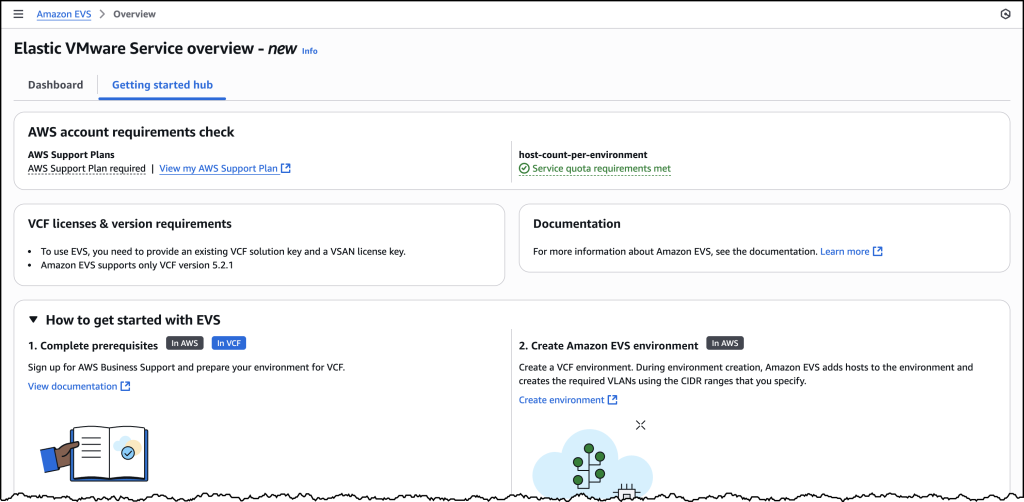
Let’s walk through the process of setting up a new VCF environment using Amazon EVS.
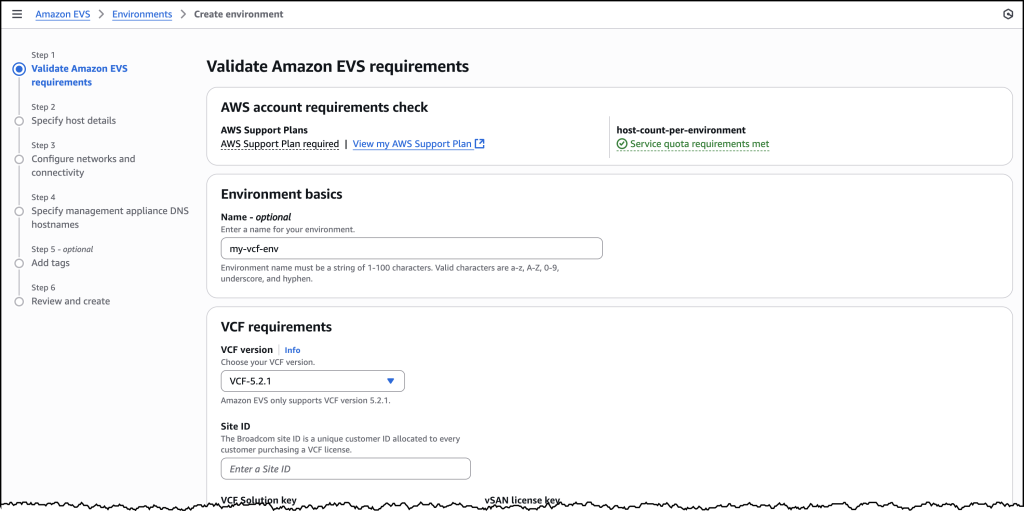
You will need to provide your Site ID, which is allocated by Broadcom when purchasing VCF licenses, along with your license keys. To ensure a successful initial deployment, you should verify you have sufficient licensing coverage for a minimum of 256 cores. This translates to at least four i4i.metal instances, with each instance providing 64 physical cores.
This licensing requirement helps you maintain optimal performance and ensures your environment meets the necessary infrastructure specifications. By confirming these requirements upfront, you can avoid potential deployment delays and ensure a smooth setup process.
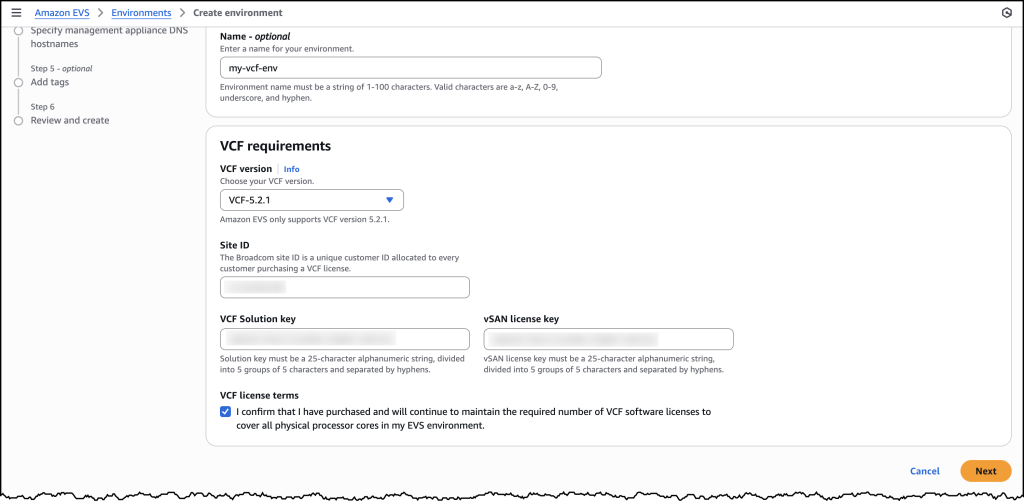
Once you have provided all the required details, you will be prompted to specify your host details. These are the underlying Amazon EC2 instances that your VCF environment will get deployed in.
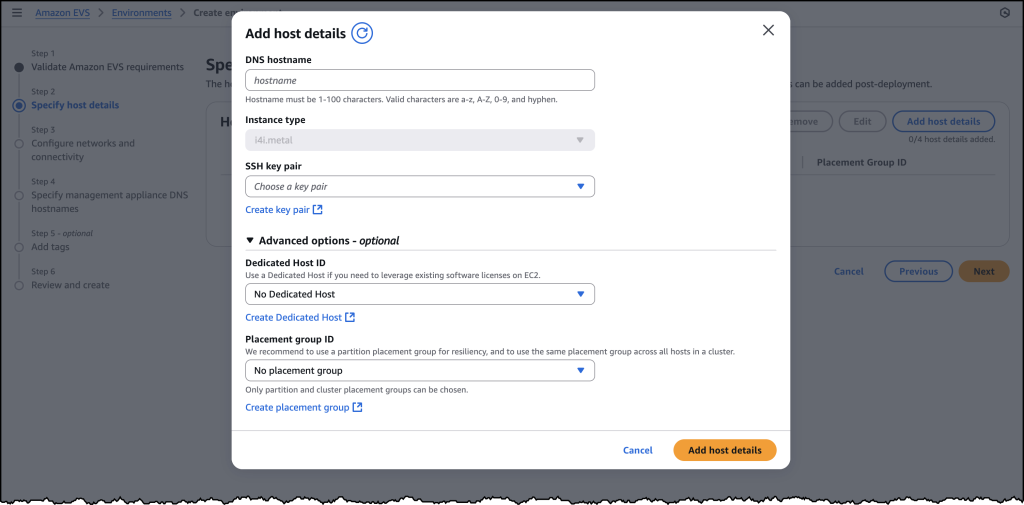
Once you have filled out details for each of your host instances, you will need to configure your networking and management appliance DNS details. For further information on how to create a new VCF environment on Amazon EVS, follow the documentation here.
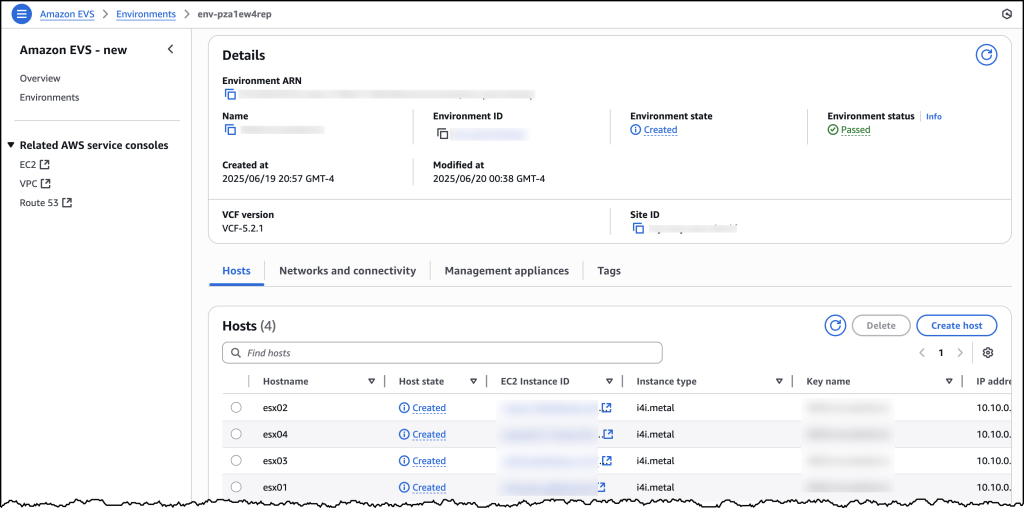
After you have created your VCF environment, you will be able to look over all of the host and configuration details through the AWS Console.
Additional things to know
Amazon EVS currently supports VCF version 5.2.1 and runs on i4i.metal instances. Future releases will expand VCF versions, licensing options, and more instance type support to provide even more flexibility for your deployments.
Amazon EVS provides flexible storage options. Your Amazon EVS local Instance storage is powered by VMware’s vSAN solution, which pools local disks across multiple ESXi hosts into a single distributed datastore. To scale your storage, you can leverage external Network File System (NFS) or iSCSI-based storage solutions. For example, Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP is particularly well-suited for use as an NFS datastore or shared block storage over iSCSI.
Additionally, Amazon EVS makes connecting your on-premises environments to AWS simple. You can connect from on-premises vSphere environment into Amazon EVS using a Direct Connect connection or a VPN that terminates into a transit gateway. Amazon EVS also manages the underlying connectivity from your VLAN subnets into your VMs.
AWS provides comprehensive support for all AWS services deployed by Amazon EVS, handling direct customer support while engaging with Broadcom for advanced support needs. Customers must maintain AWS Business Support on accounts running the service.
Availability and pricing
Amazon EVS is now generally available in US East (N. Virginia), US East (Ohio), US West (Oregon), Europe (Frankfurt), Europe (Ireland), and Asia Pacific (Tokyo) AWS Regions, with additional Regions coming soon. Pricing is based on the Amazon EC2 instances and AWS resources you use, with no minimum fees or upfront commitments.
To learn more, visit the Amazon EVS product page.
Stealing Machine Keys for fun and profit (or riding the SharePoint wave), (Tue, Aug 5th)
AWS Weekly Roundup: Amazon DocumentDB, AWS Lambda, Amazon EC2, and more (August 4, 2025)
This week brings an array of innovations spanning from generative AI capabilities to enhancements of foundational services. Whether you’re building AI-powered applications, managing databases, or optimizing your cloud infrastructure, these updates help build more advanced, robust, and flexible applications.
Last week’s launches
Here are the launches that got my attention this week:
- Amazon DocumentDB – Amazon DocumentDB Serverless is now available offering an on-demand, fully managed MongoDB API-compatible document database service. Read more in Channy’s post.
- Amazon Q Developer CLI – You can now create custom agents to help you customize the CLI agent to be more effective when performing specialized tasks such as code reviews and troubleshooting. More info in this blog.
- Amazon Bedrock Data Automation – Now supports DOC/DOCX files for document processing and H.265 encoded video files for video processing, making it easier to build multimodal data analysis pipelines.
- Amazon DynamoDB – Introduced the Amazon DynamoDB data modeling Model Context Protocol (MCP) tool, providing a structured, natural-language-driven workflow to translate application requirements into DynamoDB data models.
- AWS Lambda – Response streaming now supports a default maximum response payload size of 200 MB, 10 times higher than before. Lambda response streaming helps you build applications that progressively stream response payloads back to clients, improving performance for latency sensitive workloads by reducing time to first byte (TTFB) performance.
- Powertools for AWS – Introducing v2 of Powertools for AWS Lambda (Java), a developer toolkit that helps you implement serverless best practices and directly translates AWS Well-Architected recommendations.
- Amazon SNS – Now supports three additional message filtering operators: wildcard matching, anything-but wildcard matching, and anything-but prefix matching. SNS now also supports message group IDs in standard topics, enabling fair queue functionality for subscribed Amazon SQS standard queues.
- Amazon CloudFront – Now offers two capabilities to enhance origin timeout controls: a response completion timeout and support for custom response timeout values for Amazon S3 origins. These capabilities give you more control over how to handle slow or unresponsive origins.
- Amazon EC2 – You are now able to force terminate EC2 instances that are stuck in the shutting-down state.
- Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling – You can now use AWS Lambda functions as notification targets for EC2 Auto Scaling lifecycle hooks. For example, you can use this to trigger custom actions when an instance enters a wait state.
- Amazon SES – You can now provision isolated tenants within a single SES account and apply automated reputation policies to manage email sending.
- AWS Management Console – You can now view your AWS Applications in the Service menu in the console navigation bar. With this view you can see all your Applications and choose an Application to see all its associated resources.
- Amazon Connect – Amazon Connect UI builder now features an updated user interface to reduce the complexity to build structured workflows. It also simplified forecast editing with a new UI experience that improves planning accuracy. The Contact Control Panel now features an updated and more intuitive user interface. Amazon Connect also introduced new actions and workflows into the agent workspace. These actions are powered by third-party applications running in the background.
- AWS Clean Rooms – Now publishes events to Amazon EventBridge for status changes in a Clean Rooms collaboration, further simplifying how companies and their partners analyze and collaborate on their collective datasets without revealing or copying one another’s underlying data.
- AWS Entity Resolution – Introduced rule-based fuzzy matching using Levenshtein Distance, Cosine Similarity, and Soundex algorithms to help resolve consumer records across fragmented, inconsistent, and often incomplete datasets.
Additional updates
Here are some additional projects, blog posts, and news items that I found interesting:
- Amazon Strands Agents SDK: A technical deep dive into agent architectures and observability – Nice overview to build single and multi-agent architectures.
- Build dynamic web research agents with the Strands Agents SDK and Tavily – Showing how easy it is to add a new tool.
- Structured outputs with Amazon Nova: A guide for builders – Good tips implemented on top of native tool use with constrained decoding.
- Automate the creation of handout notes using Amazon Bedrock Data Automation – A solution to build an automated, serverless solution to transform webinar recordings into comprehensive handouts.
- Build modern serverless solutions following best practices using Amazon Q Developer CLI and MCP – Adding the AWS Serverless MCP server.
- Introducing Amazon Bedrock AgentCore Browser Tool – More info on this tool that enables AI agents to interact seamlessly with websites.
- Introducing Amazon Bedrock AgentCore Code Interpreter – A fully managed service that enables AI agents to securely execute code in isolated sandbox environments.
Upcoming AWS events
Check your calendars so that you can sign up for these upcoming events:
AWS re:Invent 2025 (December 1-5, 2025, Las Vegas) — AWS’s flagship annual conference offering collaborative innovation through peer-to-peer learning, expert-led discussions, and invaluable networking opportunities.
AWS Summits — Join free online and in-person events that bring the cloud computing community together to connect, collaborate, and learn about AWS. Register in your nearest city: Mexico City (August 6) and Jakarta (August 7).
AWS Community Days — Join community-led conferences that feature technical discussions, workshops, and hands-on labs led by expert AWS users and industry leaders from around the world: Australia (August 15), Adria (September 5), Baltic (September 10), and Aotearoa (September 18).
Join the AWS Builder Center to learn, build, and connect with builders in the AWS community. Browse here upcoming in-person and virtual developer-focused events.
That’s all for this week. Check back next Monday for another Weekly Roundup!
– Danilo
Legacy May Kill, (Sun, Aug 3rd)
Just saw something that I thought was long gone. The username "pop3user" is showing up in our telnet/ssh logs. I don't know how long ago it was that I used POP3 to retrieve e-mail from one of my mail servers. IMAP and various webmail systems have long since replaced this classic email protocol. But at least this one attacker is counting on someone still having a "pop3user" configured.
Introducing Amazon Application Recovery Controller Region switch: A multi-Region application recovery service
As a developer advocate at AWS, I’ve worked with many enterprise organizations who operate critical applications across multiple AWS Regions. A key concern they often share is the lack of confidence in their Region failover strategy—whether it will work when needed, whether all dependencies have been identified, and whether their teams have practiced the procedures enough. Traditional approaches often leave them uncertain about their readiness for Regional switch.
Today, I’m excited to announce Amazon Application Recovery Controller (ARC) Region switch, a fully managed, highly available capability that enables organizations to plan, practice, and orchestrate Region switches with confidence, eliminating the uncertainty around cross-Region recovery operations. Region switch helps you orchestrate recovery for your multi-Region applications on AWS. It gives you a centralized solution to coordinate and automate recovery tasks across AWS services and accounts when you need to switch your application’s operations from one AWS Region to another.
Many customers deploy business-critical applications across multiple AWS Regions to meet their availability requirements. When an operational event impacts an application in one Region, switching operations to another Region involves coordinating multiple steps across different AWS services, such as compute, databases, and DNS. This coordination typically requires building and maintaining complex scripts that need regular testing and updates as applications evolve. Additionally, orchestrating and tracking the progress of Region switches across multiple applications and providing evidence of successful recovery for compliance purposes often involves manual data gathering.
Region switch is built on a Regional data plane architecture, where Region switch plans are executed from the Region being activated. This design eliminates dependencies on the impacted Region during the switch, providing a more resilient recovery process since the execution is independent of the Region you’re switching from.
Building a recovery plan with ARC Region switch
With ARC Region switch, you can create recovery plans that define the specific steps needed to switch your application between Regions. Each plan contains execution blocks that represent actions on AWS resources. At launch, Region switch supports nine types of execution blocks:
- ARC Region switch plan execution block–let you orchestrate the order in which multiple applications switch to the Region you want to activate by referencing other Region switch plans.
- Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling execution block–Scales Amazon EC2 compute resources in your target Region by matching a specified percentage of your source Region’s capacity.
- ARC routing controls execution block–Changes routing control states to redirect traffic using DNS health checks.
- Amazon Aurora global database execution block–Performs database failover with potential data loss or switchover with zero data loss for Aurora Global Database.
- Manual approval execution block–Adds approval checkpoints in your recovery workflow where team members can review and approve before proceeding.
- Custom Action AWS Lambda execution block–Adds custom recovery steps by executing Lambda functions in either the activating or deactivating Region.
- Amazon Route 53 health check execution block–Let you to specify which Regions your application’s traffic will be redirected to during failover. When executing your Region switch plan, the Amazon Route 53 health check state is updated and traffic is redirected based on your DNS configuration.
- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) resource scaling execution block–Scales Kubernetes pods in your target Region during recovery by matching a specified percentage of your source Region’s capacity.
- Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) resource scaling execution block–Scales ECS tasks in your target Region by matching a specified percentage of your source Region’s capacity.
Region switch continually validates your plans by checking resource configurations and AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) permissions every 30 minutes. During execution, Region switch monitors the progress of each step and provides detailed logs. You can view execution status through the Region switch dashboard and at the bottom of the execution details page.
To help you balance cost and reliability, Region switch offers flexibility in how you prepare your standby resources. You can configure the desired percentage of compute capacity to target in your destination Region during recovery using Region switch scaling execution blocks. For critical applications expecting surge traffic during recovery, you might choose to scale beyond 100 percent capacity, and setting a lower percentage can help achieve faster overall execution times. However, it’s important to note that using one of the scaling execution blocks does not guarantee capacity, and actual resource availability depends on the capacity in the destination Region at the time of recovery. To facilitate the best possible outcomes, we recommend regularly testing your recovery plans and maintaining appropriate Service Quotas in your standby Regions.
ARC Region switch includes a global dashboard you can use to monitor the status of Region switch plans across your enterprise and Regions. Additionally, there’s a Regional executions dashboard that only displays executions within the current console Region. This dashboard is designed to be highly available across each Region so it can be used during operational events.
Region switch allows resources to be hosted in an account that is separate from the account that contains the Region switch plan. If the plan uses resources from an account that is different from the account that hosts the plan, then Region switch uses the executionRole to assume the crossAccountRole to access those resources. Additionally, Region switch plans can be centralized and shared across multiple accounts using AWS Resource Access Manager (AWS RAM), enabling efficient management of recovery plans across your organization.
Let’s see how it works
Let me show you how to create and execute a Region switch plan. There are three parts in this demo. First, I create a Region switch plan. Then, I define a workflow. Finally, I configure the triggers.
Step 1: Create a plan
I navigate to the Application Recovery Controller section of the AWS Management Console. I choose Region switch in the left navigation menu. Then, I choose Create Region switch plan.
After I give a name to my plan, I specify a Multi-Region recovery approach (active/passive or active/active). In Active/Passive mode, two application replicas are deployed into two Regions, with traffic routed into the active Region only. The replica in the passive Region can be activated by executing the Region switch plan.
Then, I select the Primary Region and Standby Region. Optionally, I can enter a Desired recovery time objective (RTO). The service will use this value to provide insight into how long Region switch plan executions take in relation to my desired RTO.
I enter the Plan execution IAM role. This is the role that allows Region switch to call AWS services during execution. I make sure the role I choose has permissions to be invoked by the service and contains the minimum set of permissions allowing ARC to operate. Refer to the IAM permissions section of the documentation for the details.
When the two Plan evaluation status notifications are green, I create a workflow. I choose Build workflows to get started.
Plans enable you to build specific workflows that will recover your applications using Region switch execution blocks. You can build workflows with execution blocks that run sequentially or in parallel to orchestrate the order in which multiple applications or resources recover into the activating Region. A plan is made up of these workflows that allow you to activate or deactivate a specific Region.
For this demo, I use the graphical editor to create the workflow. But you can also define the workflow in JSON. This format is better suited for automation or when you want to store your workflow definition in a source code management system (SCMS) and your infrastructure as code (IaC) tools, such as AWS CloudFormation.
I can alternate between the Design and the Code views by selecting the corresponding tab next to the Workflow builder title. The JSON view is read-only. I designed the workflow with the graphical editor and I copied the JSON equivalent to store it alongside my IaC project files.
Region switch launches an evaluation to validate your recovery strategy every 30 minutes. It regularly checks that all actions defined in your workflows will succeed when executed. This proactive validation assesses various elements, including IAM permissions and resource states across accounts and Regions. By continually monitoring these dependencies, Region switch helps ensure your recovery plans remain viable and identifies potential issues before they impact your actual switch operations.
However, just as an untested backup is not a reliable backup, an untested recovery plan cannot be considered truly validated. While continuous evaluation provides a strong foundation, we strongly recommend regularly executing your plans in test scenarios to verify their effectiveness, understand actual recovery times, and ensure your teams are familiar with the recovery procedures. This hands-on testing is essential for maintaining confidence in your disaster recovery strategy.
Step 3: Create a trigger
A trigger defines the conditions to activate the workflows just created. It’s expressed as a set of CloudWatch alarms. Alarm-based triggers are optional. You can also use Region switch with manual triggers.
From the Region switch page in the console, I choose the Triggers tab and choose Add triggers.
For each Region defined in my plan, I choose Add trigger to define the triggers that will activate the Region. Finally, I choose the alarms and their state (OK or Alarm) that Region switch will use to trigger the activation of the Region.
Finally, I choose the alarms and their state (OK or Alarm) that Region switch will use to trigger the activation of the Region.
I’m now ready to test the execution of the plan to switch Regions using Region switch. It’s important to execute the plan from the Region I’m activating (the target Region of the workflow) and use the data plane in that specific Region.
Here is how to execute a plan using the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI):
aws arc-region-switch start-plan-execution
--plan-arn arn:aws:arc-region-switch::111122223333:plan/resource-id
--target-region us-west-2
--action activatePricing and availability
Region switch is available in all commercial AWS Regions at $70 per month per plan. Each plan can include up to 100 execution blocks, or you can create parent plans to orchestrate up to 25 child plans.
Having seen firsthand the engineering effort that goes into building and maintaining multi-Region recovery solutions, I’m thrilled to see how Region switch will help automate this process for our customers. To get started with ARC Region switch, visit the ARC console and create your first Region switch plan. For more information about Region switch, visit the Amazon Application Recovery Controller (ARC) documentation. You can also reach out to your AWS account team with questions about using Region switch for your multi-Region applications.
I look forward to hearing about how you use Region switch to strengthen your multi-Region applications’ resilience.